Sciatica is a condition that causes pain radiating along the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back down each leg. The pain can be debilitating and impact daily activities, making it essential to find effective treatment options. One such option is the use of Gabapentin, a medication that has shown promise in providing relief for sciatica pain. In this article, we will explore the causes and symptoms of sciatica, provide an overview of Gabapentin, discuss its effectiveness in relieving sciatica pain, highlight potential side effects and precautions, and explore alternative treatments.[1][2][3][4]
Understanding Sciatica: Causes and Symptoms
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve becomes compressed or irritated. This can be due to a herniated disc, bone spurs, or narrowing of the spinal canal (spinal stenosis). The most common cause of sciatica is a herniated disc, which occurs when the soft inner core of a disc protrudes through its outer shell. The symptoms of sciatica typically include sharp, shooting pain in the lower back, buttocks, and legs, numbness or tingling, and muscle weakness.
What is Sciatica?
Sciatica is a condition in which the sciatic nerve, the longest nerve in the body, becomes irritated or compressed. The sciatic nerve starts in the lower back and extends down each leg. When the nerve is irritated or compressed, it can cause pain, numbness, and tingling, often radiating from the lower back to the buttocks and legs.
Chronic sciatica can be a debilitating condition, affecting a person’s daily activities and quality of life. It can make it difficult to sit, stand, walk, or even sleep comfortably depending on leg pain intensity. The pain can range from mild to severe, and it may come and go or persist for long periods of time. Understanding the causes and symptoms of sciatica is crucial in seeking appropriate treatment and finding relief.
Common Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica can be caused by various factors, including herniated discs, bone spurs, spinal stenosis, and even muscle inflammation. A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner core of a disc protrudes through its outer shell, pressing on the sciatic nerve. This can happen due to age-related degeneration, injury, or excessive strain on the spine.
Bone spurs, also known as osteophytes, can develop on the spinal bones, causing compression on the nerve. These bony outgrowths can form as a result of arthritis or other degenerative conditions affecting the spine. They can narrow the space through which the sciatic nerve passes, leading to irritation and symptoms of sciatica.
Spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can lead to nerve compression. This condition is often associated with aging and can be caused by degenerative changes in the spine, such as the thickening of ligaments or the growth of bone spurs. When the spinal canal narrows, the sciatic nerve may become compressed, resulting in sciatica symptoms.
Lastly, muscle inflammation or irritation can also contribute to sciatica symptoms. Muscles in the lower back and buttocks can become tight or spasmodic, putting pressure on the sciatic nerve. This can occur due to poor posture, muscle imbalances, or overuse injuries.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Sciatica
Symptoms of sciatica include pain, numbness, and tingling that radiates from the lower back to the buttocks and legs. The pain is often described as sharp, sometimes severe shooting pain, or severe burning pain, and it can vary in pain intensity. It may worsen with certain movements, such as bending, twisting, or sitting for prolonged periods. In some cases, weakness or difficulty moving the leg or foot may also be present.
It is important to note that the severity and location of symptoms can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience pain primarily in the buttocks, while others may feel it more in the leg or foot. The pain intensity may be constant or intermittent, and it may worsen at night or after prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
It is advisable to seek medical attention if you experience severe or chronic sciatica symptoms. A healthcare professional can perform a thorough evaluation, including physical examination and imaging tests, to determine the underlying cause of your sciatica and recommend appropriate treatment options.[5][6]
An Overview of Gabapentin
Gabapentin is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as anticonvulsants. It was initially developed to treat epilepsy but has also been found to be effective in relieving certain types of nerve pain, including peripheral neuropathic pain syndromes. Gabapentin works by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain that can lead to seizures and by affecting the transmission of pain signals in the nervous system.
What is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin, also sold under the brand name Neurontin, is a medication approved by the FDA to treat epilepsy and certain types of nerve pain. It is not classified as a narcotic or an opioid and does not have the same potential for abuse. Gabapentin is available in tablet, capsule, and oral solution forms and is usually taken multiple times a day as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
How Does Gabapentin Work?
