Obesity is the number one epidemic in today’s modern world. People eat food of the worst quality. They rarely sit down to have a proper meal and often opt for dishes rich in calories. The diet is responsible for an increased risk of diabetes, heart attacks, and stroke, with the overall quality of life being affected. Weight loss is a matter of concern for a lot of people. But the process is never as easy as one might think. It is difficult to cut back on calories and re-accustom yourself to eating the right foods. Technology is on our side, with smartphone apps allowing us to document every step of the weight loss journey. Through nutrition logs, we can become more aware of the food we eat and the changes that we need to make.
Tracking Weight Loss & Healthy Eating with Nutrition Logs
If you have decided to change your life for the better and return to healthy eating, you might want to consider using the CareClinic health app. This helpful resource can be used by anyone who is planning on losing weight, eating healthy, and maintaining an adequate lifestyle in general. It acts as a nutrient counter. Allowing you to record the daily intake of calories. As well as macronutrients (carbs, proteins, and fats), sugar, sodium etc.
For each of your meals, you can record the date and time. As well as the duration and circumstances. You can make records for the three main meals (breakfast, lunch and dinner). As well as for any snacks you might enjoy throughout the day. Food journaling has been made a lot easier thanks to applications such as CareClinic. Which helps one keep track of the calories consumed and the exact quantity of macronutrients contained in each meal.
Meal Logging using Apps
Even though one can still use a pen and paper to log meals, it would be a shame not to take advantage of the technology and rely on smartphones for a quick recording of your meals. The CareClinic health app is easy to use. Allowing you to plan your meals in advance and log them as they occur. Make sure that you stay on the right track where your nutritional goals are concerned.
By keeping a nutrition diary, you will get a clearer perspective on your diet and the changes that have to be made. You might also find it easier to change your diet. Documenting your meals will reveal how nutritious these actually are. Within the application, you can record how healthy your meals are, what are your most frequent cravings and how qualitative is the food going into your body every day. All of this information will paint the picture of your current health status, and whether excess weight is an issue or not.
Weight loss through healthy eating
While there are hundreds of dietary regimes out there, the best experts will tell you that healthy eating, in moderation, will help you reach your weight loss goals better than any diet. Many people have difficulties losing weight. As they have a crazy daily schedule that allows for anything but healthy eating. So, if you are serious about making a change, you need to start with the way you organize your life and daily schedule.
The nutrition logging in the CareClinic app can be used to create customized diet goals. But – be careful – you should not make weight loss as your number one priority. Instead, you should concentrate on healthy eating. Combined with adequate levels of physical activity. You can use the app to set goals for the daily intake of micro and macronutrients. Making sure to prepare your meals accordingly.
In the situation that you are battling obesity, you might rely on the health app to set a limit for the daily intake of calories. With each meal prepared, you can refer to the app and ensure that you have stayed within that limit. If you have a little bit more time available, you can record the nutritional analysis of each meal or food product. In this way, you will know if your meals contain unhealthy ingredients, such as added sugar, trans fats or high fructose corn syrup.
Your Personalized Nutritional Plan
 Once you have decided that healthy eating is an objective for the near future or even the present, the first thing that you need to do is come up with a plan. With the CareClinic health app, you can stay organized, creating a plan for eating healthier and making mindful nutritional decisions. Each “check-in” will be comprised of the food your consumed. Which will add to your nutrition log. These nutrition logs can then be shared or printed as needed.
Once you have decided that healthy eating is an objective for the near future or even the present, the first thing that you need to do is come up with a plan. With the CareClinic health app, you can stay organized, creating a plan for eating healthier and making mindful nutritional decisions. Each “check-in” will be comprised of the food your consumed. Which will add to your nutrition log. These nutrition logs can then be shared or printed as needed.
As part of this plan, you can enter additional health information, such as your weight and height, blood pressure, blood glucose values, sleep information, fitness goals and so on. These should be monitored at all times so that you are able to notice the difference healthy eating has brought into your life. And, yes, small habits indeed make a difference whereas nutritional goals are concerned.
