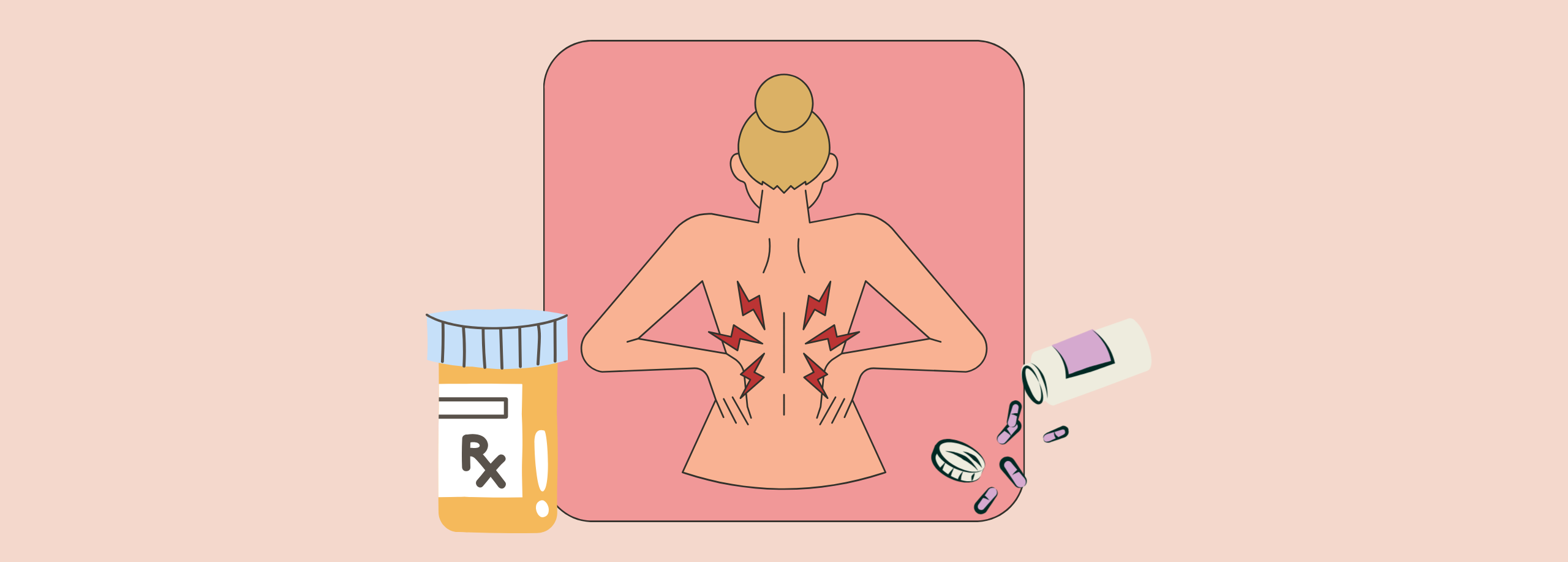
 Back pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether it is caused by an injury, strain, or underlying medical condition, the pain can be debilitating and significantly impact one’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are various medication options available that can provide relief and help manage back pain effectively. In this article, we will explore the best medications for treating back pain and discuss their benefits, risks, and side effects.[1][2][3][4]
Back pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide. Whether it is caused by an injury, strain, or underlying medical condition, the pain can be debilitating and significantly impact one’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are various medication options available that can provide relief and help manage back pain effectively. In this article, we will explore the best medications for treating back pain and discuss their benefits, risks, and side effects.[1][2][3][4]
Understanding Back Pain
Before delving into the best medications for back pain, it’s essential to understand what causes it and the different types of back pain. Back pain can occur for numerous reasons, such as muscle strains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or arthritis. It can manifest as acute pain, which lasts less than six weeks, or chronic pain, which persists for more than several weeks to three months.
different types of back pain. Back pain can occur for numerous reasons, such as muscle strains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or arthritis. It can manifest as acute pain, which lasts less than six weeks, or chronic pain, which persists for more than several weeks to three months.
Back pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be debilitating, making it difficult to perform daily activities and impacting overall quality of life. Understanding the causes and types of back pain is crucial in finding effective treatment options and managing the condition effectively.
Causes of Back Pain
Back pain can be triggered by various factors, including poor posture, improper lifting techniques, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, or certain medical conditions. Poor posture, for example, can put excessive strain on the muscles and ligaments of the back, leading to discomfort and pain. Similarly, using improper lifting techniques, such as bending and twisting simultaneously, can cause muscle strains and sprains.