Gabapentin helps relieve pain by affecting the transmission of pain signals in the nervous system. It does this by binding to certain receptors in the brain, reducing the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain perception. By modulating the release of these neurotransmitters, Gabapentin can help reduce nerve-related pain, such as that experienced in sciatica.
Common Uses of Gabapentin
Aside from its approved uses for epilepsy and nerve pain, Gabapentin is also sometimes prescribed off-label for conditions such as restless leg syndrome, fibromyalgia, and certain mood disorders. However, it is important to note that the off-label use of medications should always be discussed with and supervised by a healthcare professional.
Gabapentin has been found to be particularly effective in the treatment of epilepsy. It works by stabilizing the electrical activity in the brain, preventing the occurrence of seizures. This can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with epilepsy, allowing them to live more independently and engage in activities that they may have previously been unable to do.
When it comes to nerve pain, Gabapentin has shown promising results in relieving the symptoms of conditions such as acute sciatica. Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down the back of each leg. This pain can be debilitating and greatly affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities. Gabapentin works by reducing the transmission of pain signals along the nerves, providing immediate pain relief to individuals suffering from sciatica. However, it can vary, causing only limited pain relief in some patients to having the pain resolved completely in others.
Fibromyalgia is another condition in which Gabapentin has shown some promise. Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness. Gabapentin can help reduce the pain associated with fibromyalgia by modulating the release of neurotransmitters involved in pain perception. This can provide much-needed relief to individuals suffering from this debilitating condition.[7][8][9][10]
Gabapentin for Sciatica Pain Relief
When it comes to relieving chronic sciatica pain, Gabapentin has shown promise in providing limited pain relief, for some individuals. By targeting the transmission of pain signals in the nervous system, Gabapentin can help alleviate the sharp, shooting pain associated with sciatica. In addition to its potential pain-relieving effects, Gabapentin may also help improve sleep and overall quality of life for those with sciatica.
Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back through the hips and down each leg. This pain can be debilitating, making it difficult for individuals to perform daily activities and affecting their overall well-being.
How Gabapentin Helps with Sciatica Pain
Gabapentin’s ability to alleviate sciatica pain lies in its mechanism of action. By modulating the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain perception, Gabapentin can reduce the intensity and frequency of pain signals traveling from the sciatic nerve to the brain. This can lead to a significant reduction in sciatica-related pain, allowing individuals to regain comfort and function in their daily lives.
Moreover, Gabapentin’s effects on pain modulation extend beyond the sciatic nerve. It can also target other nerve pathways involved in pain transmission, providing a comprehensive approach to pain relief. This multi-targeted action sets Gabapentin apart from other medications commonly used for sciatica, making it a valuable option for individuals seeking long-lasting neuropathic pain relief.
Clinical Trials Supporting Gabapentin Use for Sciatica
Several clinical studies have explored the effectiveness of Gabapentin in relieving sciatica pain. These studies have shown positive results, with Gabapentin demonstrating significant pain reduction compared to a placebo. The findings from these studies have provided valuable insights into the potential benefits of Gabapentin for individuals suffering from sciatica.
Furthermore, these studies and clinical trials have also highlighted the importance of individualized treatment plans. While Gabapentin may be effective for some individuals, it may not be the ideal choice for everyone. Factors such as underlying health conditions, medication interactions, and individual responses to treatment must be carefully considered when determining the most appropriate course of action.
It is worth noting that Gabapentin is not without its potential side effects. Common side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, and coordination difficulties. However, most individuals tolerate the medication well, and these side effects can often be managed with proper dosage adjustments and monitoring.
Overall, Gabapentin offers a promising option for individuals seeking relief from sciatica pain. Its ability to target pain signals in the nervous system, coupled with its potential to improve sleep and overall quality of life, make it a valuable tool in the management and treatment of sciatica. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and to discuss any potential risks or concerns.[11][12][13]
Potential Side Effects of Gabapentin
Like any medication, Gabapentin can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them. Common side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and coordination difficulties. These symptoms are typically mild and temporary, resolving on their own as the body adjusts to the medication.
