
During menopause, many changes occur in a woman’s body, including fluctuations in blood pressure. Understanding what is considered normal blood pressure during menopause is important for maintaining overall health and well-being.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of blood pressure during menopause and provide insights on how to manage it effectively.[1][2]
Understanding Menopause and Its Effects on the Body
Before delving into the specifics of blood pressure during the menopause transition, it’s essential to have a grasp of what menopause entails. Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life, marking the end of her reproductive years. It usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, and the menopausal transition is characterized by the cessation of menstruation and a significant decline in hormone production.
The Biological Process of Menopause
During menopause, the ovaries gradually decrease the production of estrogen and progesterone, leading to numerous physiological changes in the body. These changes can range from hot flashes and night sweats to mood swings and changes in blood pressure.
How Menopause Affects the Cardiovascular System
 One of the aspects affected by menopause symptoms is the cardiovascular system. Estrogen, a hormone responsible for maintaining healthy blood vessels, declines during menopause. This can lead to an increase in cardiovascular disease and risk factors of heart disease, including high blood pressure.
One of the aspects affected by menopause symptoms is the cardiovascular system. Estrogen, a hormone responsible for maintaining healthy blood vessels, declines during menopause. This can lead to an increase in cardiovascular disease and risk factors of heart disease, including high blood pressure.
Additionally, the decrease in estrogen levels can impact cholesterol levels in the body. Estrogen helps maintain a healthy balance of cholesterol by increasing levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, also known as “good” cholesterol. With the decline in estrogen during menopause, there may be a shift in the cholesterol profile, potentially leading to an increase in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol, which can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and heart disease. This underscores the importance of monitoring cardiovascular health during menopause and adopting lifestyle changes to mitigate associated risks.
Importance of Lifestyle Changes:
Given the cardiovascular risk and implications of menopause, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle becomes crucial for women transitioning through this phase. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as maintaining a healthy weight and body mass index, can help mitigate the risk of heart disease associated with menopause. Additionally, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are essential steps in promoting cardiovascular health during this transformative period.[3][4]