A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by long hours of sitting or lack of physical activity, can weaken the muscles supporting the spine, making them more susceptible to injury and pain. Obesity is another common cause of back pain, as excess weight puts additional stress on the spine and its supporting structures. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as osteoporosis, scoliosis, or spinal stenosis, can contribute to chronic back pain.
Identifying the underlying cause of back pain is crucial in determining the most effective treatment approach. A thorough medical evaluation, including physical examination and diagnostic tests, may be necessary to pinpoint the exact cause and develop an individualized treatment plan.
Types of Back Pain
There are different types of back pain that individuals may experience. These include upper back pain, lower back pain, and sciatica. Each type has its own set of characteristics and potential treatment options.
Upper back pain, also known as thoracic back pain, is less common than lower back pain but can still cause significant discomfort. It often arises from poor posture, muscle strain, or underlying medical conditions affecting the thoracic spine. Treatment options for upper back pain may include physical therapy, pain medication, and exercises to improve posture and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine.
Lower back pain is the most prevalent type of back pain, affecting a large portion of the population at some point in their lives. It can result from muscle strains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease. Treatment options for lower back pain may include rest, physical therapy, pain medication, and in some cases, surgical intervention.
Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down through the hips, buttocks, and legs. It is often caused by a herniated disc pressing on the nerve roots. Treatment options for sciatica may include pain medication, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery to relieve the pressure on the nerve.
Understanding the different types of back pain can help individuals and healthcare professionals determine appropriate treatment strategies. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to accurately diagnose the type of back pain and develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs.[5][6][7][8]
Non-Prescription Pain Relief Medications
Non-prescription medications, also known as over-the-counter (OTC) medications, can provide relief for mild to moderate back pain. These medications are easily accessible and can be obtained without a doctor’s prescription.
Back pain is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by various factors, such as muscle strain, poor posture, or underlying medical conditions. While it is always advisable to seek medical advice for persistent or severe back pain, non-prescription medications can offer temporary relief and help manage the symptoms.
Over-the-Counter NSAIDs
![]() Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used as a first-line treatment for relieving back pain. Medications such as ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, and aspirin reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and help with muscle relaxation. These medications work by blocking certain enzymes in the body that cause pain and inflammation.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used as a first-line treatment for relieving back pain. Medications such as ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, and aspirin reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and help with muscle relaxation. These medications work by blocking certain enzymes in the body that cause pain and inflammation.
NSAIDs are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquids. They are typically taken orally, with or without food, and the dosage depends on the individual’s age, weight, and the severity of the pain. It is important to follow the recommended dosage and avoid prolonged use to minimize potential side effects.
While NSAIDs can be effective in reducing back pain, they may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as stomach ulcers, kidney problems, or allergies to NSAIDs, should consult a healthcare professional before taking these medications as they may experience possible side effects. Additionally, pregnant women or those who are breastfeeding should also seek medical advice before using NSAIDs.
Topical Pain Relievers
Topical pain relievers, such as creams, gels, or patches, are another option for managing back pain. These products contain ingredients like menthol, capsaicin, or lidocaine, which provide a numbing or warming sensation to alleviate discomfort locally. They work by stimulating the nerve endings in the skin, distracting the brain from the pain signals.
Topical pain relievers are particularly useful for localized pain or sore muscles. They can be applied directly to the affected area, allowing for targeted relief. These products are available in various strengths and formulations, and it is important to carefully read the instructions and follow the recommended usage guidelines.
It is worth noting that topical pain relievers may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with sensitive skin or allergies to certain ingredients should perform a patch test before applying the product to a larger area. If any adverse reactions occur, such as redness, itching, or swelling, the use of the product should be discontinued, and a healthcare professional should be consulted.
Prescription Medications for Back Pain
For individuals with severe or chronic low back pain, stronger medications may be necessary to provide relief and improve functionality. These medications require a doctor’s prescription and should be used under medical supervision. The doctor will provide varying prescription strengths depending on your situation.
Living with back pain can be debilitating and impact daily activities. Fortunately, there are various prescription medications available that doctors prescribe to help alleviate the discomfort and promote a better quality of life. Let’s explore some of these medications in more detail.
Opioids for Severe Back Pain
Opioids, also known as narcotics, are potent pain relievers that can be prescribed for severe back pain.![]() They bind to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, reducing the perception of pain. However, it’s important to note that opioids come with the risk of dependence and should only be used as a last resort or for short-term management of acute pain.