Gabapentin, also known by its brand name Neurontin, is a medication primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It belongs to a class of drugs called anticonvulsants, which work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. While it is generally well-tolerated, there are some potential side effects that patients should be aware of.
Common Side Effects
The most common side effects of Gabapentin include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and difficulties with coordination. These side effects are usually mild and tend to diminish over time as the body becomes accustomed to the medication. It is important to note that not everyone will experience these side effects, and some individuals may have a higher tolerance for the medication.
Dizziness is a common side effect of Gabapentin and may be more pronounced when starting the medication or increasing the dosage. This can make activities such as driving or operating heavy machinery potentially dangerous. It is advisable to avoid these activities until the dizziness subsides and you are certain of how the medication affects you.
Drowsiness and fatigue are also common side effects of Gabapentin. These symptoms can affect daily functioning and may interfere with work or other activities. It is important to get enough rest and avoid activities that require alertness until these side effects subside.
Difficulties with coordination may also occur while taking Gabapentin. This can manifest as unsteady movements or clumsiness. It is important to be cautious when engaging in activities that require precise coordination, such as walking on uneven surfaces or participating in sports.
Serious Side Effects
While serious adverse effects are rare, there are some serious side effects associated with Gabapentin use, including abnormal mood changes, suicidal thoughts or behaviors, allergic reactions, and severe skin reactions. If any of these symptoms occur, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention and discontinue the medication.
Abnormal mood changes, such as feeling unusually agitated, irritable, or depressed, may occur while taking Gabapentin. It is important to monitor your mood closely and report any significant changes to your healthcare provider. Suicidal thoughts or behaviors should be taken seriously and require immediate medical attention.
Allergic reactions to Gabapentin are rare but can occur. Symptoms may include rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Severe skin reactions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis, are extremely rare but potentially life-threatening. These conditions cause the skin to blister and peel, leading to severe pain and discomfort. If you develop a rash or notice any changes in your skin while taking Gabapentin, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention.
In conclusion, while Gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects associated with its use. Common side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and coordination difficulties are usually mild and temporary. However, serious side effects such as abnormal mood changes, suicidal thoughts or behaviors, allergic reactions, and severe skin reactions require immediate medical attention and discontinuation of the medication. If you have any concerns or questions about the side effects of Gabapentin, it is best to consult with your healthcare provider.[14][15][16][17]
Precautions and Contraindications When Using Gabapentin
While Gabapentin can be an effective treatment option for sciatica pain relief, certain precautions and contraindications should be considered before starting this medication.
Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly prescribed to manage nerve pain. It works by reducing abnormal activity in the brain that can cause seizures and nerve pain. However, before starting Gabapentin, it is important to be aware of the precautions and contraindications associated with its use.
Who Should Avoid Gabapentin?
While Gabapentin can provide significant relief for many individuals, there are certain groups of people who should avoid using this medication. Firstly, individuals who have had a previous allergic reaction to Gabapentin or any of its components should not take this medication. Allergic reactions can range from mild symptoms, such as rash or itching, to more severe reactions that can be life-threatening.
In addition, individuals with a history of kidney problems should exercise caution when considering Gabapentin. This medication is primarily eliminated from the body through the kidneys, so any impairment in kidney function can affect how the drug is processed and eliminated. It is crucial to discuss any kidney issues with a healthcare professional before starting Gabapentin.
Interactions with Other Medications
![]() Gabapentin has the potential to interact with certain other medications, which can impact its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects. It is essential to inform a healthcare professional about all medications being taken, including prescription, over-the-counter, and herbal supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
Gabapentin has the potential to interact with certain other medications, which can impact its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects. It is essential to inform a healthcare professional about all medications being taken, including prescription, over-the-counter, and herbal supplements, to avoid potential interactions.
