ALS Twitching is a symptom that is commonly associated with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). It can be both physically and emotionally distressing for individuals who experience it. In order to better understand this symptom, it is important to delve into the definition of ALS and its symptoms, explore the science behind ALS twitching, differentiate it from other types of twitching, discuss the diagnosis and detection of ALS twitching, and lastly, address the management and emotional impact of this symptom.
Defining ALS and Its Symptoms
ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the nerve cells called motor neurons. These motor neurons are responsible for transmitting signals from the brain to the muscles, enabling voluntary movements. In ALS, these motor neurons degenerate and eventually die, leading to muscle weakness, loss of coordination, and eventually paralysis.
Common symptoms of ALS include muscle weakness, muscle cramps, difficulty speaking and swallowing, and muscle twitches or fasciculations. It is these muscle twitches, also known as ALS twitching, that can cause significant concern and distress for individuals experiencing them.
When it comes to muscle weakness, individuals with ALS may notice a gradual decline in their ability to perform everyday tasks that require muscle strength. Simple activities such as lifting objects, walking, or even holding a cup can become increasingly challenging. This progressive weakness can affect various muscle groups, including those in the arms, legs, and even the muscles responsible for breathing.
Muscle Weakness as ALS Symptom
In addition to muscle weakness, muscle cramps are another common symptom experienced by individuals with ALS. These cramps can be painful and occur spontaneously, often causing discomfort and frustration. The exact cause of muscle cramps in ALS is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the degeneration of motor neurons and the resulting disruption in muscle function.
Difficulty speaking and swallowing, known as dysarthria and dysphagia, respectively, are also prevalent symptoms of ALS. As the disease progresses, the muscles responsible for speech and swallowing become weaker, leading to slurred speech and difficulty in articulating words. Swallowing becomes increasingly challenging, and individuals may experience choking or aspiration, which can lead to further complications.
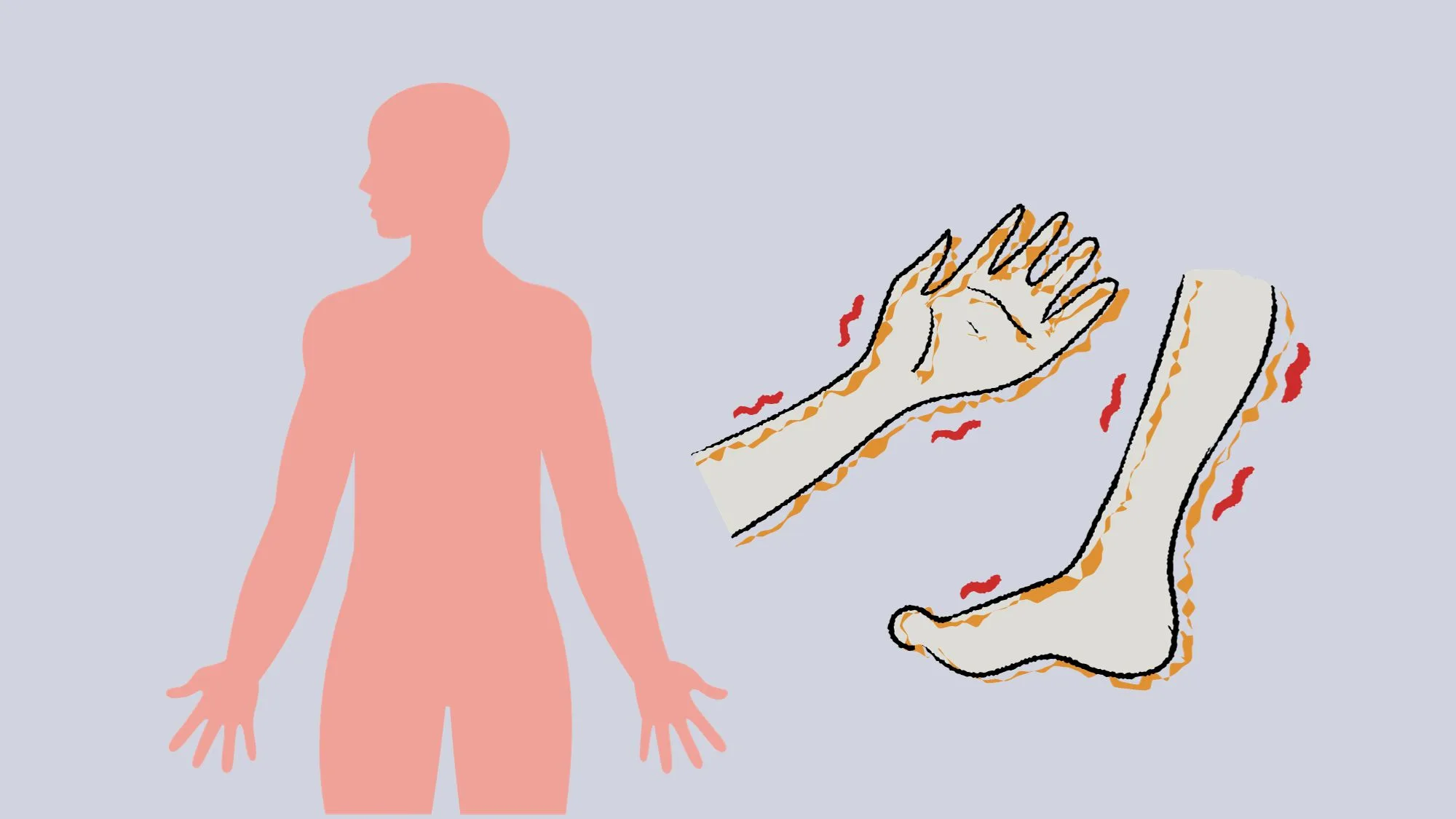
One of the most distinctive symptoms of ALS is muscle twitches or fasciculations. These involuntary contractions of muscle fibers can occur randomly and affect various parts of the body. ALS twitching can be bothersome and alarming, as individuals may worry about the underlying cause or fear that it signifies a worsening of their condition. However, it is important to note that muscle twitches alone do not necessarily indicate ALS, as they can occur in other conditions as well.
