Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by symptoms such as difficulty paying attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. ADHD can have a significant impact on a person’s daily functioning, including their academic performance, relationships, and overall quality of life. In this article, we will discuss ADHD and some tests for ADHD.[1][2][3][4]
What is ADHD?
ADHD, which stands for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder [1], is a complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a neurodevelopmental disorder, meaning it affects the brain’s development and functioning. ADHD is characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can interfere with daily functioning and development.
ADHD is not simply a matter of being easily distracted or having a lot of energy. It is a legitimate medical condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s life. While ADHD is commonly diagnosed in childhood, it can persist into adolescence and adulthood, causing symptoms and affecting individuals throughout their lives.
The exact causes of ADHD are still not fully understood, but research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors contribute to its development. Studies have shown that ADHD tends to run in families, indicating a strong genetic component. However, it is important to note that not everyone with a family history of ADHD will develop the disorder, and not everyone with ADHD has a family history of the condition.
Symptoms of ADHD
The symptoms of ADHD can vary depending on the individual and their age [2]. In children, the primary symptoms are inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Children with ADHD may struggle to follow instructions, experience difficulty waiting, have difficulty concentrating and staying focused on tasks due to trouble with sustained mental effort and act impulsively without considering the consequences. They may also experience extreme restlessness and have trouble sitting still, difficulty unwinding, constantly fidgeting or squirming.
As individuals with ADHD enter adolescence and adulthood, the symptoms may change. While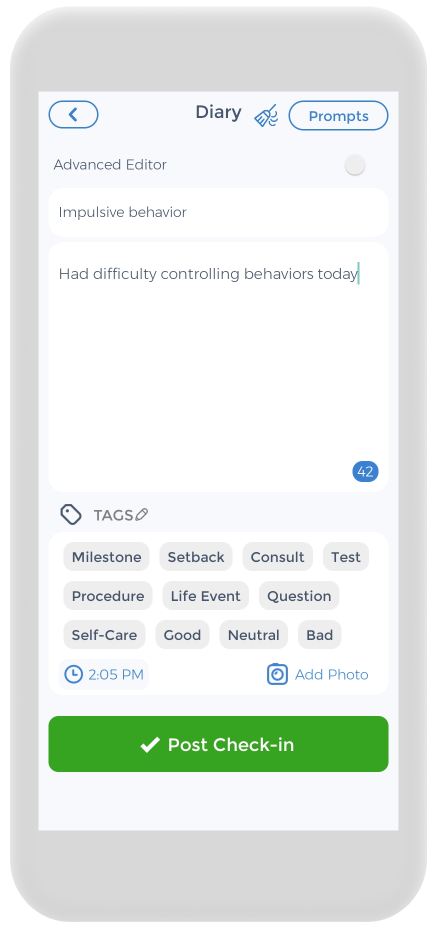 hyperactivity may decrease, difficulties with organization, making careless mistakes, trouble paying attention, time management, and maintaining relationships may become more prominent. Adults with ADHD may struggle with prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines, and managing their time effectively. They may also experience challenges in their personal relationships, as ADHD can affect communication and emotional regulation.
hyperactivity may decrease, difficulties with organization, making careless mistakes, trouble paying attention, time management, and maintaining relationships may become more prominent. Adults with ADHD may struggle with prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines, and managing their time effectively. They may also experience challenges in their personal relationships, as ADHD can affect communication and emotional regulation.
It is important to note that the severity and presentation of ADHD symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Some may have predominantly inattentive symptoms, while others may exhibit more hyperactive and impulsive behaviors. Additionally, individuals with ADHD may also experience co-occurring conditions or mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, or learning disabilities.
Causes and Risk Factors of ADHD
While the precise causes of ADHD are not yet fully understood, there are several factors that increase the risk of developing the condition. Genetics play a significant role, as ADHD tends to run in families. Research has identified specific genes that may be associated with an increased susceptibility to ADHD, although the interplay between genetics and environmental factors is complex and not fully elucidated.
In addition to genetic factors, certain environmental influences may contribute to the development of ADHD. Exposure to toxins during pregnancy or early childhood, such as lead, tobacco smoke, or certain chemicals, has been suggested as a potential risk factor. Maternal substance abuse, particularly alcohol and tobacco use, during pregnancy has also been associated with an increased risk of ADHD in children.