Defining Normal Blood Pressure
Before we discuss low blood pressure during menopause, it is crucial to understand what constitutes normal blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it throughout the body. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and consists of two numbers.
The Importance of Blood Pressure
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is vital for overall well-being. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can damage the blood vessels and increase the other risk factors of heart disease, stroke, and other complications.
Factors Influencing Blood Pressure
Various factors can influence blood pressure, including age, genetics, lifestyle, and underlying medical conditions. It is essential to consider these factors when assessing blood pressure during menopause.
Understanding Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
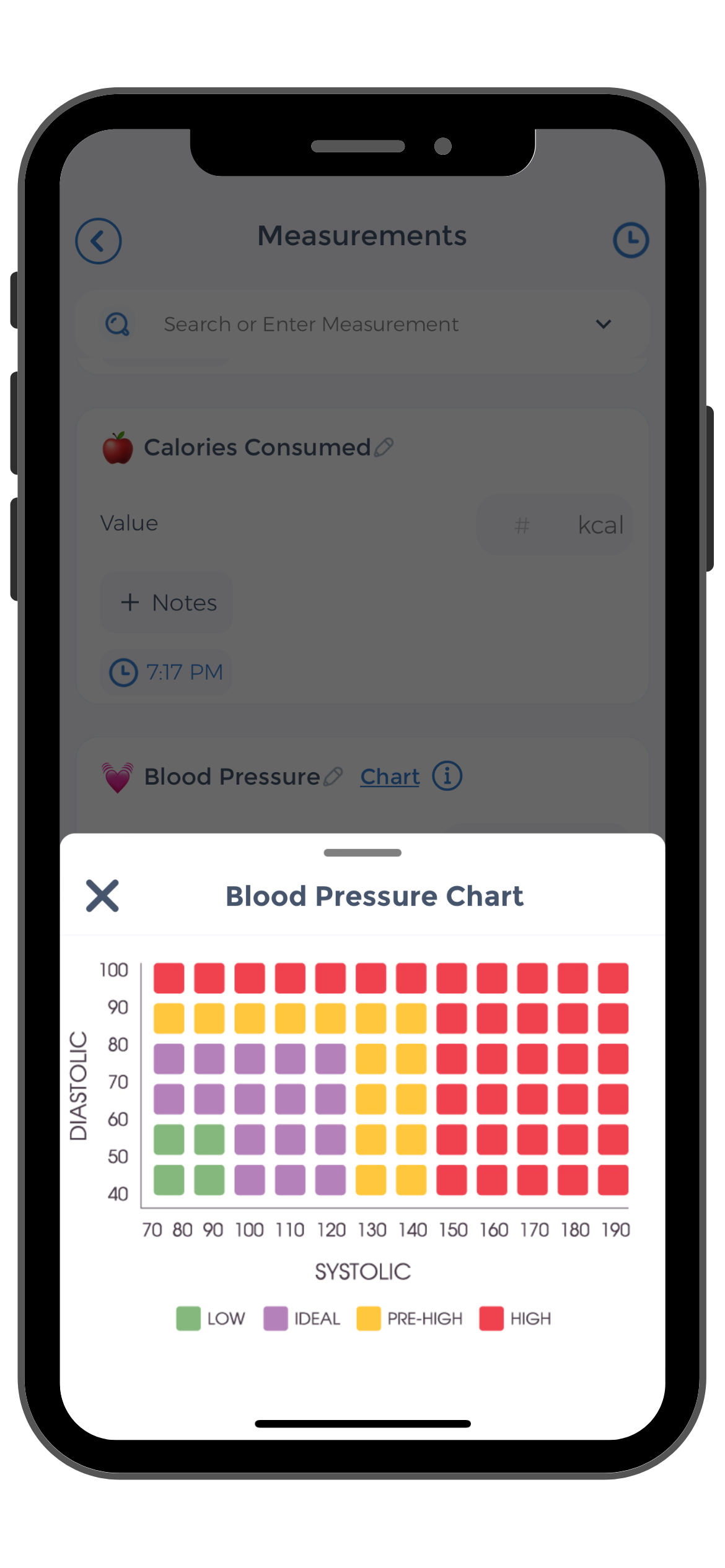
When blood pressure is measured, you will often hear two numbers, such as 120/80 mmHg. The top number is the systolic blood pressure, which represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats. The bottom number is the diastolic blood pressure, which indicates the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Healthy Blood Pressure Ranges
For adults, a normal blood pressure reading is typically considered to be below 120/80 mmHg. Elevated blood pressure falls between 120-129/<80 mmHg, while stage 1 hypertension is defined as 130-139/80-89 mmHg. Stage 2 hypertension is diagnosed at 140/90 mmHg or higher.
Blood Pressure Changes During Menopause
Menopause can contribute to fluctuations in blood pressure due to the hormonal changes that occur during this time. Let’s explore how hormonal changes and age factor into blood pressure during menopause.
Hormonal Changes and Blood Pressure
The decline in estrogen levels during menopause can impact blood vessel health and contribute to increased blood pressure levels. Estrogen helps keep blood vessels flexible and dilated, promoting healthy blood flow. With the decrease in estrogen, blood vessels may become less pliable, leading to elevated blood pressure.
The Role of Age in Blood Pressure
 Age itself is a significant factor in blood pressure regulation. As women age, their blood vessels naturally lose some of their flexibility. This, combined with the hormonal changes of menopause, can contribute to an overall increase in blood pressure.
Age itself is a significant factor in blood pressure regulation. As women age, their blood vessels naturally lose some of their flexibility. This, combined with the hormonal changes of menopause, can contribute to an overall increase in blood pressure.