They bind to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, reducing the perception of pain. However, it’s important to note that opioids come with the risk of dependence and should only be used as a last resort or for short-term management of acute pain.
When prescribed opioid pain relievers, it is crucial to follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and be aware of potential side effects and serious side effects. Regular monitoring and communication with the healthcare provider are essential to ensure the medication’s effectiveness and safety.
Muscle Relaxant
Muscle relaxants are another class of medications prescribed to alleviate muscle spasms and promote relaxation in the muscles surrounding the spine. They can help reduce pain caused by muscle tension or strains. Commonly prescribed muscle relaxants include cyclobenzaprine, methocarbamol, and baclofen.
These medications work by targeting the central nervous system, helping to relieve muscle tightness and improve mobility. It is important to note that muscle relaxants may cause drowsiness or dizziness, so caution should be exercised when operating machinery or driving.
Antidepressants for Chronic Back Pain
Antidepressant medications, such as tricyclic antidepressants or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may be prescribed for back pain relief. These medications work by altering brain chemistry and modifying the perception of pain. In addition to pain relief, they can also help manage sleep disturbances and improve mood, which are often associated with chronic pain.
It is worth noting that the use of antidepressants for back pain is not related to the presence of depression. Instead, these medications are utilized for their pain-modulating properties. As with any medication, it is important to discuss potential side effects and interactions with the prescribing healthcare provider.
In conclusion, prescription medications can play a crucial role in managing severe or chronic back pain. Opioids, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants are just a few examples of the medications that may be prescribed. However, it is important to remember that these and other medications should always be used under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional. Regular communication with the healthcare provider is essential to ensure the medication’s effectiveness and minimize any potential risks.[9][10]
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Back Pain
In addition to conventional medications, some individuals may find relief from back pain through natural remedies and supplements. It’s important to note that these options may not have extensive scientific evidence supporting their efficacy, and it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before trying them.
Living with chronic back pain can be debilitating and affect your quality of life. While conventional medications can provide temporary relief, many people are seeking alternative solutions to manage their pain. Natural remedies and supplements have gained popularity as potential options for alleviating back pain.
Herbal Supplements
Herbal supplements, like turmeric, devil’s claw, or white willow bark, have been traditionally used for their potential anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties. These natural remedies have a long history in traditional medicine and are believed to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain in the body.
Turmeric, a vibrant yellow spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, contains a compound called curcumin, which has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory effects. Devil’s claw, a plant native to southern Africa, has been used for centuries to treat various ailments, including back and stomach pain. White willow bark, derived from the bark of the white willow tree, contains a compound called salicin, which is similar to aspirin and may help reduce pain and inflammation.
However, it’s important to note that while these herbal supplements have been used for centuries, more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness and potential side effects. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any herbal supplements into your back pain management regimen.
Vitamins and Minerals
Certain vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in maintaining bone health and muscle function, which can have a direct impact on back pain. Deficiencies in these nutrients may contribute to the development or worsening of back pain. Supplementing with them under medical guidance may help alleviate symptoms and improve overall musculoskeletal health.
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and bone health. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of back pain and musculoskeletal disorders. Magnesium is involved in muscle relaxation and nerve function. Deficiency in this mineral may contribute to muscle spasms and increased pain sensitivity. Calcium is essential for bone health and muscle contraction, and inadequate intake may weaken the bones and lead to increased back pain.
Before starting any vitamin or mineral supplement, it’s important to have your nutrient levels assessed by a healthcare professional. They can determine if you have any deficiencies and recommend appropriate supplementation to address them. It’s crucial to follow their guidance and avoid excessive intake, as too much of certain nutrients can be harmful.
Natural remedies and supplements offer potential alternatives for managing back pain. However, it’s important to approach them with caution and consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating them into your treatment plan. These options may provide relief for some individuals with arthritis pain. They may not be suitable or effective for everyone. Your doctor can help determine the best course of action based on your specific needs and medical history.[11][12][13]
Risks and Side Effects of Back Pain Medications
While medications can provide much-needed relief for back pain, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with their use. Understanding these risks can help you make informed decisions about your pain management.
Potential Side Effects of NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to alleviate back pain. They work by reducing inflammation and relieving pain. However, long-term use of NSAIDs can increase the risk of gastrointestinal issues, including ulcers, bleeding, and stomach irritation. These side effects occur due to the inhibition of an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (COX) that helps protect the stomach lining.