If you want, you can also use the application to organize a list of recipes for healthy meals. These should always be based on fresh ingredients, preferably from known sources. For instance, you can visit farmer’s markets for fresh produce at the end of the week. Within the application, you can record meal plans for an entire week or even more.
Nutrition Reports for sharing with nutritionists or doctors
Based on the information you record within the application, a monthly report will be generated. This will contain health and diet-related data, which can be successfully shared with your nutritionist or treating physician. Together, you can come up with the best decisions regarding your health, eating and, if necessary, weight loss.
Easy record process, which takes a few minutes a day
For a lot of people, recording details about their meals seem tedious and consuming. However, it is once again worth mentioning that technology has made our lives easier and that smartphone apps such as CareClinic are quite easy to use. It does not take more than a few minutes to record your meals. In consequence, you won’t find it difficult to turn the recording process into a habit.
From a different perspective, you will finally come face-to-face with your meal decisions. You can review the food diary at any given moment and see your meals. How nutritious they are and whether they contribute to your weight problem or not.
Additional health log measurements that influence your diet/food choices
Aside from logging your meals, you might consider using the CareClinic health app to record additional health measurements. These might influence your diet/food choices, or they might represent the reason for which some changes in your eating habits should be made.
Among the most important health measurements that you can record are: weight, body fat percentage, blood pressure, blood glucose, level of physical activity, sleep quality and frequency. You can refer to these from time to time. AS well as see how these have changed in accordance to your new eating habits.
