As uncomfortable and embarrassing as it may be, urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are conditions that affect millions of people annually. These two conditions are often confused due to some similarities in symptoms. However, they are different, and understanding the differences is crucial in seeking the right treatment and preventing further complications. So, how does one tell the difference? In this article, we will define both UTIs vs STIs, examine the causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention, treatment options, complications, and when to seek medical attention for each condition.
Defining UTI and STI
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) and Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are two types of infections that can affect the urinary and reproductive systems. While they have different causes and sometimes similar symptoms, both can be uncomfortable and even dangerous if left untreated.
What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
A UTI is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, kidneys, urethra, or ureters. Women are more likely to experience UTIs than men, and they can be caused by a variety of factors such as sexual activity, pregnancy, and certain medical conditions. Symptoms of a UTI include pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. If left untreated, a UTI can lead to a kidney infection, which can cause more serious health problems.
Thankfully, UTIs are usually easily treatable with antibiotics. If you suspect you have a UTI, it is important to see a healthcare provider as soon as possible to get an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
What is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI)?
An STI is a viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection that spreads from one person to another during sexual activity. These infections can affect the reproductive system, genitals, and other parts of the body. STIs can be asymptomatic, with no visible signs that one has been infected, so it is important to get regular STI testing if you are sexually active.
Common examples of STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, and HIV. Symptoms of an STI can vary depending on the type of infection, but may include genital sores or blisters, discharge, and pain during sex. If left untreated, certain STIs can can lead to serious health problems such as infertility, organ damage, and even death.
It is important to practice safe sex by using condoms and getting regular STI testing to prevent the spread of infections. If you suspect you have an STI, it is important to see a healthcare provider as soon as possible to get an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Causes of UTIs and STIs
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are two common health issues that affect both men and women. UTIs are infections that occur in any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, and kidneys. On the other hand, STIs are infections that are generally transmitted through sexual contact.
Common Causes of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs are primarily caused by the E. coli bacteria, which is found in the intestines and rectum. However, other types of bacteria, such as Staphylococcus saprophyticus, can also cause UTIs. Women are more susceptible to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, making it easier for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
Dehydration can also increase the risk of UTIs as it reduces the body’s ability to flush out bacteria. Poor hygiene, such as wiping from back to front after using the toilet, can also lead to the spread of bacteria from the rectum to the urinary tract. Sexual activity can also increase the risk of UTIs, especially in women, as sexual intercourse can push bacteria into the urethra. The use of certain birth control methods, such as diaphragms and spermicides, can also increase the risk of UTIs.
Common Causes of Sexually Transmitted Infections
STIs are primarily caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections that are transmitted during sexual activity. Some of the most common causes of STIs include unprotected sex with partners who are carrying the infection, multiple sexual partners, and poor hygiene.
Using condoms during sexual activity can greatly reduce the risk of contracting STIs. However, it is important to note that condoms do not provide complete protection against all types of STIs, such as genital warts and herpes. Regular STI testing is also important, especially for those who are sexually active with multiple partners.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you may have a UTI or STI. These infections can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Your healthcare provider can provide you with the appropriate treatment and advice on how to prevent future infections.[1][2]
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common conditions that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. While both can cause discomfort and pain, they have different causes and symptoms.
Symptoms of UTIs
UTI symptoms can vary, but the most common symptoms include:
- A burning sensation during urination
- A frequent need to urinate
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back
If left untreated, UTIs can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney infections. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
Symptoms of STIs
STIs can cause a wide range of symptoms, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Genital sores or blisters
- Pain during urination
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina or penis
- Fever or flu-like symptoms
It’s important to note that many STIs are asymptomatic, which means that you may not know that you have an infection. This is why regular STI screenings are essential, especially if you are sexually active or have had multiple sexual partners.
Diagnosing UTIs and STIs
UTIs are typically diagnosed through a urine test, which can detect the presence of bacteria in the urine. STIs, on the other hand, are diagnosed through a variety of methods, including:
- Blood test or urine sample
- Swabbing the affected area
- A physical exam
It’s important to get tested regularly for STIs, even if you don’t have any symptoms. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the spread of infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common health concerns that can have serious consequences if left untreated. While they may have different causes and risk factors, there are steps you can take to prevent both.
