
Do you experience chronic pain and are worried that this affects your work? There are many people suffering from this. To make things worse, sometimes this chronic pain is caused by work tasks themself.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the many facets of pain, from its definition to its causes and management. We will take a closer look at the different types of pain, what in our body causes the pain, and the various factors that can contribute to chronic pain
We will also explore the link between chronic pain and work and provide some ways to help you at work. From various exercises to the importance of good posture to the benefits of relaxation techniques, we will cover a range of coping mechanisms and strategies that research shows can help individuals manage their chronic pain and improve their overall well-being.
Whether you are someone who experiences chronic pain on a daily basis or simply looking to research and expand your knowledge on this topic, this article provides important health information and research on this topic for the general population on working through pain.
Understanding Pain: Why it Hurts
Definition of Pain
Pain is something humans have known about for the longest time, yet still have difficulty understanding. It is often described as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain is the body’s way of telling us that something is wrong.
Previously, the International Association for the Study of Pain, a pain research group, had defined pain as “An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage.” However, recently this definition has been updated to “An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage.”
This updated definition has the potential to broaden the understanding of pain beyond the focus on the physical realm. For example, individuals who suffer from chronic pain may not necessarily have any physical damage to their tissues, yet they still experience the same unpleasant sensations. Additionally, this updated definition acknowledges the emotional component of pain, which can often be overlooked in traditional medical settings.
Furthermore, this new definition can also help to break down barriers and stigmas surrounding chronic pain. For a long time, chronic pain sufferers were often not taken seriously because their pain could not be attributed to any specific cause or illness. This updated definition recognizes that chronic pain really is complex and multifaceted. manifesting in a variety of ways.
The Physiology of Pain
Pain is a complex experience that involves the activation of specialized sensory receptors called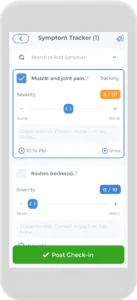 nociceptors. These receptors are expressed on the free nerve endings of primary afferent nociceptive neurons, which are found in the skin, muscles, and viscera. When these nociceptors are stimulated by something, they generate electrical impulses that are transmitted through the spinal cord and to the brain, where the signals are interpreted as pain.
nociceptors. These receptors are expressed on the free nerve endings of primary afferent nociceptive neurons, which are found in the skin, muscles, and viscera. When these nociceptors are stimulated by something, they generate electrical impulses that are transmitted through the spinal cord and to the brain, where the signals are interpreted as pain.
Nociceptors can be activated by a variety of stimuli, such as mechanical pressure, temperature extremes, and chemical irritants. Once activated, they release neuropeptides, which contribute to the inflammatory response and sensitization of nociceptors. This sensitization results in a lowered threshold for activation, which can lead to the development of hyperalgesia (an increased sensitivity to painful stimuli) and allodynia (the perception of pain in response to normally non-painful stimuli).
Thermal nociceptors are activated by temperature extremes, while mechanical nociceptors respond to mechanical stimuli. Polymodal nociceptors respond to multiple stimuli, including heat, chemicals, and mechanical pressure. The activation of nociceptors triggers a cascade of events that ultimately lead to the perception of pain.
Types of Pain
There are many different types of pain. Some of the most common types of pain are listed below:
- Nociceptive pain: This type of pain is what was discussed in the previous section, where receptors are activated in response to some stimuli. This can include neck pain, musculoskeletal pain, and other common types of pain.
- Neuropathic pain: A complex and often chronic condition that arises from damage to the nervous system. Neuropathic pain feels like shooting or burning pain, tingling or numbness, and sensitivity to touch
- Psychogenic pain: A type of pain that is caused by psychological factors and can manifest in different ways. Some people may experience psychogenic pain as a result of a past traumatic experience, while others may develop it due to ongoing stress or anxiety. Psychogenic pain can be difficult to diagnose and treat because it is often accompanied by psychological symptoms and psychosocial risk factors.
Acute versus Chronic Pain
Pain can also be classified as acute or chronic. Acute pain is usually of short duration and is often caused by injury or tissue damage. Examples of acute pain include a sprained ankle, a cut, or a broken bone. Chronic pain, on the other hand, persists for a longer period of time, usually more than 3 months. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as an underlying medical condition, nerve damage, or inflammation. Chronic knee pain affects a lot of people. In addition to physical uncomfortableness, chronic pain can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. furthermore, you could have pain fluctuations between acute and chronic. Therefore, it is important to properly manage and treat chronic pain to improve the overall well-being of the patient.
Causes of Pain
Pain is a complex phenomenon that can be caused by a multitude of factors. These factors include but are not limited to injury, disease, inflammation, stress, and psychological factors. The sensation of pain is a signal from our body that something is wrong and it is important to listen to it.
Back pain is one of the most common types of chronic pain experienced by people, and can be caused by a variety of reasons such as poor posture, muscle strain or injury. Headaches are another common cause of pain, and the causes can vary from stress, tension, lack of sleep, hormonal changes, etc. Arthritis is a chronic condition that causes joint pain, muscle stiffness and swelling, and can be caused by a variety of factors such as age, genetics, and lifestyle.