While these symptoms are commonly associated with ALS, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. ALS is a complex disease with various manifestations, and a comprehensive evaluation is necessary to differentiate it from other conditions that may present with similar symptoms. Early detection and intervention can help individuals with ALS manage their symptoms and maintain their quality of life for as long as possible.[1]
The Science Behind ALS Twitching
The role of motor neurons in ALS is crucial to understanding why muscle twitches occur. Motor neurons are responsible for controlling muscle movement by sending electrical signals to the muscles. In ALS, the degeneration of motor neurons disrupts this process, leading to muscle dysfunction.
So why does ALS cause twitching specifically? The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is believed that the abnormal electrical activity caused by the degeneration of motor neurons leads to the involuntary twitching of muscles. These twitches can occur in any muscle group, but are most commonly experienced in the arms, legs, or facial muscles.[2][3][4]
Differentiating ALS Twitching from Other Types
It is important to differentiate ALS twitching from other types of twitching to avoid unnecessary anxiety and confusion. One common condition that can cause muscle twitching is Benign Fasciculation Syndrome (BFS). Unlike ALS twitching, BFS twitching is not associated with the degeneration of motor neurons and does not progress to muscle weakness or other neurological symptoms.
Benign Fasciculation Syndrome (BFS) is a relatively harmless condition characterized by involuntary muscle twitches or fasciculations. These twitches can occur in various parts of the body, such as the arms, legs, face, or even the tongue. BFS is often triggered by stress, anxiety, or physical exertion, and the twitches tend to come and go. Unlike ALS twitching, which is a symptom of the progressive neurodegenerative disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), BFS twitching does not lead to muscle weakness or other neurological impairments.
Another important distinction is between ALS twitching and normal muscle twitching. Normal muscle twitching, also known as myoclonus, is a benign condition that can occur in healthy individuals due to various factors such as stress, fatigue, or caffeine intake. It is generally brief and not accompanied by other neurological symptoms.
Myoclonus can manifest as single twitches or repetitive muscle jerks. These twitches can affect different muscle groups, including the arms, legs, face, or even the whole body. They can be triggered by external stimuli, such as sudden movements or loud noises, or they can occur spontaneously. Unlike ALS twitching, myoclonus is not indicative of any underlying neurodegenerative disease and does not progress to muscle weakness or other severe complications.
