ADHD and alcoholism are two complex conditions that have been the subject of extensive research in recent years. Understanding the link between these two conditions is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals struggling with ADHD or alcoholism. In this article, we will delve into the definition of ADHD and alcoholism, explore their prevalence, examine the connection between them, review important scientific studies, discuss the impact of ADHD on alcoholism treatment, explore coping mechanisms, highlight the role of support systems, and conclude with the importance of understanding this link.[1][2][3][4]
Defining ADHD and Alcoholism
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in paying attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. It affects both children and young adults, with symptoms often persisting into adulthood. On the other hand, alcoholism, also known as alcohol use disorder, refers to a chronic condition where an individual has a compulsive need to consume alcohol, leading to harmful consequences in their personal and professional lives.
What is ADHD?
ADHD is a complex disorder that impacts various areas of an individual’s life. Common signs include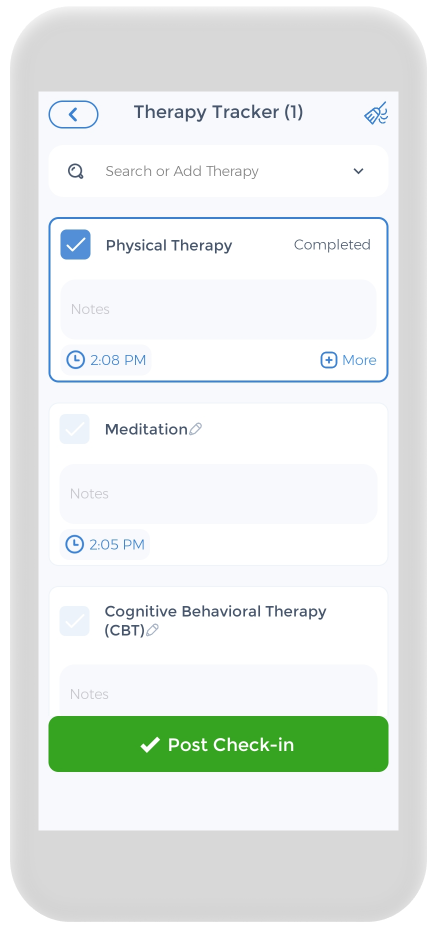 being easily distracted, having difficulty organizing tasks, and struggling to follow through with instructions. Individuals with ADHD may also exhibit impulsive behavior, such as interrupting conversations or taking risks without considering the consequences.
being easily distracted, having difficulty organizing tasks, and struggling to follow through with instructions. Individuals with ADHD may also exhibit impulsive behavior, such as interrupting conversations or taking risks without considering the consequences.
It is important to note that ADHD is not solely a childhood disorder. While symptoms often first appear during childhood, many individuals continue to experience difficulties into adulthood. In fact, studies have shown that approximately 60% of children with ADHD continue to exhibit symptoms in adulthood.
ADHD can have a significant impact on an individual’s academic and professional life. Difficulties with attention and organization can make it challenging to complete tasks and meet deadlines. Additionally, impulsivity and hyperactivity can interfere with social interactions and relationships. However, with appropriate treatment and support, individuals with ADHD can learn strategies to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
What is Alcoholism?
Alcoholism is a chronic condition characterized by compulsive alcohol use or binge drinking. It is associated with physical and psychological dependence on alcohol, leading to tolerance and withdrawal symptoms. Alcoholism can have a profound impact on an individual’s relationships, work performance, and overall well-being.
Alcoholism is a complex disorder influenced by various factors, including genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. It is important to understand that alcoholism is not a result of weak willpower or moral failure. It is a disease that requires medical intervention and support for recovery.
Individuals with alcoholism often experience negative consequences in different areas of their lives. Relationships may suffer due to conflicts related to their alcohol dependence and use, and individuals may isolate themselves from friends and family. Work performance may decline, leading to financial difficulties and potential job loss. Additionally, alcoholism can have severe health consequences, including liver damage, cardiovascular problems, and mental health disorders.
Recovery from alcoholism is possible with the right treatment and support. Treatment options may include counseling, support groups, and medication. It is essential for individuals with alcoholism to seek help and surround themselves with a supportive network to overcome this challenging condition.[5][6][7][8]
The Prevalence of ADHD and Alcoholism
Both ADHD and alcoholism have a significant impact on society due to their high prevalence rates. However, understanding the scope of these disorders requires a closer look at their statistics and how they affect different populations.