Furthermore, certain prenatal and perinatal factors have been linked to an increased risk of ADHD. Premature birth, low birth weight, and complications during pregnancy or delivery have all been identified as potential risk factors. However, it is important to note that these factors alone do not cause ADHD, but rather increase the likelihood of its development in individuals who are already predisposed to the disorder.
While our understanding of ADHD continues to evolve, it is clear that it is a complex condition influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. By gaining a deeper understanding of the causes and risk factors associated with ADHD, we can better support individuals with the disorder and work towards effective treatment and management strategies.
The Importance of ADHD Testing
ADHD screening and testing plays a crucial role in helping individuals accurately diagnose ADHD. Early detection, proper diagnosis and intervention are key to managing symptoms effectively and minimizing the impact of ADHD on a person’s life.
ADHD, or Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by symptoms such as difficulty paying attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s daily functioning, including their academic performance, relationships, and overall well-being.
Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection of ADHD is vital to ensure timely intervention and support [3]. By identifying symptoms early on, healthcare professionals can provide appropriate strategies and resources to address the challenges associated with ADHD. Early diagnosis and intervention can help children develop skills to manage their symptoms, improve academic performance, and enhance their overall well-being.
Furthermore, early detection allows for the implementation of behavior management techniques and accommodations in educational settings. With the right support, children with ADHD can thrive academically and socially, reducing the negative impact of the disorder on their lives.
Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment
ADHD testing is essential for an accurate diagnosis. An accurate diagnosis ensures that individuals receive the correct treatment and support. Without proper testing, other conditions with similar symptoms may be misdiagnosed as ADHD, leading to unnecessary treatments or interventions.
ADHD testing involves a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s symptoms, medical history, and behavior, providing healthcare professionals with the necessary information to make an accurate diagnosis of ADHD. This evaluation may include interviews with the individual, their parents or caregivers, and teachers to gather information about their behavior in different settings.
Additionally, ADHD testing may involve psychological assessments and rating scales to assess the severity of symptoms and their impact on daily functioning. These assessments help healthcare professionals determine the most appropriate treatment plan, which may include medication, behavioral therapy, and educational interventions.
Moreover, accurate diagnosis through ADHD testing can also help individuals gain a better understanding of their strengths and weaknesses. It allows them to develop self-awareness and learn effective coping strategies to manage their symptoms throughout their lives.[5][6][7]
Different Types of ADHD Tests
When it comes to assessing ADHD symptoms, healthcare professionals have a range of tests at their disposal. These tests serve specific purposes and offer valuable insights into an individual’s symptoms and overall functioning. Let’s take a closer look at some of the different types of ADHD tests available:
Behavioral Assessment
A behavioral assessment is a comprehensive process that involves gathering information about an individual’s behavior and symptoms from various sources, including parents, teachers, and healthcare professionals. This type of behavior assessment system often includes interviews, questionnaires, and observations. By collecting data from multiple perspectives, healthcare professionals can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the individual’s ADHD symptoms and how they impact their daily life.
During a behavioral assessment, parents may be asked to provide information about their child’s behavior at home, while teachers may be asked to share their observations of the child’s behavior in the classroom. Healthcare professionals may also conduct interviews with the individual to gain insight into their own experiences and perceptions.
By combining information from different sources, healthcare professionals can identify specific ADHD symptoms and assess their impact on the individual’s functioning in different settings. This comprehensive approach helps ensure a more accurate diagnosis and informs the development of an appropriate treatment plan.
Neuropsychological Testing
Neuropsychological testing is another type of assessment commonly used to evaluate ADHD symptoms. This type of testing focuses on assessing an individual’s cognitive abilities, including attention, memory, and executive function. By examining these cognitive domains, healthcare professionals can identify strengths and weaknesses that may be related to ADHD.
During a neuropsychological test, individuals may be asked to complete various tasks that assess their attention span, working memory, and ability to plan and organize. These tests provide valuable information about an individual’s cognitive functioning and can help healthcare professionals make an accurate diagnosis of mental disorders.
Neuropsychological testing is particularly useful because it allows healthcare professionals to understand how ADHD affects an individual’s cognitive abilities. This information is crucial for developing targeted treatment strategies that address the specific cognitive challenges faced by each individual.