Pain can also be a side effect of certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs. This can be a challenging aspect of chronic pain management, as the patient and healthcare provider must weigh the clinical benefits of the medication against the potential side effects. Therefore, it is essential for patients to work with a healthcare provider to find the most effective and safe treatment for managing chronic pain.
Pain Management
 Effective pain management is a key component of healthcare, as it can help individuals with chronic pain improve their quality of life and prevent long-term disability. In addition to medication, physical therapy, and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, there are many other approaches to chronic pain management that may be beneficial. For example, some individuals find relief through cognitive-behavioral therapy, while others may benefit from lifestyle changes such as exercise and stress management techniques. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive pain management plan that addresses all aspects of your individual needs, including physical, emotional, and psychological factors. By taking a holistic approach to chronic pain management, individuals can improve their overall health and well-being and experience a better quality of life.
Effective pain management is a key component of healthcare, as it can help individuals with chronic pain improve their quality of life and prevent long-term disability. In addition to medication, physical therapy, and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, there are many other approaches to chronic pain management that may be beneficial. For example, some individuals find relief through cognitive-behavioral therapy, while others may benefit from lifestyle changes such as exercise and stress management techniques. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive pain management plan that addresses all aspects of your individual needs, including physical, emotional, and psychological factors. By taking a holistic approach to chronic pain management, individuals can improve their overall health and well-being and experience a better quality of life.
Pain in the Workplace: The Importance of Occupational Health
Work and pain are inextricably linked. Chronic ain affects work and work affects pain. This section will look at how the two are linked, and some causes of one on the other.
How Pain Affects Work
Pain in the workplace can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to perform their job duties effectively. Chronic ain can cause a decrease in productivity, an increase in absenteeism, and can even lead to long-term disability. It is important for individuals to recognize the impact that chronic pain can have on their work and to take steps to manage it effectively.
Pain not only affects an individual’s work, but it can also have a burden on the employer. Work-related chronic pain can lead to increased healthcare costs, workers’ compensation claims, and decreased productivity. In addition, chronic pain can result in increased absenteeism and employee turnover, as well as decrease motivation. An injured employee can be out for several weeks or more than three months at a given time. Employers should take steps to promote a healthy work environment and provide accommodations for employees who experience chronic pain, reducing injuries in the first place. By focusing on pain management and prevention, employers can improve the overall well-being of their employees and create a more productive work environment.
Common Work-Related Injuries
While pain has an impact on work, one should realize the importance and influence of work on pain. Work is a huge source of chronic pain, which leads to a vicious cycle. It causes pain in an employee, and that pain then affects the employee’s work.
Work is a significant source of chronic pain for many individuals, and can lead to a vicious cycle where work causes pain, which then affects an employee’s ability to perform their job duties effectively. Many work-related injuries are caused by poor ergonomics, repetitive motions, and heavy lifting. These types of occupational injuries can cause significant chronic pain and discomfort, affecting an individual’s own performance, ability to work and their overall quality of life.
Strains and sprains are among the most common types of work-related injuries and can be caused by overexertion, awkward postures, and sudden movements. For example, lifting heavy objects improperly can cause strain on the muscles and joints, leading to pain and discomfort. Back injuries are also common and can be caused by lifting heavy objects, twisting or bending, or sitting in a chair for long periods of time. Prolonged sitting or standing can also cause chronic pain in the legs, feet, and back.
To prevent work-related injuries, it is important for individuals to take steps to minimize their risk. This includes practicing proper lifting techniques, such as bending at the knees and keeping the back straight, and using tools and equipment designed to reduce the strain on the body. Taking regular breaks to stretch and move around can also be beneficial and help to prevent injuries caused by repetitive motions and prolonged sitting or standing.
Dealing with Pain at Work
Dealing with chronic pain at work can be challenging and intimidating, but there are steps that individuals can take to manage their workplace pain effectively. One of the most important steps is to communicate with your employer and healthcare provider about your chronic pain and any limitations it may cause. Your employer may be able to get medical care or provide accommodations, such as ergonomic equipment or modified job duties, to help you manage your pain while still performing your job duties effectively.
If an injury does occur, it is important to seek prompt medical attention and to follow the recommended treatment plan. This process of rehabilitation may include rest, physical or occupational therapy, or in some cases, surgery. A physical therapist is often important. A physical therapist can help assess your situation and provide tailored exercises for only you to live a pain free life. It is also important to communicate with your employer about any work restrictions or accommodations that may be necessary to help you recover and to prevent further injury.
In addition, it is important for patients to practice good self-care, such as exercise, taking regular breaks to stretch and move around, practicing stress management techniques, and seeking treatment for pain as needed. By taking a proactive approach to pain management, individuals can improve their overall well-being and continue to perform their job duties effectively.
Working Through Pain: How to Push Through
Tips to Work and Push Through Pain
If you are experiencing chronic pain while at work, there are several tips and exercises that you can follow to help you manage your symptoms and continue to perform your job duties effectively.