It’s important to note that not everyone who uses NSAIDs will experience these side effects. However, certain factors can increase the risk, such as a history of stomach ulcers, older age, and prolonged use of high doses of NSAIDs.
Overusing these medications or exceeding the recommended dosage may also lead to kidney problems. NSAIDs can reduce blood flow to the kidneys, potentially causing kidney damage or worsening existing kidney conditions. Individuals with pre-existing kidney issues or those taking medications that affect kidney function should exercise caution when using NSAIDs and consult with their healthcare provider.
To minimize the risk of side effects, it’s essential to use NSAIDs responsibly and follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals. They can help determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on your specific needs.
Risks of Long-Term Opioid Use
In cases where NSAIDs are not effective or suitable for managing back pain, opioids may be prescribed. Opioids, such as codeine, oxycodone, and morphine, work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, reducing pain signals. However, long-term use of opioids to treat pain carries the risk of developing dependence or addiction.
It’s crucial to use opioids under close medical supervision and strictly follow the prescribed dosage. Regular monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are essential to ensure the safe and effective use of opioids for back pain management. They can help assess your pain levels, adjust the dosage if necessary, and provide guidance on tapering off the medication when appropriate.
In addition to the risk of dependence or addiction, opioids can cause other side effects. These may include drowsiness, constipation, and respiratory depression. The sedative effects of opioids can impair coordination, concentration, and judgment, making it unsafe to drive or operate machinery while taking these medications.
Exploring alternative treatment options whenever possible is recommended to minimize the reliance on opioids. Physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, and exercise programs can be effective in managing back pain and reducing the need for long-term opioid use.
It’s essential to have open and honest discussions with your healthcare provider about the risks and benefits of back pain medications. They can help you weigh the potential side effects against the potential benefits. Work with you to develop a comprehensive back pain medication management plan.[14][15]
When to Consult a Doctor for Back Pain
While self-care measures and over-the-counter medications may help manage mild back and neck pain, certain situations warrant medical attention.
Back pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide. It can range from a dull ache to a sharp, debilitating pain that interferes with daily activities. In most cases, back pain is caused by muscle strain or injury and can be relieved with rest and conservative treatment. However, there are instances when back pain could be a sign of a more serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Recognizing Serious Back Pain Symptoms
If backside pain persists or is accompanied by symptoms such as persistent fever, unexplained weight loss, loss of bowel or bladder control, or numbness in the legs, immediate medical attention is required. These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment.
When experiencing back pain, it is important to pay attention to any additional symptoms that may accompany it. Fever can be a sign of infection, while unexplained weight loss may indicate an underlying disease. Loss of bowel or bladder control can be a sign of nerve compression, which requires immediate medical intervention. Numbness in the legs could be a sign of nerve damage or a herniated disc, which may require further evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Preparing for Your Doctor’s Appointment
Before consulting a healthcare professional about back pain, it is helpful to document any relevant information, such as the onset of pain, its intensity, triggers, and any associated symptoms. This information can assist the doctor in making an accurate diagnosis and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
When preparing for a doctor’s appointment, it is important to gather as much information as possible about your back pain. Keep a record of when the pain started, what activities or movements worsen or alleviate the pain, and any other symptoms you may be experiencing. This information will help your doctor understand the nature of your pain and guide them in determining the most effective treatment approach.
In addition to documenting your symptoms, it may also be helpful to write down any questions or concerns you have regarding your back pain. This will ensure that you address all your concerns during the appointment. Have a clear understanding of your condition and treatment options.[16][17][18][19][20]
Lifestyle Changes to Complement Medication
In addition to medication, making certain lifestyle changes can support back pain management and reduce the frequency and intensity of episodes. Other therapies can help relieve pain.
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Engaging in regular exercise, particularly exercises that strengthen the core, improve flexibility, and promote proper posture, can help reduce back pain and prevent future episodes. Physical therapy sessions may also be beneficial in addressing underlying muscular imbalances or promoting better body mechanics.
Proper Posture and Ergonomics
Maintaining good posture while sitting, standing, or lifting objects is crucial in preventing back pain. It’s important to pay attention to ergonomics, especially when working at a desk or engaging in repetitive activities. Using ergonomic chairs, supportive cushions, and positioning computer screens at eye level can help minimize strain on the back.
Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
Stress and tension can exacerbate back pain. Practicing stress management techniques to ease pain. Such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help alleviate both physical and mental stress, reducing the severity of back pain episodes.