Side Effects of Medications
It is important to note that muscle twitching can also occur as a side effect of certain medications or as a result of electrolyte imbalances in the body. Medications such as corticosteroids, diuretics, or stimulants can sometimes cause muscle twitches as an adverse reaction. Electrolyte imbalances, particularly low levels of magnesium or potassium, can also lead to muscle twitching. These causes of muscle twitching are generally temporary and resolve once the underlying issue is addressed.
While muscle twitching can be a concerning symptom, it is crucial to differentiate between ALS twitching, Benign Fasciculation Syndrome (BFS) twitching, normal muscle twitching (myoclonus), and twitching caused by medication or electrolyte imbalances. Understanding the characteristics and distinctions of each type of twitching can help alleviate unnecessary anxiety and provide a clearer understanding of the underlying causes.[5][6][7]
Diagnosis and Detection of ALS Twitching
Diagnosing ALS twitching involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, supported by medical tests. These tests may include electromyography (EMG), nerve conduction studies, MRI scans, and blood tests. These tests help determine the presence of motor neuron degeneration and rule out other potential causes of muscle twitching.
During an electromyography (EMG) test, small electrodes are inserted into the muscles to record the electrical activity. This test can provide valuable information about the health of the motor neurons and the muscles they control. Nerve conduction studies, on the other hand, measure the speed and strength of electrical signals as they travel through the nerves. This can help identify any abnormalities in the nerve function.
In addition to these tests, MRI scans may be used to obtain detailed images of the brain and spinal cord. These images can reveal any structural abnormalities or signs of degeneration that may be indicative of ALS. Blood tests may also be conducted to check for specific biomarkers associated with ALS, although no definitive diagnostic blood test currently exists.
Importance of Early Detection for ALS
Early detection of ALS twitching is crucial for timely intervention and management. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent muscle twitches that are accompanied by other neurological symptoms or if there is a family history of ALS.
When it comes to ALS, early intervention can make a significant difference in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life. While there is currently no cure for ALS, various treatment options are available to help alleviate symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease.
Benefits of Different Therapies for ALS
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle strength and mobility. It focuses on exercises that target specific muscle groups, helping individuals with ALS maintain their independence for as long as possible. Occupational therapy can also be beneficial. As it focuses on adapting the environment and teaching individuals new ways to perform daily tasks.
Speech therapy may be recommended if ALS affects the muscles responsible for speech and swallowing. This therapy can help individuals improve their communication skills and learn techniques to manage swallowing difficulties. Assistive devices, such as speech-generating devices and feeding tubes, may also be used to support individuals with ALS in maintaining their ability to communicate and eat.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms such as muscle cramps, excessive saliva production, and difficulty breathing. These medications can help improve comfort and quality of life. Additionally, clinical trials and research studies are constantly exploring new treatment options and potential breakthroughs in the field of ALS.
It is important for individuals with ALS to have a comprehensive care team that includes healthcare professionals from various disciplines. Such as neurologists, physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, and social workers. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the disease are addressed and that individuals receive the support they need.[8][9][10][11]
Managing ALS Twitching
While there is no cure for ALS, there are medications and therapies that can help manage the symptoms, including twitching. ALS, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. It leads to the loss of muscle control and eventually affects the ability to speak, eat, and breathe.
One of the medications that has been approved for the treatment of ALS is riluzole. Riluzole works by reducing the levels of glutamate, a neurotransmitter that is believed to contribute to the death of nerve cells. By reducing the levels of glutamate, riluzole may help slow down the progression of the disease and alleviate twitching.
Another medication that has shown promise in the treatment of ALS is edaravone. Edaravone is an antioxidant that helps reduce oxidative stress, which is believed to play a role in the progression of ALS. By reducing oxidative stress, edaravone may help protect nerve cells and slow down the disease progression.
In addition to medication, physical therapy can also play a crucial role in managing ALS twitching. Physical therapists can work with individuals with ALS to develop exercise programs that help maintain muscle strength and mobility. These exercises may include stretching, range-of-motion exercises, and low-impact aerobic exercises. Physical therapy can also help individuals with ALS learn how to use assistive devices, such as braces or wheelchairs, to improve their mobility and independence.