Computerized Tests
In addition to behavioral and neuropsychological assessments, computerized tests are also used to assess ADHD symptoms. These tests focus on specific areas of ADHD, such as attention or impulsivity, and are often performed using specialized software or online platforms.
Computerized tests provide objective measurements of specific cognitive functions related to ADHD. These tests are designed to be standardized and reliable, allowing healthcare professionals to compare an individual’s performance to established norms. By analyzing the results of computerized tests, healthcare professionals can gather valuable data to support an ADHD diagnosis.
One advantage of computerized tests is their ability to provide precise and quantifiable measurements of ADHD symptoms. These tests can track an individual’s performance over time, allowing healthcare professionals to monitor treatment progress and make adjustments as needed.
It’s important to note that while computerized tests can provide valuable information, they should be used in conjunction with other assessment methods to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of ADHD symptoms.
There are various types of tests available to assess ADHD symptoms. Behavioral assessments provide a comprehensive view of an individual’s symptoms of mood disorder and their impact on daily functioning. Neuropsychological testing focuses on evaluating cognitive abilities related to ADHD, while computerized tests offer objective measurements of specific ADHD symptoms. By utilizing a combination of these and other tests together, healthcare professionals can gather a wealth of information to inform accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning for individuals with ADHD.[8][9][10]
Understanding the ADHD Testing Process
The ADHD testing process involves several stages, from initial consultation with medical doctor to post-testing analysis. Understanding this process can help individuals and their families prepare for what to expect during the evaluation.
ADHD, or Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. The testing process aims to assess these symptoms and determine if an individual meets the criteria for an ADHD diagnosis.
Pre-Testing Consultation
Before the testing begins, a pre-testing consultation is usually conducted. During this consultation, the healthcare provider or professionals explain the purpose of the evaluation, gather relevant information, and address any concerns or questions. This discussion helps ensure that the testing is tailored to the individual’s unique needs and circumstances.
The healthcare professionals may ask questions about the individual’s medical and other family members’ mental health history first, including any previous diagnoses or treatments. They may also inquire about the individual’s developmental milestones, academic performance, and social interactions. Gathering this information provides healthcare provider with a comprehensive background for the mental health evaluation process.
In addition to gathering information, the pre-testing consultation is an opportunity for individuals and their families to express any concerns or anxieties they may have about the testing process. The well trained healthcare providers and professionals can provide reassurance, answer questions, and alleviate any fears. Establishing a comfortable and supportive environment is crucial for accurate testing results.
During the Test
The actual testing process varies depending on the specific psychological or behavioral tests being used. Behavioral assessments typically involve interviews and questionnaires, while neuropsychological testing may include a series of tasks or puzzles. Computerized psychological tests also are usually self-administered on a computer or other electronic devices. Throughout the testing, healthcare professionals monitor and document the individual’s performance and behavior.
Behavioral assessments often involve interviews with the individual and their parents, teachers, or other caregivers. These interviews provide valuable insights into the individual’s behavior in different settings, such as home and school. Questionnaires may also be given to gather information about the individual’s symptoms and their impact on daily functioning.
Neuropsychological testing assesses cognitive abilities such as attention, memory, and executive functions. These tests are designed to evaluate specific areas of functioning that may be affected by ADHD. The individual may be asked to complete tasks that require problem-solving, memory recall, or sustained attention.
Computerized tests, on the other hand, are often used to measure attention and impulse control. These tests are typically interactive and engaging, designed to capture the individual’s responses in real-time. They provide objective data that can be compared to normative samples.
Post-Testing Analysis
 After the testing is complete, the healthcare professionals analyze the gathered data to form a comprehensive understanding the type of ADHD and the individual’s symptoms and functioning. The results of the tests, along with other relevant information, are used to make an accurate diagnosis of ADHD and develop personalized treatment plans.
After the testing is complete, the healthcare professionals analyze the gathered data to form a comprehensive understanding the type of ADHD and the individual’s symptoms and functioning. The results of the tests, along with other relevant information, are used to make an accurate diagnosis of ADHD and develop personalized treatment plans.
