
Anxiety and mild to major depression is a common and debilitating mental health disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide. In order to combat the symptoms and possible side effects, healthcare professionals often prescribe standard treatment and different antidepressants. Which are designed to help restore the brain and body’s balance of neurotransmitters. While this both drug and standard treatment can be effective in alleviating symptoms of depression, it is important to be aware of their potential negative side effects on the brain.[1][2][3]
Understanding Antidepressants: A Brief Overview
Antidepressants are a class of medications specifically developed to treat mental health disorders. They work by altering the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain chemistry, such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine. By doing so, antidepressants aim to regulate mood and bipolar disorder, improve sleep patterns and insomnia, and enhance overall well-being, including sexual dysfunction.
What are Antidepressants?
Antidepressants are medications that can be prescribed by a doctor or healthcare professional to help manage the symptoms of depression. They come in various forms, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
The Role of Antidepressants in the Body
Antidepressants are commonly used to treat moderate to severe depression when other treatment options, such as talk therapy, have not been successful. They can provide relief from symptoms such as persistent sadness, including suicidal thoughts, loss of interest in activities, weight gain and weight loss, and insomnia.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of antidepressants can vary from person to person. While some individuals may experience significant improvement in their symptoms. Others may not respond to other drugs as well or may experience side effects. Therefore, finding the right antidepressant and different medication may require some trial and error for few weeks.
Additionally, it is crucial for individuals taking antidepressants to follow their healthcare professional’s instructions and attend regular follow-up appointments. This allows the healthcare provider to monitor the individual’s progress, adjust the dosage if necessary, and address any risks, concerns or common side effects that may occur.
Furthermore, it is worth mentioning that antidepressants are not a cure. They are a tool that can help manage life-threatening symptoms and improve quality of life. In many cases, a combination of medication and therapy may be the most effective approach.[4][5]
The Brain and Antidepressants: A Complex Relationship
The brain is an intricate organ composed of billions of neurons that communicate with each other through neurotransmitters. These chemical messengers play a crucial role in regulating mood, emotions, and cognitive functions. When it comes to the effects of antidepressants on the brain, it is important to consider the brain’s neurotransmitter system and how these medications interact with it.
The Brain’s Neurotransmitter System
Neurotransmitters act as chemical signals that transmit information between neurons. Serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are among the key neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation. Alterations in the levels of these neurotransmitters are thought to contribute to the development of depression and anxiety.
How Antidepressants Interact with the Brain Chemistry
 Antidepressants work by blocking the reabsorption or reuptake of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. This allows these neurotransmitters to remain active for longer periods of time, and serotonin levels thereby enhancing their mood-regulating effects and obsessive obsessive-compulsive disorder. However, the precise mechanisms by which these antidepressants work and exert their side effects are still not fully understood.
Antidepressants work by blocking the reabsorption or reuptake of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. This allows these neurotransmitters to remain active for longer periods of time, and serotonin levels thereby enhancing their mood-regulating effects and obsessive obsessive-compulsive disorder. However, the precise mechanisms by which these antidepressants work and exert their side effects are still not fully understood.
One theory suggests that antidepressants drug may also promote neurogenesis, the growth and development of new neurons, in certain regions of the brain. This could potentially contribute to the long-term effects of these medications on mood and overall brain function.
Another fascinating aspect of the brain’s response to antidepressant drugs is the phenomenon known as neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt its structure and function in response to experiences and environmental changes. Some studies have suggested that antidepressant drugs may enhance neuroplasticity. Allowing the brain to better adapt to stress and improve resilience to anxiety.[6][7][8]
 Antidepressants work by blocking the reabsorption or reuptake of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. This allows these neurotransmitters to remain active for longer periods of time, and serotonin levels thereby enhancing their mood-regulating effects and obsessive obsessive-compulsive disorder. However, the precise mechanisms by which these antidepressants work and exert their side effects are still not fully understood.
Antidepressants work by blocking the reabsorption or reuptake of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. This allows these neurotransmitters to remain active for longer periods of time, and serotonin levels thereby enhancing their mood-regulating effects and obsessive obsessive-compulsive disorder. However, the precise mechanisms by which these antidepressants work and exert their side effects are still not fully understood.
One theory suggests that antidepressants drug may also promote neurogenesis, the growth and development of new neurons, in certain regions of the brain. This could potentially contribute to the long-term effects of these medications on mood and overall brain function.