While medical interventions are important, making certain lifestyle changes can also help alleviate ALS twitching. It is important for individuals with ALS to avoid triggers that may worsen twitching, such as caffeine. Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase muscle activity and may exacerbate twitching in individuals with ALS. Managing stress levels is also crucial, as stress can worsen symptoms and increase muscle tension. Finding healthy ways to cope with stress, such as through relaxation techniques or engaging in enjoyable activities, can help reduce twitching.
Other Essentials for Management of ALS Twitching
Proper rest and nutrition are also essential in managing ALS twitching. Fatigue can worsen muscle weakness and twitching, so it is important for individuals with ALS to get enough rest and sleep. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients can also help support overall health and muscle function. Working closely with healthcare professionals, such as neurologists, physical therapists, and dietitians, can help individuals with ALS develop a comprehensive management plan tailored to their specific needs.
While there is no cure for ALS, there are medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes that can help manage the symptoms, including twitching. By working closely with healthcare professionals and following a comprehensive management plan, individuals with ALS can improve their quality of life and maintain their independence for as long as possible.[12]
The Emotional Impact of ALS Twitching
Living with ALS twitching can have a significant emotional impact. The physical symptoms and the uncertainty of the disease can cause anxiety, depression, and stress. It is important to address these emotional challenges and seek support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends.
Coping with the anxiety of ALS twitching can be facilitated through various strategies. Such as therapy, mindfulness techniques, and support groups. These resources provide individuals with ALS and their caregivers a platform to share experiences, gain valuable insights, and find emotional support.
One of the most common emotional challenges faced by individuals with ALS twitching is anxiety. The constant twitching and the fear of the disease progressing can lead to heightened levels of worry and apprehension. This anxiety can have a profound impact on a person’s mental well-being, making it crucial to find effective coping mechanisms.
Factors that may be Beneficial for Individuals Suffering from ALS
Therapy is an essential tool in managing anxiety related to ALS twitching. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often recommended as it helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to their anxiety. Through CBT, individuals can learn to challenge their fears and develop healthier coping strategies.
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can also be beneficial in reducing anxiety. These practices help individuals focus on the present moment, allowing them to let go of worries about the future. By incorporating mindfulness into their daily routine, individuals with ALS twitching can experience a greater sense of calm and relaxation.
Support groups play a crucial role in providing emotional support to individuals with ALS twitching and their caregivers. These groups offer a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, fears, and frustrations. Connecting with others who are going through similar challenges can provide a sense of validation and understanding.
Support groups also provide an opportunity to gain valuable insights and information about managing ALS twitching. Members can share tips and strategies that have worked for them, as well as learn about new research and treatments. This exchange of knowledge can empower individuals with ALS twitching to take an active role in their own care and well-being.
In addition to therapy, mindfulness techniques, and support groups, it is important for individuals with ALS twitching to have a strong support system. Family and friends can play a crucial role in providing emotional support and helping with daily tasks. Having a network of loved ones who understand and empathize with the challenges of living with ALS twitching can make a significant difference in a person’s emotional well-being.
What it’s like to Live with ALS?
Living with ALS twitching can have a profound emotional impact. Anxiety, depression, and stress are common challenges faced by individuals with this condition. However, by utilizing resources such as therapy, mindfulness techniques, and support groups, individuals with ALS twitching can find effective ways to cope with their emotions. It is important for healthcare professionals, family, and friends to provide the necessary support. Understanding to help individuals navigate the emotional challenges associated with ALS twitching.
Furthermore, living with ALS can be challenging, and muscle twitching is one of the most common symptoms experienced by individuals with this disease. Twitching can occur in various parts of the body, such as the arms, legs, face, or even the vocal cords. It can be disruptive and uncomfortable, affecting daily activities and overall quality of life.[13][14][15]
CareClinic App for Managing ALS Twitching
The CareClinic app is a valuable tool for individuals living with ALS and experiencing twitching. This app allows you to track and monitor your symptoms, including the frequency and severity of muscle twitches. It also enables you to record any triggers or patterns that may be influencing your twitching episodes.