One significant interaction to be aware of is with opioids, which are commonly prescribed for pain management. Combining Gabapentin with opioids can enhance the sedative effects of both medications, leading to increased drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. It is important to follow the guidance of a healthcare professional when using these medications together.
Another potential interaction is with antacids, which are commonly used to relieve symptoms of heartburn or indigestion. Antacids can reduce the absorption of Gabapentin, leading to lower levels of the medication in the bloodstream. This can decrease its effectiveness in managing nerve pain. If antacids are necessary, it is recommended to take them at least two hours apart from Gabapentin to minimize the interaction.
Lastly, certain antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), can interact with Gabapentin. These interactions can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by symptoms such as agitation, hallucinations, rapid heartbeat, and high blood pressure. It is important to discuss drug interactions with all current antidepressant medications with a healthcare professional before starting Gabapentin.[18]
How to Take Gabapentin for Sciatica Pain
The dosage and administration of Gabapentin for sciatica pain relief can vary depending on individual factors, such as the severity of the pain and the patient’s response to the medication. Therefore, it is crucial to follow the advice of a healthcare professional and strictly adhere to the prescribed dosage.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of Gabapentin for sciatica pain relief is typically started at a low dose, which is gradually increased over time. The healthcare professional will determine the optimal dosage based on individual needs and response to the medication. It is important to take Gabapentin exactly as prescribed and not to adjust the dosage without medical guidance.
What to Do If You Miss a Dose?
If a dose of Gabapentin is missed, it is important to take it as soon as it is remembered. However, if it is close to the time for the next scheduled dose, it is advisable to skip the missed dose and continue with the regular dosing schedule. Taking a double dose to make up for a missed dose is not recommended.[19][20]
Alternatives to Gabapentin for Sciatica Pain Relief
While Gabapentin can be an effective option for sciatica pain relief, it is essential to explore alternative treatments for those treating sciatica who may not be suitable candidates for this medication or who prefer different approaches.
Other Medications
There are other medications available that can be used for sciatica pain relief, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and muscle relaxants. These medications work by reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and relaxing the muscles. However, it is important to discuss with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication based on individual needs and medical history.
Non-Pharmacological Alternatives
Non-pharmacological treatments can also provide relief for sciatica pain. These include physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, and exercises targeting the sciatic nerve. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining good posture, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and engaging in regular exercise, can help manage sciatica symptoms and reduce the recurrence of flare-ups.
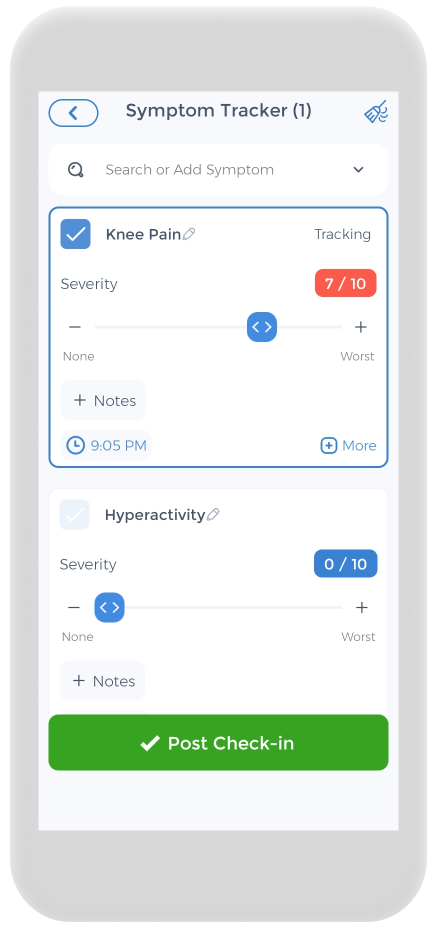
Using the CareClinic App to Manage Pain
Keeping a pain journal is important for your health, and the CareClinic app can help you do so. The app can be used as a clinical and health journal. Simply go to the app’s pain diary section and keep track of your daily symptoms, medications, and any triggers. Other sections of the program are dedicated to tracking each of these. This can help you identify early warning signs. Whether you have chronic low back pain, neck pain, acute injuries or traumatic injuries, the app is designed to help you improve your acute pain-related health.