Keeping Nutrition Logs for All Meals
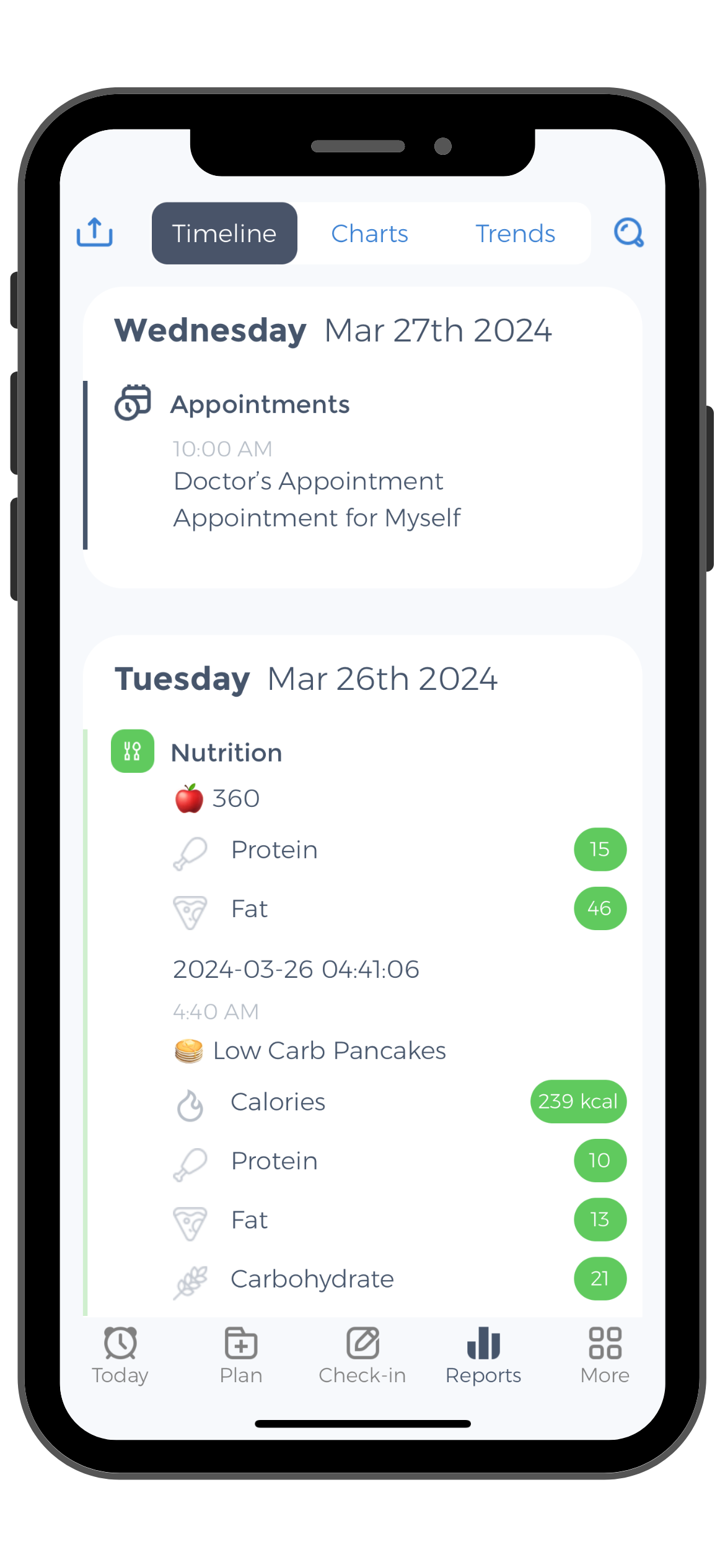 When it comes to eating healthy, it is recommended to have three main meals – breakfast, lunch and dinner – as well as two snacks. If you live a hectic lifestyle, it might be difficult to check all the meals. As a result, you might even eat the wrong foods.
When it comes to eating healthy, it is recommended to have three main meals – breakfast, lunch and dinner – as well as two snacks. If you live a hectic lifestyle, it might be difficult to check all the meals. As a result, you might even eat the wrong foods.
Thanks to the CareClinic health app, you can set meal reminders and make sure that you stay on the right track where healthy eating is concerned. These alerts can be sent through text message, e-mail or as push notifications, allowing you to eat healthily and at the right moment of the day. Moreover, by eating at regular intervals, you will protect yourself against cravings and the discomforting sensation of hunger.
Planning your meals in advance
This is another benefit that the CareClinic health app brings to the table. You can use it to plan your meals in advance so that you keep on eating healthy despite your schedule. You can take your time and choose the best ingredients, enjoying a home-cooked meal.
These recordings can be easily made into the built-in journal, which is one of the most beneficial features of the app. It might also help you document meals, in case you have specific dietary demands – for example if you are lactose intolerant or you suffer from gluten sensitivity.
Water intake for adequate hydration
Even though water is not a nutrient or food in itself, it is vital to healthy living. You can use the CareClinic’s health app to document your daily intake of water, so that you ensure adequate hydration. It is also possible to set up reminders for drinking fluids.
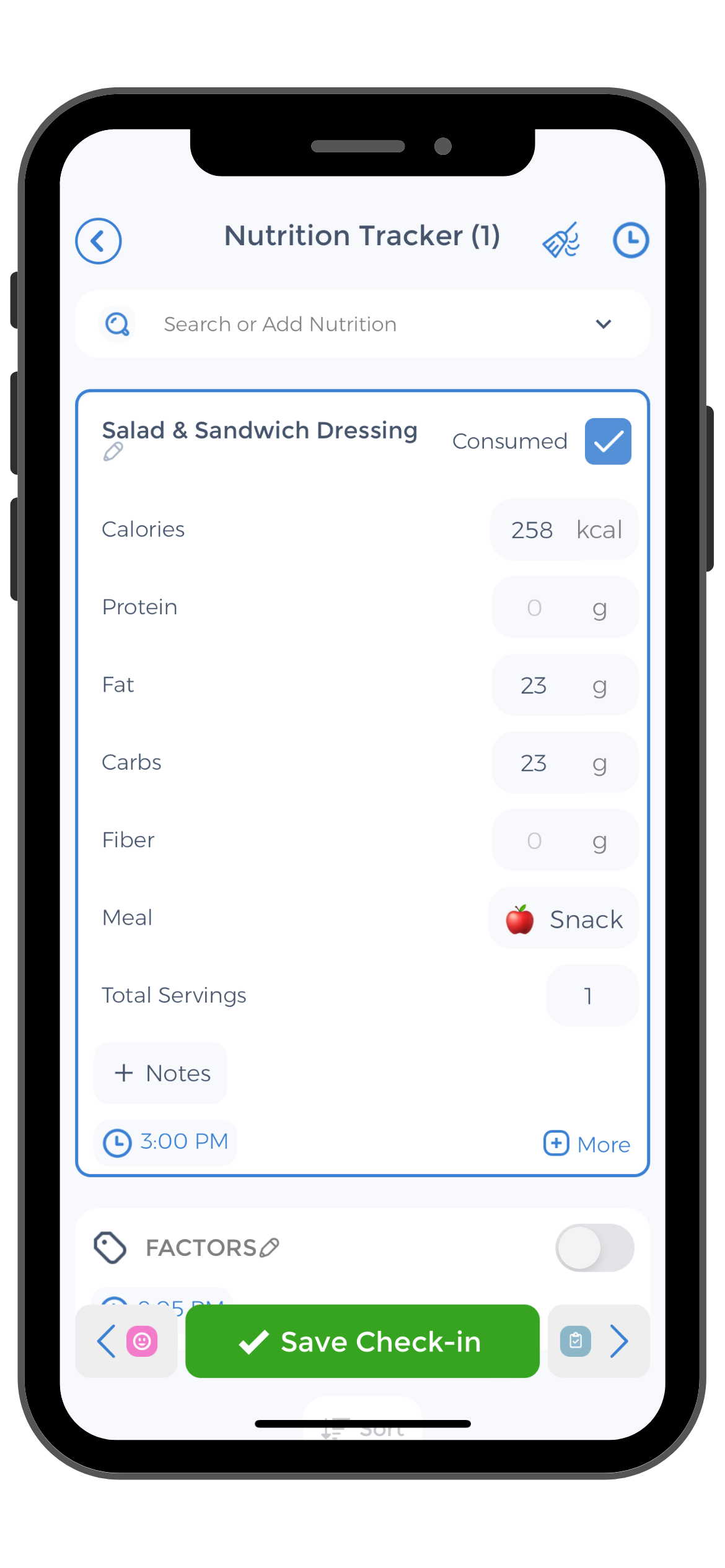
Carb control with Nutrition Logs