Risk Factors for UTIs
UTIs are more common in women than in men due to their shorter urethras, which makes it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder. However, men can also get UTIs, especially if they have an enlarged prostate or kidney stones. Other risk factors for UTIs include:
- Not drinking enough water
- Holding in urine for extended periods
- Using certain birth control methods, such as diaphragms or spermicides
- Having a weakened immune system due to conditions like diabetes or HIV
- Having a urinary catheter
While some risk factors, such as age and genetics, cannot be changed, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of getting a UTI:
- Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria
- Urinate frequently to prevent bacteria from building up in the bladder
- Wipe from front to back after using the bathroom to avoid spreading bacteria from the anus to the urethra
- Take showers instead of baths, as sitting in a bathtub can increase the risk of infection
- Avoid using feminine hygiene sprays or douches, which can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina
- Wear cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting clothing, as this can trap moisture and create a breeding ground for bacteria
Risk Factors for STIs
STIs are infections that are spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Anyone![]() who is sexually active can get an STI, but some sexually active people are at higher risk than others. Risk factors for STIs include:
who is sexually active can get an STI, but some sexually active people are at higher risk than others. Risk factors for STIs include:
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Having unprotected vaginal sex or anal sex
- Using drugs or alcohol, which can lead to risky sexual behavior
- Being under the age of 25
- Having a history of STIs
- Intravenous drug use
- Having sex with an infected partner
STIs can have serious health consequences if left untreated, including infertility, cancer, and even death. However, many STIs can be easily treated with antibiotics or antiviral medications if caught early. To reduce your risk of getting an STI:
- Use condoms or dental dams during sexual activity
- Get regular STI screenings, especially if you have multiple sexual partners
- Limit your number of sexual partners
- Avoid having sex with someone who has symptoms of an STI, such as genital sores or discharge
- Discuss your sexual history with your healthcare provider to determine if you should be screened for STIs
Preventing UTIs and STIs
While both UTIs and STIs have different causes and risk factors, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk of both:
- Practice good hygiene, including washing your hands frequently and keeping your genital area clean and dry
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and avoiding sugary or caffeinated beverages
- Avoid using scented products, such as soaps or lotions, on your genital area, as these can irritate the skin and increase the risk of infection
- Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which can boost your immune system and help fight off infection
- Get enough sleep and manage stress, as these can weaken your immune system and make you more susceptible to infection
By taking these steps, you can help reduce your risk of getting a UTI or STI and protect your overall health and well-being.[3][4][5]
Treatment Options
When it comes to treating infections, there are a variety of options available depending on the type and severity of the infection. In this section, we will explore two common types of infections and their treatment options.
Treating Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are a common type of infection that can affect the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. Symptoms of a UTI include a frequent and urgent need to urinate, pain or burning during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
If you suspect you have a UTI, it’s important to see a healthcare provider as soon as possible. They will likely prescribe antibiotics, which kill the bacteria responsible for the infection. It’s important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if your symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
In addition to antibiotics, there are a few things you can do at home to help alleviate symptoms of a UTI. Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria from your urinary tract, while urinating frequently can help prevent bacteria from building up.
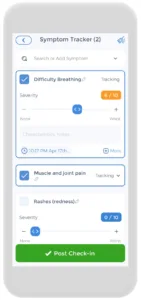
Keeping track of your symptoms can also make a big difference in your recovery. A uti tracker helps you note when symptoms start, how they change, and which treatments work best for you. This information becomes really helpful when talking to your doctor about the best treatment plan.
Applying heat to the lower abdomen can also help relieve pain and discomfort.
Treating Sexually Transmitted Infections
Sexually transmitted infections, or STIs, are infections that are spread through sexual contact. There are many different types of STIs, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, and HIV. Symptoms of an STI can vary depending on the type, but other symptoms may include genital sores, discharge, or pain during sex.
If you suspect you have an STI, it’s important to see a healthcare provider as soon as possible. They will likely perform a physical exam and order tests to determine the type of infection. Treatment options for STIs vary depending on the type, but typically involve antibiotics or antiviral medication.
It’s important to remember that many STIs can be asymptomatic, meaning you may not experience any symptoms even if you are infected. That’s why it’s important to get tested regularly if you are sexually active, even if you feel fine. Practicing safe sex, such as using condoms, can also help reduce your risk of contracting an STI.
Whether you’re dealing with a UTI or an STI, it’s important to seek a medical professional for attention as soon as possible to get the proper treatment. In addition to medication, there are also things you can do at home to help alleviate symptoms and prevent future infections.[6]
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Complications of Untreated UTIs
Untreated UTIs can lead to more severe infections and have long-term effects on the kidneys if left untreated. Chronic UTIs can cause permanent kidney damage, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a UTI, as early treatment can prevent the infection from spreading and causing more serious complications. Common symptoms of a UTI include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation when urinating, passing frequent, small amounts of urine, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
If left untreated, a UTI can spread to the kidneys, causing a more serious infection known as pyelonephritis. Symptoms of pyelonephritis include high fever, chills, back pain, nausea, and vomiting. This type of infection can cause permanent kidney damage and may even be life-threatening.
Complications of Untreated STIs
Untreated STIs can lead to serious health problems such as infertility, organ damage, and even death. Many STIs can also be passed from mother to child during childbirth, resulting in serious health problems for the baby.
It is important to practice safe sex and get tested regularly for STIs, as many infections do not have noticeable symptoms. Common symptoms of STIs include pain or discomfort during sex, unusual discharge from the genitals, and sores or bumps in the genital area.