The analysis involves a qualified mental health professional reviewing the individual’s performance on each test and comparing it to established norms. The healthcare professionals look for patterns and discrepancies that may indicate the presence of ADHD. They consider the severity and frequency of symptoms, as well as the impact on daily life.
In addition to test results, the healthcare professionals take into account other factors that may contribute to the individual’s symptoms. These factors may include environmental influences, family history, and co-occurring medical conditions, such as an anxiety disorder or learning disabilities.
The comprehensive understanding gained from the post-testing analysis allows healthcare professionals to provide tailored recommendations for treatment and support. Treatment options may include medication, therapy, behavioral interventions, and accommodations in educational or work settings.
It is important to note that the ADHD testing process is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each evaluation is unique and takes into account the individual’s specific circumstances and needs. Through a thorough and comprehensive evaluation, individuals and their families can gain a better understanding of ADHD and access the appropriate resources for managing the disorder.[11][12]
How ADHD Tests Can Help Diagnose ADHD
ADHD tests provide valuable information that can significantly impact the lives of individuals with ADHD, their families, and their support networks. The comprehensive assessment process involved in ADHD testing goes beyond just diagnosing the condition; it plays a crucial role in developing personalized treatment plans, improving academic performance, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Personalized Treatment Plans
ADHD tests help healthcare professionals develop individualized treatment plans that address the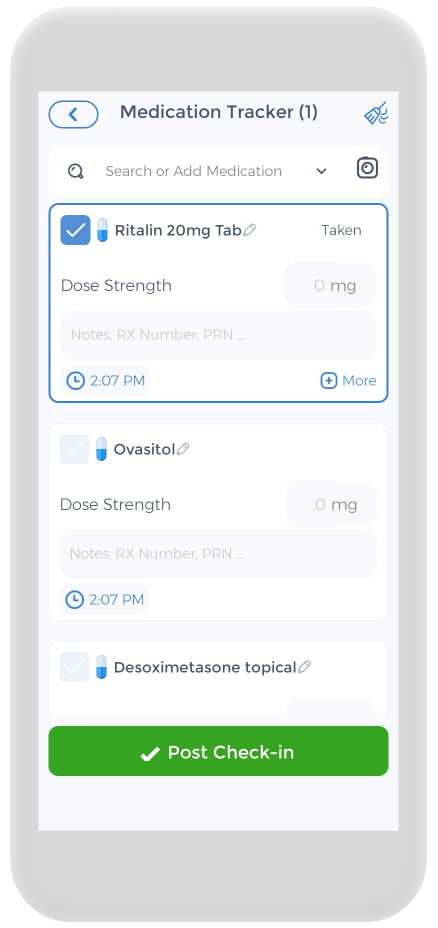 specific needs and challenges of each person. These tests involve a thorough evaluation of various factors, including medical and family health history, behavioral patterns, and cognitive functioning. By gathering this comprehensive data, healthcare professionals can gain a deeper understanding of the individual’s unique strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to tailor the treatment plan accordingly.
specific needs and challenges of each person. These tests involve a thorough evaluation of various factors, including medical and family health history, behavioral patterns, and cognitive functioning. By gathering this comprehensive data, healthcare professionals can gain a deeper understanding of the individual’s unique strengths and weaknesses, enabling them to tailor the treatment plan accordingly.
Treatment plans may include a combination of behavioral interventions, medication management, therapy, and educational accommodations. Behavioral interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals develop coping mechanisms and strategies to manage their ADHD symptoms effectively. Medication management, on the other hand, involves finding the right medication and dosage to alleviate symptoms and improve focus and attention. Educational accommodations, such as extended time on exams or preferential seating, can create a supportive environment for individuals with ADHD to thrive academically.
By tailoring the treatment to the unique needs of each individual, ADHD tests facilitate better outcomes and improved quality of life. With a personalized treatment plan in place, individuals with ADHD can experience reduced symptoms, enhanced self-esteem, and improved overall functioning in various aspects of life.
Improved Academic Performance
Accurate diagnosis and appropriate interventions can help children and adults with ADHD improve their academic performance. ADHD tests play a crucial role in identifying the specific challenges that individuals face in educational settings. By understanding these challenges, educators can implement targeted support strategies to address them effectively.