One important strategy is to take regular breaks to stretch and move around. This can help to prevent stiffness and soreness, and the exercise can also help to improve circulation. Sitting or standing in one position for extended periods can cause muscles to tighten and lead to pain and discomfort. Taking a few minutes every hour to move around and stretch can help to alleviate these symptoms and improve overall comfort.
Another important aspect of managing chronic pain at work is practicing good posture. Poor posture can contribute to pain and discomfort by putting unnecessary strain on muscles and joints. When sitting, make sure to sit up straight with your shoulders back and your feet flat on the ground. Avoid slouching or hunching over, as this can cause strain on the back and neck. When standing, distribute your weight evenly on both feet and avoid locking your knees. Also, if you are doing specific work tasks, make sure you practice good form and be aware of your physical limits.
Finally, consider using ergonomic equipment to minimize strain on your body. Ergonomic equipment, such as a supportive chair or keyboard, can help to reduce the various risk factors of injury and improve overall comfort while working. When choosing ergonomic equipment, look for products that are adjustable and can be customized to your individual needs. For example, a chair with adjustable height and backrest can help to provide optimal support and reduce strain on the back and neck.
Accommodations in the Workplace
If you are experiencing chronic pain at work, it is important to communicate with your employer about your symptoms and any limitations they may cause. Your employer may be able to provide accommodations, such as ergonomic equipment or modified job duties, to help you manage your pain while still performing your job duties effectively. This process can help to reduce the risk of further injury and can also improve your overall well-being.
Employers have a responsibility to provide a safe and healthy work environment for their employees. This includes taking steps to prevent work-related injuries and illness and providing accommodations and support for employees who experience pain. Not only is this necessary for keeping employees safe, it also improve work outcomes for them.
Workplace Policies Related to Pain Management
Many workplaces have policies in place to help manage chronic pain and prevent work-related injuries. These policies may include regular breaks, ergonomic equipment, and modified job duties. It is important to familiarize yourself with your workplace policies and to communicate with your employer about any concerns or questions you may have. By working together, you can help to create a safe and healthy work environment that supports the well-being of all employees.
A healthy work enviroment and work culture will value the importance of employee and community health and well being.
Coping Mechanisms for Pain
Chronic pain can be a challenging and debilitating experience, and it is important for individuals to have![]() effective coping mechanisms to manage their symptoms. One important strategy is to practice relaxation techniques, using exercises such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. These techniques can help to reduce stress and tension in the body, which can exacerbate pain.
effective coping mechanisms to manage their symptoms. One important strategy is to practice relaxation techniques, using exercises such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. These techniques can help to reduce stress and tension in the body, which can exacerbate pain.
Another effective coping and relief mechanism is to engage in regular physical activity. Exercise can help to improve circulation, reduce muscle inflammation, and promote the release of endorphins, which are natural painkillers produced by the body. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to develop an exercise program that is safe and effective for your individual needs and limitations.
In addition to relaxation and exercise, social support can also be an important coping and relief mechanism for individuals with chronic pain. This support can include talking to friends or family members about your experiences, joining a support group, or working with a mental health professional to address any emotional or psychological aspects of your pain.
Mental Health and Pain
Chronic pain can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health and well-being. It is not uncommon for individuals with chronic pain to experience depression, anxiety, or other mood disorders as a result of their symptoms. It is important to address these clinical and psychological aspects of pain in order to improve overall clinical outcomes, well-being and quality of life.
One effective strategy is to work with a mental health professional to develop coping mechanisms and strategies for managing the emotional impact of chronic pain, illness or disability. This intervention may include talk therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or other forms of psychotherapy. In addition, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms of depression or anxiety.
Using an App for Occupational Rehabilitation
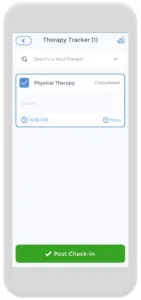
Having an occupational pain action plan is crucial, and the CareClinic app can help with that. You can use the app as your health and clinical journal. Just go to the diary section of the app and enter your daily symptoms, medications, and other triggers, as they occur. There are also specific sections on the app to track each of these. This can help you be aware of early warning signs. For example, if you have any musculoskeletal disorders, you may be at a higher risk of muscle pain. Next time you visit the doctor’s office, this information will be handy in your pocket.
The app also has a medication section where you can precisely track the doses you are taking and receive reminders on when to take each medication. We know how difficult but important keeping track of your medications is, so we hope to make it as easy and streamlined as possible.
In conclusion, pain is a complex phenomenon that affects us all at some point in our lives. Whether it is acute or chronic, physical or psychological, pain can have a significant impact on our well-being and quality of life. However, with effective pain management strategies, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and improve their overall health and well-being. From good posture and relaxation techniques to physical activity and social support, there are many coping mechanisms that can help individuals work through the pain and continue to perform their job duties effectively. By taking a holistic approach to pain management, individuals can improve their overall quality of life and experience a better sense of well-being.
Sources
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/pain
- https://painbc.ca/health-professionals/education/OT-workshop
- https://austinpaindoctor.com/your-pain-care-plan-to-occupational-pain-management