Another fascinating aspect of the brain’s response to antidepressant drugs is the phenomenon known as neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt its structure and function in response to experiences and environmental changes. Some studies have suggested that antidepressant drugs may enhance neuroplasticity. Allowing the brain to better adapt to stress and improve resilience to anxiety.
Unveiling the Negative Side Effects of Antidepressant Drugs
While antidepressant drugs can be beneficial in treating depression, it is crucial to be aware of their potential negative side effects on the brain. These effects can manifest in various ways and may have an impact on cognitive function, emotional well-being, body weight, and even brain structure.
Cognitive Impairments Linked to Antidepressant Drugs
Some studies have suggested that long-term use of certain antidepressant drugs may be associated with cognitive impairments. Such as memory problems and difficulties with attention and concentration. These cognitive side effects can vary in severity and may impact an individual’s daily functioning.
Imagine struggling to remember important details, like the name of a close friend or a significant event from your past. For individuals experiencing these cognitive impairments, it can be frustrating and disheartening. Simple tasks that were once effortless may now require extra effort and concentration.
Furthermore, the impact of cognitive impairments can extend beyond one’s personal life. In professional settings, individuals may find it challenging to stay focused during meetings or complete tasks that require sustained attention. This can lead to decreased productivity and potential setbacks in one’s career.
Emotional Blunting and Antidepressants
Emotional blunting, also known as emotional numbing, is another potential side effect of antidepressant use. It refers to a reduced ability to experience and express emotions. While this side effect sometimes may be beneficial for individuals experiencing intense emotional distress, it can impact one’s overall emotional well-being and interpersonal relationships.
Imagine a world where colors appear dull and emotions feel muted. For individuals experiencing emotional blunting, the vibrancy of life may seem diminished. They may struggle to connect with others on an emotional level. Leading to strained relationships and a sense of isolation.
Moreover, emotional blunting can affect one’s ability to navigate social situations. Expressing empathy and understanding becomes challenging when emotions are dulled. This can create misunderstandings and hinder the formation of meaningful connections with others.
The Long-Term Impact on Brain Structure
Emerging research suggests that long-term use of certain antidepressants may have an impact on brain structure. Specifically, these medications may affect the size and functioning of certain brain regions involved in mood regulation. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent and implications of these changes.
Imagine the brain as a complex network of interconnected pathways. Antidepressants have the potential to influence the structure and function of these pathways, altering the body’s cells delicate balance of neurotransmitters and receptors. While this may bring relief to those suffering from depression, it raises questions about the long-term consequences.
Understanding the long-term impact on brain structure is crucial for developing safer and more effective treatments. Researchers are working diligently to unravel the complexities of these changes in brain chemistry and their implications for mental health. By gaining a deeper understanding, we can strive to minimize the negative effects while maximizing the benefits of antidepressant medications.
The Controversy Surrounding Antidepressant Use
Antidepressant use has sparked considerable debate within the medical community and among the general public. While many doctor believe that the benefits of these medications outweigh the potential risks, others question their efficacy and express concerns about their side effects.
The Medical Community’s Perspective
The majority of medical professionals agree that antidepressants can be a valuable tool in treating depression when used appropriately. They emphasize the importance of individualized treatment plans and close monitoring of patients to ensure optimal outcomes. It is important for individuals considering or already using antidepressants to consult with their doctor or a qualified healthcare professional to understand the drug, potential benefits and risks.
Public Perception and Misconceptions
Public perception of antidepressants can vary, and there are often misconceptions surrounding these medications. Some individuals may view antidepressants as a “quick fix” or a cure-all for depression, while others may harbor concerns about their safety and long-term effects. Open and honest discussions about antidepressants can help dispel misconceptions and provide individuals with accurate information.
One common misconception about antidepressants is that they are addictive. While it is true that some individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms when discontinuing certain antidepressant medications, this does not mean they are addictive in the same way as drugs like opioids or benzodiazepines. Antidepressants work by balancing chemicals in the brain, and when someone stops taking them abruptly, it can disrupt this balance and lead to withdrawal symptoms. However, with proper medical guidance, individuals can safely taper off antidepressants to minimize these effects.