With targeted support, individuals can develop strategies to manage their symptoms in educational settings. Leading to enhanced focus, organization, and productivity. For example, educators can provide visual aids, establish structured routines, and implement behavior management techniques to create an optimal learning environment for students with ADHD. Additionally, students can learn techniques such as time management, prioritization, and self-regulation to overcome obstacles and achieve academic success.
By addressing the unique needs of students with ADHD through appropriate interventions, ADHD tests contribute to improved academic performance, increased engagement, and a greater sense of accomplishment. These positive outcomes not only benefit the individuals themselves but also have a ripple effect on their overall well-being and future prospects.
Enhanced Quality of Life
Ultimately, ADHD tests contribute to an enhanced quality of life for individuals with ADHD. By understanding their symptoms and receiving appropriate treatment, individuals can better manage their challenges. Improve their relationships, and thrive in both academic and personal pursuits.
With the help of ADHD tests, individuals can gain valuable insights into their condition. Allowing them to develop a sense of self-awareness and self-acceptance of mental illness. This understanding of mental illness can empower individuals to advocate for themselves. Seek support when needed, and make informed decisions about their treatment and lifestyle choices.
Moreover, the benefits of ADHD tests extend beyond the individual with ADHD. Family members and support networks also benefit from the knowledge gained through testing. Understanding the unique needs and challenges of individuals with ADHD can foster empathy, patience, and effective communication within relationships. By providing appropriate support and accommodations, family members and support networks can contribute to a positive and nurturing environment that promotes the well-being and success of individuals with ADHD.
ADHD tests are essential in providing valuable information that goes beyond diagnosis. These tests play a crucial role in developing personalized treatment plans. Improving academic performance, and enhancing overall quality of life for individuals with ADHD. By tailoring interventions to address the unique needs of each individual, ADHD tests pave the way for better outcomes. Increased self-awareness, and improved functioning in various aspects of life.[13]
Common Misconceptions About ADHD Testing
There are several misconceptions surrounding ADHD testing that may prevent individuals from seeking the necessary evaluations. It is essential to debunk these myths and understand the truth about ADHD testing.
Debunking ADHD Testing Myths
One common misconception is that ADHD testing is unnecessary and that symptoms will improve over time. However, without an accurate diagnosis and appropriate interventions, ADHD symptoms often persist and can have long-term consequences. Comprehensive testing ensures that individuals receive the necessary support to manage their symptoms effectively.
The Truth About ADHD Testing
ADHD testing is a vital step towards understanding and managing ADHD symptoms. It provides valuable insights into an individual’s unique challenges and helps healthcare professionals develop personalized treatment plans. By shedding light on the underlying causes of symptoms, ADHD testing offers a path towards a better future.[14]
Printable DSM 5 ADHD Symptom Checklist
This questionnaire relies on a globally recognized screening tool for ADHD. While it is not diagnostic, it may offer insights into whether ADHD is a condition for which you might want to pursue a comprehensive, professional assessment.
⬇️ Printable DSM 5 ADHD Symptom Checklist PDF[15]
Interpreting Your ADHD Test Result
To meet DSM-V criteria for ADHD in childhood, a child must have at least 6 responses of “Often” or “Very Often” (scored 2 or 3) to either the 9 inattentive items (1-9) or the 9 hyperactive-impulsive items (10-18), or both.
While for older adolescents and adults (age 17 and older), at least five symptoms are required. The clinician may consider ADHD as a possible diagnosis if 5 or more symptoms are scored 2 or 3 in either one or both domains.