ADHD Statistics
According to recent studies, approximately 5-10% of children and 2-5% of adults worldwide have ADHD. These numbers may seem relatively small, but when we consider the global population, it translates to millions of individuals affected by this disorder. ADHD is more commonly diagnosed in males than females, with a ratio of about 3:1. However, it is important to note that ADHD can affect people from all walks of life, regardless of gender, age, or socioeconomic background.
Severe childhood ADHD is not just a childhood disorder that magically disappears with age. Many individuals continue to struggle with ADHD symptoms well into early adulthood too [1]. In fact, studies suggest that around 60% of children with ADHD carry their symptoms into adulthood. This can have a significant impact on various aspects of their lives, including education, employment, and relationships.
ADHD is often associated with difficulties in attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. However, it is essential to recognize that ADHD is a complex disorder that manifests differently in each individual. Some may primarily struggle with attention deficits, while others may exhibit more hyperactive or impulsive behaviors. Additionally, ADHD can present with various comorbidities, such as anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities, further complicating the diagnosis and treatment process.
Alcoholism Statistics
Alcoholism is a global concern, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. The World Health Organization estimates that about 5.1% of the global population suffers from alcohol use disorder. This staggering statistic highlights the widespread impact of alcoholism on society.
Alcohol and drug abuse does not discriminate based on gender or age. While it is true that men are more likely to develop alcohol abuse than women, it is crucial to recognize that alcoholism affects individuals of all genders and ages. The reasons behind this gender disparity are multifaceted, including biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors.
Alcoholism is not solely a personal struggle; it also has far-reaching consequences for families, communities, and societies as a whole. It can lead to mental health problems, impaired judgment, relationship difficulties, and even legal issues. Moreover, the economic burden of alcoholism is significant, with costs related to healthcare, law enforcement, and lost productivity.
It is important to note that alcoholism is a complex disorder with various contributing factors. While genetics and family history play a role, environmental influences, such as peer pressure and societal norms, also contribute to the development of alcohol use disorder. Understanding these factors can help inform prevention and intervention efforts to address alcoholism effectively.[9][10][11][12][13][14]
The Connection Between ADHD and Alcoholism
Research has revealed a significant association between ADHD and alcoholism. While the exact mechanisms underlying this link are complex and multifaceted, several factors contribute to their interconnection.
 One factor that contributes to the connection between ADHD and alcohol or substance use disorder is the presence of shared risk factors. Both ADHD and alcoholism have been found to have a genetic component, meaning that individuals with a family history of either condition may be more predisposed to developing the other. Additionally, environmental influences, such as growing up in a household where alcohol or substance abuse itself is prevalent, can increase the risk of both ADHD and alcoholism.
One factor that contributes to the connection between ADHD and alcohol or substance use disorder is the presence of shared risk factors. Both ADHD and alcoholism have been found to have a genetic component, meaning that individuals with a family history of either condition may be more predisposed to developing the other. Additionally, environmental influences, such as growing up in a household where alcohol or substance abuse itself is prevalent, can increase the risk of both ADHD and alcoholism.
Another shared risk factor between ADHD and alcohol use disorder is altered brain chemistry. Research has shown that individuals with ADHD often have imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which are also implicated in the development of alcoholism. These imbalances may contribute to the increased likelihood of individuals with ADHD developing alcoholism.
Shared Risk Factors
ADHD and alcohol use disorder share certain risk factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and altered brain chemistry. Understanding these shared risk factors is crucial in comprehending the link between the two conditions and developing targeted treatment strategies.
Furthermore, the role of impulsivity cannot be overlooked when examining the connection between ADHD and alcoholism. Impulsivity, a hallmark symptom of ADHD, plays a significant role in the development of alcoholism in individuals with ADHD. Those with ADHD often struggle with self-control and exhibit impulsive behavior, which can increase the likelihood of engaging in risky and addictive behaviors, such as excessive alcohol consumption.
Impulsivity can lead individuals with ADHD to make impulsive decisions, such as drinking excessively and without considering the potential consequences. This impulsive behavior and binge drinking can be seen as a form of self-medication, as individuals with ADHD may turn to alcohol and binge drink as a way to cope with anxiety symptoms and the challenges and difficulties they face due to their condition. However, this self-medication can quickly spiral into alcoholism, as individuals with ADHD may develop a dependence on alcohol to manage their symptoms and regulate their emotions.