It’s important to note that menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s menstrual cycles. During this transition, the body undergoes various changes, including fluctuations in hormone levels. These hormonal shifts can have a direct impact on blood pressure regulation, as evidenced by the potential increase in blood pressure levels seen in many menopausal women.
Furthermore, lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and stress management play a crucial role in managing blood pressure during menopause. Engaging in regular physical activity, consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and practicing relaxation techniques can help support overall cardiovascular health and potentially mitigate the effects of hormonal and age-related changes on blood pressure.[7][8]
Blood Pressure Monitors that You Can Buy
Monitoring blood pressure at home is essential for managing heart health and hypertension. Personal blood pressure monitors allow individuals to track their readings regularly and share the data with their healthcare providers. Here are some top options available for purchase that offer accuracy, ease of use, and helpful features to suit your needs.
Checkme Blood Pressure Monitor
This FSA/HSA eligible digital blood pressure monitor provides accurate and easy readings with a large screen and voice broadcast. It displays the last 7 days’ readings and average blood pressure, helping you monitor your health. Smart indicators ensure proper cuff placement and alert you if movement affects accuracy. The XL size cuff fits most adults, and the device stores up to 250 readings each for 2 users, plus a guest mode for quick checks. With simple one-button operation, you get a reading in 30 seconds. It comes with a 5-year warranty and professional support.
Wellue Blood Pressure Monitor
This FDA-cleared blood pressure monitor accurately measures systolic and diastolic blood pressure and heart rate. Easy to use with a single button press, it provides readings in 30 seconds and features a wide-range automatic cordless cuff that fits arms from 8.6 to 16.5 inches (22-42cm). Equipped with a rechargeable battery, a full charge lasts several months, making it portable for continuous tracking. The monitor itself stores up to 50 BP readings, allowing you to review and share your historical data directly.
ASTART Blood Pressure Monitor
This blood pressure monitor features a large backlit LED screen with clear digits for quick and easy reading, making it user-friendly for the elderly. The one-button design ensures simple and convenient measurements within a minute. It supports two users, storing up to 120 readings each, allowing easy tracking of blood pressure trends over time. The device operates on either 3 AA batteries or a Type-C interface, ensuring it’s always ready to use at home or on the go. The adjustable arm cuff fits sizes from 8.7 to 15.7 inches (22-40 cm), providing a comfortable fit for most adults. (Batteries and AC adapter not included; the machine is not rechargeable.)
Managing Blood Pressure During Menopause
While menopause-related blood pressure changes may seem daunting, several strategies can help manage and maintain healthy blood pressure levels. Let’s explore some lifestyle changes and medical interventions that can be beneficial.
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s menstrual cycles. During this time, hormonal changes, particularly a decrease in estrogen levels, can impact various aspects of health, including blood pressure regulation. Understanding how menopause affects blood pressure can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their cardiovascular health.
Lifestyle Changes to Treat High Blood Pressure
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
- Limit sodium intake to reduce water retention and blood pressure levels.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, to promote overall cardiovascular health.
- Maintain a healthy weight and avoid excessive weight gain through portion control and regular exercise.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation.
Furthermore, incorporating foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and calcium can also support blood pressure management. These nutrients play a role in muscle function and blood vessel relaxation, contributing to healthy blood pressure levels. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water is essential for overall cardiovascular health.
Medical Interventions for High Blood Pressure
If lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient in managing and developing high blood pressure during menopause, medical interventions may be necessary. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate course of action. Some medical interventions may include:
- Prescription medications specifically targeting blood pressure regulation.
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to help balance hormone levels and potentially alleviate blood pressure fluctuations.
It’s important to note that individual responses to medications and therapies may vary, highlighting the significance of personalized healthcare approaches in addressing blood pressure concerns during menopause. Regular monitoring of blood pressure levels and ongoing communication with healthcare providers can aid in the effective management of this aspect of menopausal health.
FAQs About Menopause and Blood Pressure
Here are answers to common questions regarding menopause and its relationship to blood pressure.