In addition, symptoms must have occurred by age 12. They must impair the individual’s functioning in two or more settings, and they must not be primarily due to any other factors or conditions. Depending on the domains affected, ADHD is predominantly inattentive type. ADHD, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type; or ADHD, combined type may be considered. Using a rating scale such as this, however, is not sufficient in and of itself to diagnose ADHD. Other sources of information should be considered and an appropriate health professional should be consulted.[16]
Using the CareClinic App to Help with ADHD
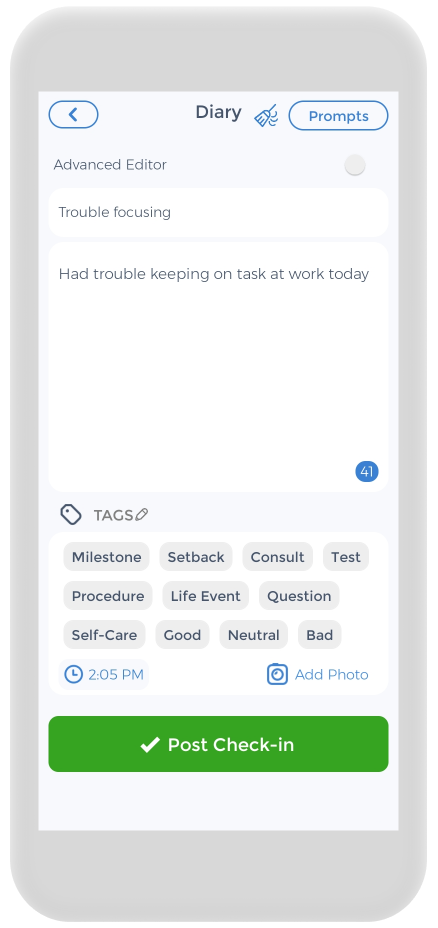
Keeping track of your own mental health, and medications is crucial. and the CareClinic app can help with that. You can use the app as your clinical journal. Just go to the diary section of the app and enter your daily symptoms, medications, and other triggers, as they occur. There are also specific sections on the app to track each of these. For example, if you have ADHD symptoms, you can track down symptoms you have on a daily basis.
The app also has a medication section where you can precisely track the doses of the pills you are taking and receive reminders. Whether you are taking stimulant medication or herbs for ADHD, we know how difficult but important keeping track of your medications is, so we hope to make it as easy and streamlined as possible. This way, you can take your medications and experience consistent relief.
Understanding ADHD tests and their importance is key to supporting individuals with ADHD. Through accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and thrive in their personal and academic lives. Embracing ADHD testing opens the door to a brighter future, full of opportunities for growth, success, and well-being.
⬇️ Download the CareClinic App
Sources
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html
- Klarity (2023). ADHD Tools For Organization & Time Management https://www.klarityadhd.com/post/adhd-tools/
- MayoClinic (2023). Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/adult-adhd/symptoms-causes/syc-20350878
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd/index.shtml
References
- “Diagnosing ADHD | Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | CDC”. https://www.cdc.gov/adhd/diagnosis/index.html
- “Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vanderbilt_ADHD_diagnostic_rating_scale
- “Swanson, Nolan and Pelham Teacher and Parent Rating Scale”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swanson%2C_Nolan_and_Pelham_Teacher_and_Parent_Rating_Scale
- “Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adult_ADHD_Self-Report_Scale
- “Benefits of Early ADHD Diagnosis in Children”. https://www.berkeleypsychiatrists.co.uk/blog/benefits-of-early-adhd-diagnosis-in-children
- “Diagnosis of ADHD in Adults – CHADD”. https://chadd.org/for-adults/diagnosis-of-adhd-in-adults/
- “Early ADHD Diagnosis and Intervention | Benefits | Significance”. https://cpdonline.co.uk/knowledge-base/safeguarding/early-adhd-diagnosis-intervention-benefits/
- “Test of Variables of Attention”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Test_of_Variables_of_Attention
- “Neuropsychological Testing for ADHD: A Comprehensive Guide”. https://www.donefirst.com/blog/neuropsych-testing-adhd
- “ADHD Testing – Attention, Executive Functioning And Memory”. https://www.mentalhealth.com/library/adhd-testing-attention-executive-functioning-memory
- “Evaluating attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): a review of current methods and issues – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11891363/
- “ADHD Screening: What To Expect”. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/24758-adhd-screening
- “Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, School Performance, and Effect of Medication – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30768391/
- “Understanding ADHD: The Importance of Comprehensive Testing”. https://www.copaceticahealth.com/post/understanding-adhd-the-importance-of-comprehensive-testing
- “Symptoms | AADD-UK”. https://aadduk.org/symptoms-diagnosis-treatment/symptoms/
- “Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) – Pediatrics – Merck Manual Professional Edition”. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/pediatrics/learning-and-developmental-disorders/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd
- “A systematic review of the effectiveness of mobile apps for monitoring and management of mental health symptoms or disorders – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30347316/