Another aspect of public perception is the belief that antidepressants are only effective for severe depression. While antidepressants are often prescribed for moderate to severe depression, they can also be beneficial for individuals with milder forms of depression. In fact, research has shown that antidepressants can be effective in treating a range of depressive symptoms, including persistent sadness, loss of interest, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns. It is important for individuals to discuss their symptoms with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Alternatives to Antidepressants in Treating Depression
While antidepressants can be effective in treating depression, they are not the only option available. In fact, there are several alternative approaches that may be considered, either as standalone treatments or in combination with medication.
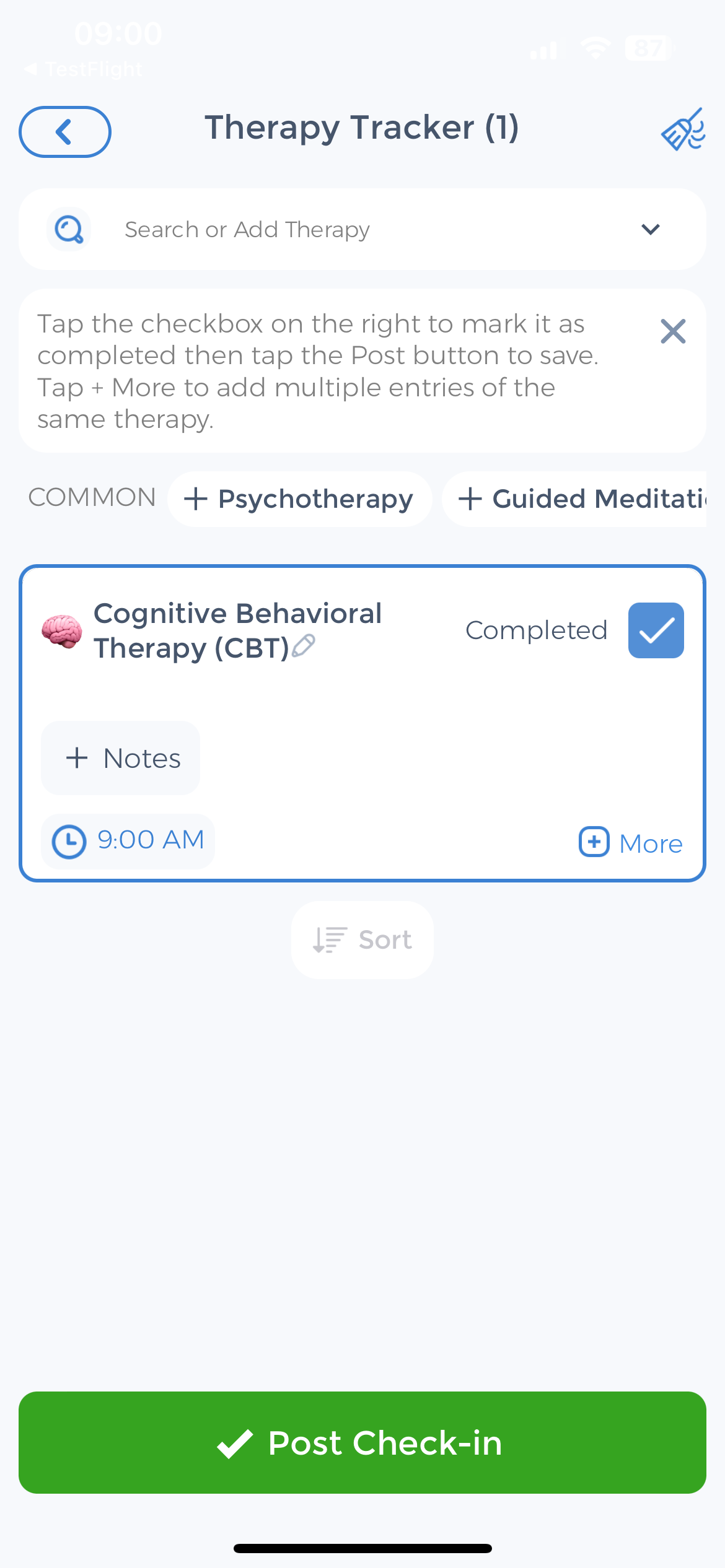
Psychotherapy and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a widely used treatment option for depression. By working with a trained therapist or counselor, individuals can explore their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in a supportive environment. This therapeutic approach provides a safe space for individuals to express their feelings and gain insight into the underlying causes of their depression.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a specific type of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative patterns of thinking and behavior that contribute to depression. Through CBT, individuals learn new coping skills and strategies to challenge negative thoughts and replace them with more positive and adaptive ones. This therapy can empower individuals to take control of their mental health and develop healthier ways of thinking and behaving.
Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies
 Adopting healthy lifestyle practices can also play a significant role in managing depression. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, has been shown to increase the production of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Engaging in physical activity not only improves physical health but also enhances mental well-being.
Adopting healthy lifestyle practices can also play a significant role in managing depression. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, has been shown to increase the production of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Engaging in physical activity not only improves physical health but also enhances mental well-being.
In addition to exercise, proper nutrition is essential for supporting mental health. Consuming a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide the necessary nutrients for optimal brain function. Avoiding excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and caffeine can also help stabilize mood and energy levels.
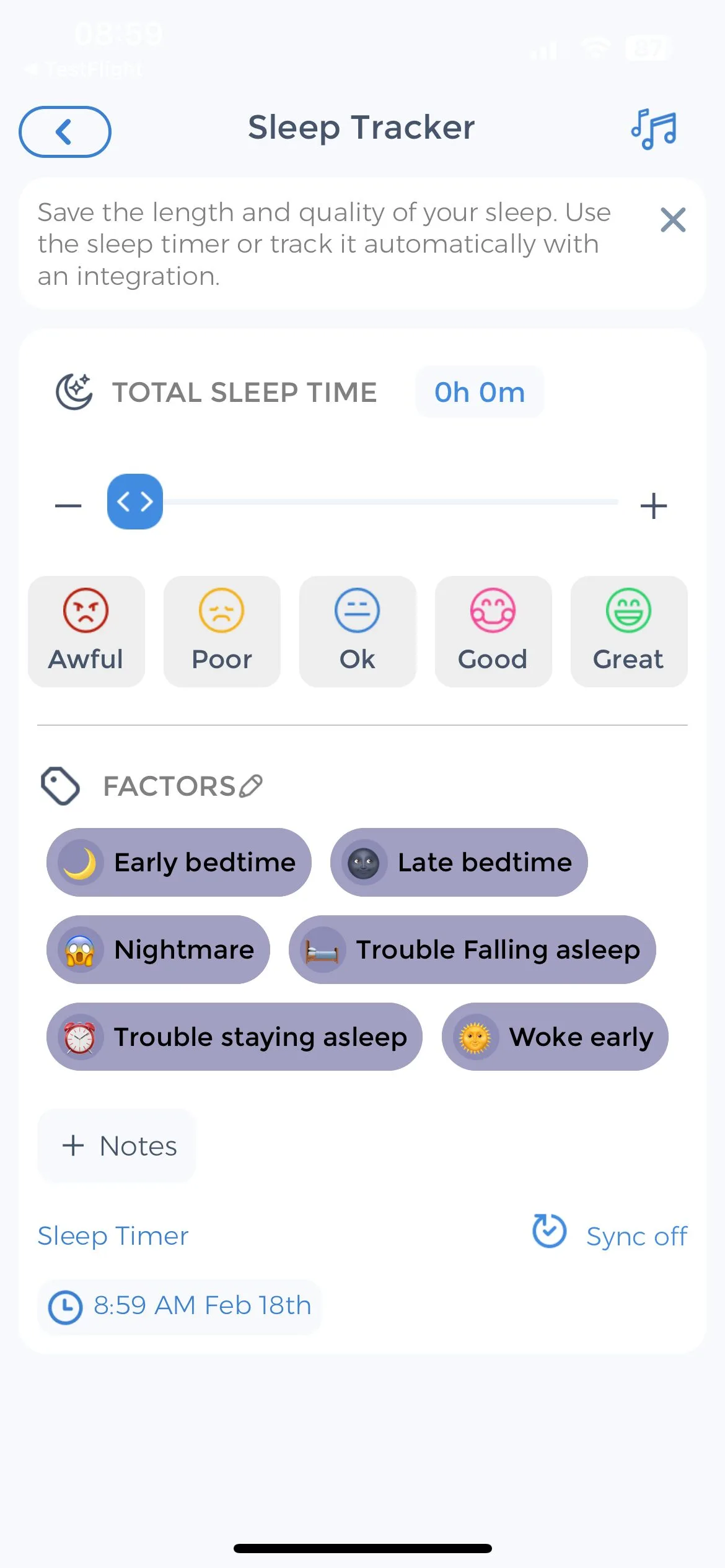
Furthermore, sufficient sleep is crucial for maintaining emotional balance. Establishing a consistent sleep routine, practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime, and creating a comfortable sleep environment can promote restful sleep and improve overall mood.