Overall, the best medications for treating back pain depend on individual circumstances and the severity of the pain. Non-prescription medications like NSAIDs and topical pain relievers can provide temporary relief for mild to moderate back pain. However, when back pain becomes severe or chronic, prescription medications like opioids, muscle relaxants, or antidepressants may be necessary under medical supervision. Natural remedies, supplements, and lifestyle changes can also complement medication and help manage back pain effectively. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan. That considers the underlying causes, risks, and potential side effects. With the right approach, it is possible to find relief and regain control over back pain, improving overall quality of life.
Using the CareClinic App to Manage Pain
Your health depends on keeping a pain diary, which the CareClinic app helps facilitate. The app can serve as your personal health and clinical journal. Simply use the app’s pain diary and log your daily symptoms, meds, and other triggers as they happen. The app also has dedicated sections for tracking each of these. This can assist you in recognizing early warning indicators.
The app also contains a section for medications where you can accurately track the pain treatments you are doing. Whether they involve transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, spinal manipulation, relaxation therapy, or superficial heat. Hopefully, having all of this knowledge on hand will assist you in managing illnesses associated with chronic pain.
Sources
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/pain
- https://painbc.ca/health-professionals/education/OT-workshop
References
- “Certain medications are better than others for managing spine pain – Harvard Health”. https://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/certain-medications-are-better-than-others-for-managing-spine-pain
- “Pharmacotherapy for Spine-Related Pain in Older Adults – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35754070/
- “The best meds for back pain – Harvard Health”. https://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/the-best-meds-for-back-pain
- “Before You Take Ibuprofen, Try This”. https://time.com/4784602/ibuprofen-natural-pain-relievers/
- “What Causes Back Pain? – Mayo Clinic Press”. https://mcpress.mayoclinic.org/living-well/not-all-low-back-pain-is-the-same/
- “Back Pain – Causes & Treatment | Made for This Moment”. https://madeforthismoment.asahq.org/pain-management/types-of-pain/back-pain/
- “Common Causes of Back Pain – Types & Treatment | NIAMS”. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/back-pain
- “Back Pain Symptoms & Causes | Dignity Health | Dignity Health”. https://www.dignityhealth.org/conditions-and-treatments/orthopedics/common-back-and-spine-injuries-and-conditions/back-pain
- “Medicines for back pain: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia”. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007486.htm
- “Pharmacological treatments for low back pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10072849/
- “The Spice Ingredient That Can Block Bad Memories”. https://time.com/3649565/curcumin-ptsd/
- “Turmeric May No Longer Be So Miraculous”. https://time.com/4634897/turmeric-health-benefits-overblown/
- “Association of back pain with hypovitaminosis D in postmenopausal women with low bone mass – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23758943/
- “Pain Medicines (Analgesics) | National Kidney Foundation”. https://www.kidney.org/kidney-topics/pain-medicines-analgesics
- “Are Opioids Needed to Treat Chronic Low Back Pain? A Review of Treatment Options and Analgesics in Development – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7234959/
- “Top causes of back pain and when to see a doctor”. https://www.summahealth.org/flourish/entries/2020/07/top-causes-of-back-pain-and-when-to-see-a-doctor
- “5 signs your back pain might be an emergency | Back and Spine | Orthopaedics | Rehabilitation | UT Southwestern Medical Center”. https://utswmed.org/medblog/5-signs-your-back-pain-might-be-emergency/
- “5 Ways to Prepare to See a Spine Doctor for Back or Neck Pain | Nuvance Health”. https://www.nuvancehealth.org/health-tips-and-news/do-these-five-things-before-your-first-visit-with-a-neurosurgeon-for-spine-pain
- “How to Prepare for a Consultation With Your Spine Doctor – Desert Institute for Spine Care”. https://www.sciatica.com/blog/how-to-prepare-for-a-consultation-with-your-spine-doctor/
- “Preparing for Your Doctor's Visit – OrthoInfo – AAOS”. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/getting-the-most-out-of-your-doctors-visit
- “Yoga Works as Well as Physical Therapy for Back Pain”. https://time.com/4825261/back-pain-yoga-physical-therapy/
- “7 Effective Techniques for Back Pain Relief – Calhoun Spine Care & Wellness Center”. https://calhounspinecare.com/7-effective-techniques-for-back-pain-relief/
- “3 Science-Backed Ways to Relieve Pain and Stress”. https://time.com/4884052/how-to-relieve-pain-stress/