If left untreated, common STIs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), a serious infection of the reproductive organs that can lead to infertility. Other STIs, such as HIV and syphilis, can cause damage to the immune system and other organs, leading to serious health problems and even death.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have an STI, as early treatment can prevent the infection from spreading and causing more serious complications. Treatment may involve antibiotics, antiviral medications, or other medications depending on the type of infection.
Remember, practicing safe sex and getting tested regularly for STIs is the best way to prevent complications and protect your overall health.[7][8][9][10]
When to Seek Medical Help
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common health issues that can cause discomfort and inconvenience. While some cases may resolve on their own, it’s important to know when to seek medical help to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
When to Consult a Doctor for UTI Symptoms
 UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing symptoms such as frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor, especially if they persist or worsen. Other signs that you should seek medical attention include:
UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing symptoms such as frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a doctor, especially if they persist or worsen. Other signs that you should seek medical attention include:
- Blood in your urine
- Fever or chills
- Pain in your back or side
- Nausea or vomiting
These symptoms may indicate a more serious infection that requires prompt medical attention. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection and may recommend additional tests or treatment if necessary.
When to Consult a Doctor for STI Symptoms
STIs are infections that are spread through sexual contact, and they can cause a range of symptoms, including genital sores, discharge, and pain during sex. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Other signs that you should consult a doctor include:
- Fever or flu-like symptoms
- Pain or swelling in your genitals or pelvic area
- Unusual discharge or bleeding from your genitals
These symptoms may indicate an underlying health problem, and prompt medical attention can help prevent long-term complications and ensure that you receive the appropriate treatment. Your doctor may recommend testing for STIs and may prescribe antibiotics or other medications to treat the infection.
Remember, it’s important to take care of your sexual and urinary health by practicing safe sex, staying hydrated, and seeking medical attention when necessary. By doing so, you can minimize your risk of complications and enjoy a healthy, active lifestyle.[11][12]
Using the Careclinic app to track UTIs and STIs
While UTIs and STIs share some similarities, they are different conditions that require unique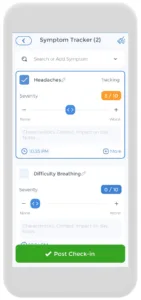 treatments and preventive measures. On the Careclinic app, you can track the STD symptoms you are experiencing and try to understand what you may have based on the key differences mentioned in this article. Whether or not you have an STI or UTI, regular STD testing is important, and you can track your appointments on the app.
treatments and preventive measures. On the Careclinic app, you can track the STD symptoms you are experiencing and try to understand what you may have based on the key differences mentioned in this article. Whether or not you have an STI or UTI, regular STD testing is important, and you can track your appointments on the app.
Staying informed about UTIs and STIs and taking preventive measures can help reduce your risk of infection and improve your sexual health. By practicing good hygiene, using condoms during sexual activity, and undergoing regular STI screenings, you can protect your health and reduce the risk of complications or long-term effects. Remember, your health is in your hands, and taking charge of it is the most important step towards a healthy life.
References
- “Urinary Tract Infection Basics | Urinary Tract Infection | CDC”. https://www.cdc.gov/uti/about/index.html/
- “Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)”. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sexually-transmitted-infections-%28stis%29
- “Urinary Tract Infection Basics | Urinary Tract Infection | CDC”. https://www.cdc.gov/uti/about/
- “What doctors wish patients knew about UTI prevention | American Medical Association”. https://www.ama-assn.org/delivering-care/public-health/what-doctors-wish-patients-knew-about-uti-prevention
- “How to Prevent STIs | STI | CDC”. https://www.cdc.gov/sti/prevention/
- “Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)”. https://www.who.int/health-topics/sexually-transmitted-infections/
- “Untreated UTI: What Are the Risks? – GoodRx”. https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/urinary-tract-infection/untreated-uti-risks-dangers
- “Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development – NICHD”. https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/factsheets/stds
- “The Dangers of Undiagnosed Sexually Transmitted Infections”. https://asm.org/Articles/2022/December/The-Dangers-of-Undiagnosed-Sexually-Transmitted-In
- “Major Health Conditions Caused by Untreated STDs | AtHomeSTDKit.com”. https://www.athomestdkit.com/topics/top-5-major-health-conditions-caused-by-untreated-stds/
- “When to See a Doctor for a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) | Houston Methodist On Health”. https://www.houstonmethodist.org/blog/articles/2022/apr/when-to-see-a-doctor-for-a-urinary-tract-infection-uti/
- “Recognizing STD Symptoms & Early Detection | MedicineContact.com”. https://www.medicinecontact.com/blog/40538/std-symptoms-signs
- “UTI vs. STI: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment | Equality Health”. https://www.ehg.health/uti-vs-sti/
- “Spotting the difference: UTIs and STIs – Ada Editorial”. https://ada.com/editorial/uti-or-sti-how-to-spot-the-difference/