Additionally, some individuals may find relief through complementary and alternative therapies, such as meditation, yoga, or herbal supplements. Meditation and yoga can help reduce stress, promote relaxation, and increase self-awareness. Certain herbal supplements, such as St. John’s wort and omega-3 fatty acids, have also shown potential in alleviating symptoms of depression. However, it is important to discuss any alternative treatments with a healthcare professional to ensure their safety and efficacy. If interested, read more on using CareClinic as a daily supplement tracker for managing your treatment.
Incorporating Self-Care into Daily Life
Self-care is an essential aspect of promoting mental health and well-being. In addition to seeking appropriate treatment options, individuals can engage in self-care practices to support their recovery from depression. This may include activities such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies or creative outlets, maintaining social connections, and setting realistic goals.
Practicing mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment and non-judgmentally observing one’s thoughts and feelings. This can help individuals cultivate a sense of calm and reduce stress. Engaging in hobbies or creative outlets, such as painting, writing, or playing a musical instrument, can provide a sense of fulfillment and serve as a positive distraction from negative thoughts and emotions.
Maintaining social connections is also crucial for mental well-being. Spending time with loved ones, participating in group activities, or joining support groups can provide a sense of belonging and support. Sharing experiences and emotions with others who may be going through similar struggles can be comforting and validating.
Setting realistic goals can help individuals regain a sense of purpose and accomplishment. Breaking larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps can make them feel more attainable. Celebrating even small achievements along the way can boost self-esteem and motivation.
Developing a self-care routine tailored to one’s individual needs and preferences can empower individuals to take an active role in their mental health journey. By incorporating these practices into daily life, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and find additional support in their journey towards recovery.
Role of SSRI Antidepressants
Antidepressants can be valuable tools in the treatment of depression, but it is important to be aware of their potential negative effects on the brain. Understanding how antidepressants interact with the brain’s neurotransmitter system and the possible implications of long-term use is crucial for informed decision-making. It is equally important to consider alternative treatments and engage in self-care practices to support one’s mental health journey. By working closely with healthcare professionals and adopting a holistic approach, individuals can navigate the complexities of depression treatment and strive towards improved well-being.
Use the CareClinic App to Track Tricyclic Antidepressants
If you’re navigating the complexities of depression treatment and considering the role of antidepressants, the CareClinic App can be a valuable ally in managing your mental health journey. The app offers a comprehensive platform to track your mood, medication and sexual side effects, and overall well-being, allowing for a personalized approach to treatment. By monitoring symptoms and side effects, you can work with your healthcare provider to make informed decisions about your medication regimen.
Download the CareClinic App and Manage Serotonin Syndrome
With the CareClinic App, you can set reminders for medication, therapy sessions, and self-care activities, ensuring consistency in your treatment plan. The app’s reporting features allow you to observe trends over time, which can be crucial in understanding the impact of antidepressants on your cognitive and emotional health. Install the CareClinic App today to take control of your mental health and move towards improved outcomes. Install App today!
References
- “One Dose of Antidepressant Changes the Brain, Study Finds”. https://time.com/3399344/antidepressant-changes-the-brain-study-finds/
- “Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antidepressant_discontinuation_syndrome
- “Persistent adverse effects of antidepressants – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8061256/
- “What you should know about antidepressants – Harvard Health”. https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/what-you-should-know-about-antidepressants-
- “Antidepressants: What They Are, Uses, Side Effects & Types”. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/9301-antidepressants-depression-medication
- “Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Selective_serotonin_reuptake_inhibitor
- “Biology of depression”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Biology_of_depression
- “Neuroplasticity”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroplasticity
- “Emotional Blunting, Cognitive Impairment, Bone Fractures, and Bleeding as Possible Side Effects of Long-Term Use of SSRIs – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8650205/
- “Emotional Blunting in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder: A Brief Non-systematic Review of Current Research – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8712545/