With the CareClinic app, you can gain a deeper understanding of your twitching episodes. By tracking the frequency and severity of your muscle twitches, you can identify patterns and potential triggers. This information can be invaluable when discussing your symptoms with healthcare professionals, as it provides them with a comprehensive overview of your condition.
Furthermore, the app provides medication reminders and allows you to log your medications, ensuring that you never miss a dose. Medications prescribed for ALS, such as riluzole, can help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. By staying on top of your medication schedule, you can optimize their effectiveness and potentially reduce the frequency or intensity of your twitching episodes.
Managing ALS Tracking
Managing ALS goes beyond just tracking symptoms and taking medication. The CareClinic app recognizes this and includes features to support your overall well-being. It includes a journal where you can record your thoughts and emotions, providing an outlet for self-expression and reflection. This can be particularly helpful when dealing with the emotional impact of living with a progressive disease.
In addition, the app offers a comprehensive list of resources for ALS support and information. It connects you to organizations, support groups, and educational materials that can provide guidance and assistance throughout your journey. Having access to reliable and up-to-date information can empower you to make informed decisions about your health and treatment options.
Important Aspects of CareClinic App for ALS
Another important aspect of the CareClinic app is its ability to facilitate communication with healthcare professionals or loved ones. You can easily share your symptoms, progress, and medication records with your healthcare team. Allowing them to monitor your condition remotely and make adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary. This level of collaboration and transparency can lead to more personalized and effective care.
The CareClinic app empowers individuals with ALS to take an active role in managing their symptoms. Fostering better communication with healthcare professionals and ultimately improving their overall quality of life. By providing a comprehensive platform for symptom tracking, medication management, emotional well-being, and access to resources, this app becomes an essential companion for those living with ALS and experiencing twitching.
Understanding ALS twitching involves gaining knowledge about the disease itself. Its symptoms, the scientific mechanisms behind twitching, differentiating it from other types of twitching. Diagnosing and detecting the symptom, managing it through interventions and lifestyle changes, and addressing the emotional impact it can have. With the help of resources like the CareClinic app, individuals living with ALS and experiencing twitching can take control of their symptom management journey.
References
- “Early Signs and Symptoms of ALS | ALS United Greater Chicago”. https://alsunitedchicago.org/early-signs-and-symptoms-of-als/
- “Disease Mechanisms | The ALS Association”. https://www.als.org/research/als-research-topics/disease-mechanisms
- “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Other Motor Neuron Diseases (MNDs) – Neurologic Disorders – Merck Manual Professional Edition”. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/neurologic-disorders/peripheral-nervous-system-and-motor-unit-disorders/amyotrophic-lateral-sclerosis-als-and-other-motor-neuron-diseases-mnds
- “Neuronal Circuit Dysfunction in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis”. https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/13/10/792
- “Benign Fasciculation Syndrome: Symptoms & Treatment”. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24812-benign-fasciculation-syndrome
- “ALS Muscle Twitching vs BFS Muscle Twitching – Target ALS”. https://www.targetals.org/2022/06/01/als-muscle-twitching-vs-bfs-muscle-twitching-knowing-the-differences/
- “Electrolyte Imbalance: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment”. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/24019-electrolyte-imbalance
- “The Role of Electromyography (EMG) in ALS”. https://www.massgeneral.org/neurology/als/patient-education/electromyography-emg
- “How ALS Is Diagnosed I Massachusetts General Hospital”. https://www.massgeneral.org/neurology/als/patient-education/diagnosing-als
- “Therapies and Care | The ALS Association”. https://www.als.org/navigating-als/living-with-als/therapies-care
- “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Treatment | University of Utah Health”. https://healthcare.utah.edu/neurosciences/neurology/motor-neuron-disorders/als/treatment
- “ALS”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ALS
- “Symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and their relatives during the disease trajectory – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37976792/
- “ALS Mental Health | ALS Network”. https://alsnetwork.org/navigating-als/living-with-als/resource-guides-for-daily-living/als-home-and-daily-living-guide/als-mental-health/
- “Understanding ALS Twitching | ALS United Greater Chicago”. https://alsunitedchicago.org/understanding-als-twitching/