As it was already mentioned above, you can rely on the CareClinic health app to document your daily intake of each macronutrient. People who are trying to lose weight are generally interested in monitoring their carb intake, as carbohydrates are often responsible for the added weight. Those who suffer from diabetes might also benefit from keeping track of their carb intake.
The health app can be used for adequate carb control. You can log your meals and break them down into macronutrients, ensuring that you are eating a reduced quantity of carbohydrates. In this way, you will ensure the success of your diet and reach the desired nutritional goals.
Keeping track of your protein intake
If you are not necessarily interested in losing weight but you do want to build up your muscle mass, keeping track of your daily protein intake is a must. Once again, you can record your meals, paying attention to how much protein you are consuming. Thanks to this application, you will no longer have to guess the macronutrient content of your meals, as you can break down the meals and record each percentage yourself.
Healthy Eating Habits
 These are some of the healthy eating habits you might consider adopting:
These are some of the healthy eating habits you might consider adopting:
- Eating a healthy breakfast every day, preferably with proteins (prolonged satiety sensation)
- Drinking at least eight glasses of water per day (tea, coffee and other beverages do not count)
- Home-cooked meals prepared from fresh ingredients as an alternative to fast food and junk food
- Eating several servings of fresh fruits and vegetables every day
- Mindful eating to replace emotional eating
Free Nutrition Logging App
CareClinic helps you maintain nutrition logs. The app comes with an intuitive interface that makes recording any kind of information quite easy. It is continuously developed by a team of specialists, in accordance with the feedback you and other users have provided.
Give CareClinic a try by downloading the app for iOS or Android or use the web version as needed. All data from mobile is synced to the web and you can print nutrition logs or export them as needed.