Sources
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/pain
- https://painbc.ca/health-professionals/education/OT-workshop
References Drug interactions happen with many common medications, not just prescription ones. If you get headaches along with your nerve pain, you might wonder what can i take with excedrin migraine safely. These kinds of questions are important to discuss with your doctor since mixing medications can be tricky.
- “A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness and adverse events of gabapentin and pregabalin for sciatica pain – ScienceDirect”. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0212656721001785
- “Effect of Gabapentin vs Pregabalin on Pain Intensity in Adults With Chronic Sciatica: A Randomized Clinical Trial – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6439871/
- “Gabapentin”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gabapentin
- “Gabapentin for Sciatica: A Comprehensive Review – Kaly”. https://www.kaly.com/blog/gabapentin-for-sciatica/
- “Sciatica”. https://ask-ahd.ahdubai.com/con-20377416
- “Sciatica”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sciatica
- “Implications and mechanism of action of gabapentin in neuropathic pain – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23435945/
- “Gabapentin – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493228/
- “Gabapentin (Neurontin) | Pain Management Education at UCSF”. https://pain.ucsf.edu/non-opioid-analgesics/gabapentin-neurontin
- “Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4171034/
- “A systematic review and meta-analysis of the effectiveness and adverse events of gabapentin and pregabalin for sciatica pain – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8515246/
- “A randomized controlled trial of gabapentin for chronic low back pain with and without a radiating component – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26963844/
- “Gabapentin for Adults with Neuropathic Pain: A Review of the Clinical Efficacy and Safety [Internet]”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26180879/
- “”. https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/gabapentin/side-effects-of-gabapentin/
- “Gabapentin: Uses, Side Effects, Dosages, Interactions & More”. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/21561-gabapentin
- “Gabapentin: MedlinePlus Drug Information”. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a694007.html
- “FDA warns about serious breathing problems with seizure and nerve pain medicines gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica, Lyrica CR) | FDA”. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-warns-about-serious-breathing-problems-seizure-and-nerve-pain-medicines-gabapentin-neurontin
- “Gabapentin – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK493228/
- “Gabapentin for sciatica: Efficacy and safety”. https://www.singlecare.com/blog/gabapentin-for-sciatica/
- “”. https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/gabapentin/how-and-when-to-take-gabapentin/
- “Sciatic Medications for Nerve Pain: 6 Prescriptions That May Help – GoodRx”. https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/pain/lyrica-vs-gabapentin-which-is-better-for-sciatica-pain
- “Optimizing Treatment for Patients With Chronic Sciatica: Gabapentin vs Pregabalin – MPR”. https://www.empr.com/home/news/optimizing-treatment-for-patients-with-chronic-sciatica-gabapentin-vs-pregabalin/
- “Sciatica home remedies and self-care – Harvard Health”. https://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/sciatica-home-remedies-and-self-care
- “Sciatica Pain Relief: Effective Treatments and Prevention Tips — Optimal Wellness Health Center (UT)”. https://www.owchealth.com/blog/2024/10/21/sciatica-pain-relief-a-comprehensive-guide-to-managing-and-preventing-sciatica
- “Health Rounds: Acupuncture reduces leg pain from a herniated disk”. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/health-rounds-acupuncture-reduces-leg-pain-herniated-disk-2024-10-25/
- “Sciatica Pain Relief: Treatment Methods to Address Sciatica”. https://wellnessandpain.com/sciatica-pain-reliefs/
- “9 Best Treatment Options for Sciatica Pain – PainSpectrum”. https://painspectrum.com/treatment-options-for-sciatica-pain/