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s menstrual cycles. During this phase, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes, including a decrease in estrogen levels. While menopause itself does not cause high blood pressure, these hormonal fluctuations, along with other factors such as aging, genetics, and lifestyle habits, can contribute to elevated blood pressure levels in some women. It is essential to monitor blood pressure during menopause and take appropriate measures to manage it effectively to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Can Menopause Cause High Blood Pressure?
While menopause itself does not cause high blood pressure, the hormonal changes and other factors associated with this phase of life can contribute to elevated blood pressure levels. It is essential to monitor blood pressure during menopause and take appropriate measures to manage it effectively.
During menopause, women may experience symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and changes in sleep patterns. These symptoms, combined with the potential increase in blood pressure, highlight the importance of maintaining overall health and well-being during this transitional period.
How to Monitor Blood Pressure at Home During Menopause?
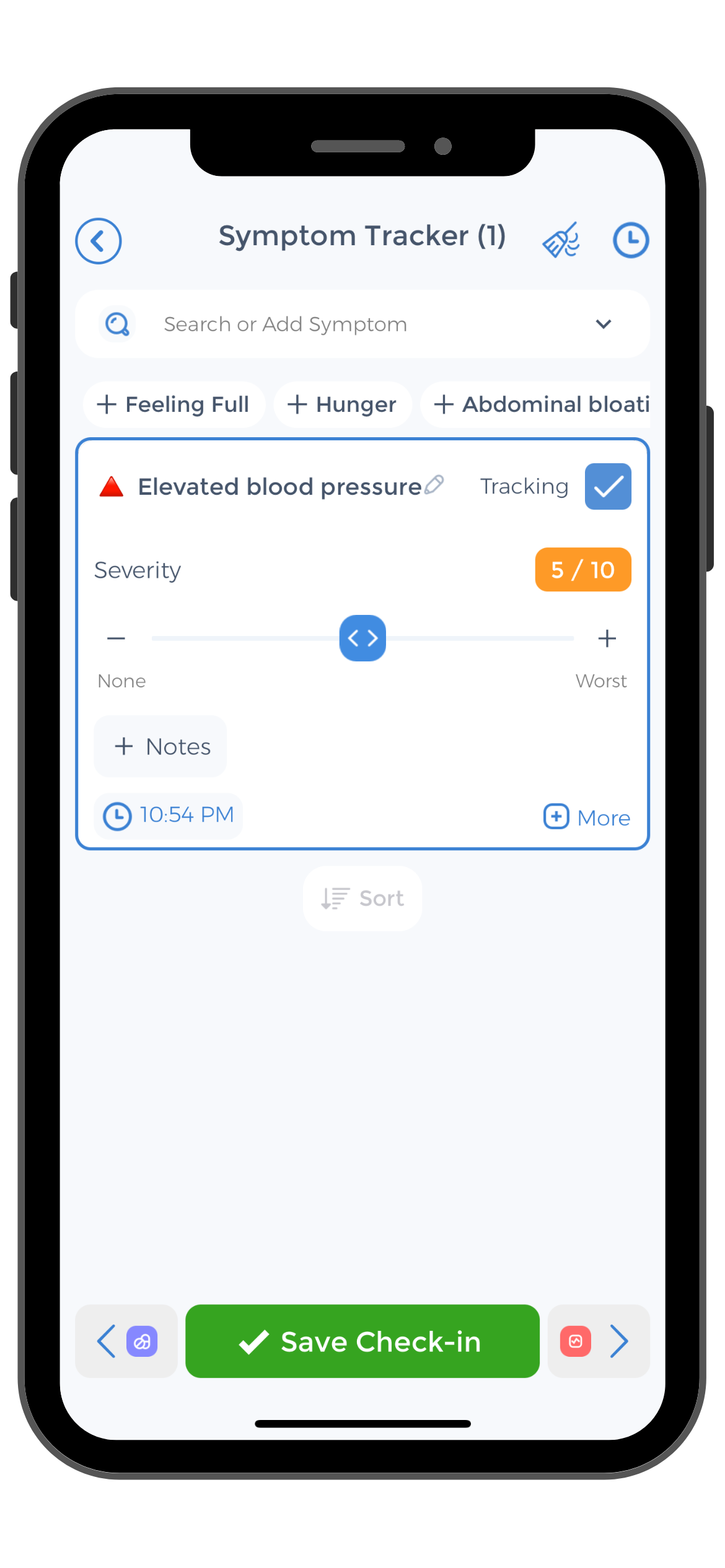
 Monitoring blood pressure at home during menopause can provide valuable information and help individuals take proactive steps towards managing their health. Utilizing a reliable blood pressure monitoring device can make monitoring blood pressure accessible, convenient, and accurate. The CareClinic App allows users to record and track their blood pressure readings, providing actionable insights for better management.
Monitoring blood pressure at home during menopause can provide valuable information and help individuals take proactive steps towards managing their health. Utilizing a reliable blood pressure monitoring device can make monitoring blood pressure accessible, convenient, and accurate. The CareClinic App allows users to record and track their blood pressure readings, providing actionable insights for better management.
Regular monitoring of blood pressure at home, in conjunction with regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, can help women navigate the changes that occur during menopause and make informed decisions about their health. By understanding the normal range of blood pressure during menopause and implementing lifestyle changes and medical interventions when necessary, individuals can maintain optimal cardiovascular health and well-being during this transformative phase of life.
Use the CareClinic App to Manage High Blood Pressure
As you navigate the complexities of managing and control high blood pressure during menopause, the CareClinic App emerges as a vital tool for tracking and understanding your cardiovascular health. With features that allow you to record daily blood pressure monitor, the app helps you identify patterns and trends that may correlate with lifestyle choices or symptoms.
By consistently using the CareClinic App, you can gain insights into how different factors affect your blood pressure, enabling you to make informed decisions alongside your healthcare provider.
Download the CareClinic App and Monitor Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
The app’s intuitive interface simplifies the process of monitoring your health, offering reminders for medication and appointments, ensuring you stay on top of your management plan. With the ability to generate reports, the CareClinic App makes it easy to share your progress with your doctor, facilitating a collaborative approach to your health during menopause. For a comprehensive way to manage your blood pressure and overall well-being during this transitional phase, install the CareClinic App today.
References
- “Increased blood pressure variability in menopause”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18575158/
- “Autonomic regulation of blood pressure in menopause – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19530068/
- “Menopause and the Cardiovascular System | Johns Hopkins Medicine”. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/menopause-and-the-cardiovascular-system
- “Menopause and Heart Health”. https://womenshealth.gov/nwbpaw/menopause-and-heart-health
- “Understanding Blood Pressure Readings | American Heart Association”. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/understanding-blood-pressure-readings
- “High Blood Pressure Risk Factors | High Blood Pressure | CDC”. https://www.cdc.gov/high-blood-pressure/risk-factors/index.html
- “Blood pressure through aging and menopause”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19811239/
- “Aging, Arterial Stiffness and Hypertension – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4288978/
- “Customer reviews for Checkme Blood Pressure Monitors with EKG Monitor,Free AI ECG Analysis Report,Automatic Upper Arm Cuff BP Machine,Red Dot 2022 Winner,BP2 | Walmart.com”. https://www.walmart.com/reviews/product/205162988
- “Amazon.com: Wellue Blood Pressure Monitor for Home Use, Bluetooth Smart Blood Pressure Machine Upper Arm Cuff, Portable Wireless Automatic BP Monitor, USB Rechargeable Battery, Free APP for iOS & Android, BP2A : Health & Household”. https://www.amazon.com/Wellue-Bluetooth-Blood-Pressure-Monitor/dp/B0BZHK95G3