Furthermore, the relationship between impulsivity and alcoholism in individuals with ADHD can create a vicious cycle. Alcohol affects judgment and decrease inhibitions, leading to even more impulsive behavior and make ADHD symptoms worse. This cycle can perpetuate the development and progression of alcoholism in individuals with ADHD.[15][16][17][18]
ADHD and Alcohol Research
Over the past decades, numerous scientific studies have been conducted to investigate the relationship between ADHD and alcoholism. Understanding this link is crucial for developing effective interventions and treatment strategies for individuals with ADHD who are at risk for alcoholism.
One key finding from these studies is the higher prevalence of alcoholism among individuals with ADHD compared to the general population [2]. This suggests that there may be a significant association between ADHD and alcohol use disorder. Researchers have hypothesized several explanations for this relationship.
Firstly, individuals with ADHD may be more vulnerable to alcohol misuse due to shared risk factors. Both ADHD and alcoholism have been linked to genetic factors, environmental influences, and neurobiological differences. These shared vulnerabilities may increase the likelihood of developing alcoholism in individuals with ADHD.
Secondly, underlying neurological differences may contribute to the increased risk of alcoholism among individuals with ADHD. Studies have shown that individuals with ADHD often have deficits in executive functioning, impulse control, and reward processing. These deficits may make it more difficult for individuals with ADHD to regulate their alcohol consumption and make informed decisions about drinking.
However, it is important to note the limitations of the current research on the ADHD-alcoholism link. While the existing studies provide valuable insights, they also have certain methodological constraints. For instance, some studies rely on self-report measures to assess alcoholism, which may introduce bias. Additionally, the majority of studies are cross-sectional, meaning they only provide a snapshot of the relationship between ADHD and alcoholism at a specific point in time.[19][20][21]
The Impact of ADHD on Alcoholism Treatment
Understanding the impact of ADHD on alcoholism treatment is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking help. ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. When ADHD co-occurs with alcoholism, it can present unique challenges during the treatment process.
Challenges in Treatment
Individuals with co-occurring ADHD and alcoholism may face unique challenges during treatment. The presence of alcohol addiction and ADHD can complicate the recovery process, as it can impair an individual’s ability to stay focused, comply with treatment plans, and manage impulsive behaviors. These challenges can make it difficult for individuals to fully engage in their treatment and maintain sobriety.
One of the key challenges is the difficulty in staying focused. Individuals with ADHD often struggle with maintaining attention on a task or topic, which can hinder their progress in alcoholism treatment. They may find it hard to concentrate during therapy sessions or educational workshops, making it challenging to absorb the necessary information and skills to address their alcoholism.
Another challenge is impulsivity. People with ADHD often have difficulty controlling their impulses and may act without thinking. This can lead to impulsive decisions regarding alcohol consumption, even during the treatment process. It is essential for healthcare professionals to address and provide strategies for managing impulsive behaviors to prevent relapse.
Strategies for Success
Despite the challenges, several strategies can enhance treatment outcomes for individuals with both ADHD and alcoholism. Tailoring treatment approaches to address the specific needs of these individuals is crucial. This may involve implementing structured routines, breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable steps, and providing clear instructions to help individuals with ADHD stay focused and engaged in their treatment.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is another effective strategy for individuals with co-occurring ADHD and alcoholism. CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to alcohol use. It can also help individuals develop coping mechanisms for managing impulsivity and improving attention and focus.
In addition to tailored treatment approaches and CBT, ongoing support is essential for individuals with co-occurring ADHD and alcoholism. This support can come in the form of individual therapy, group therapy, or support groups specifically designed for individuals with ADHD and substance use disorders. Ongoing support provides a safe and understanding environment where individuals can share their experiences, receive guidance, and learn from others who have faced similar challenges.
In conclusion, the impact of ADHD on alcoholism treatment should not be overlooked. Understanding the unique challenges faced by individuals with co-occurring ADHD and alcoholism is crucial for healthcare professionals to provide effective and comprehensive treatment. By tailoring treatment approaches, offering cognitive-behavioral therapy, and providing ongoing support, individuals with both ADHD and alcoholism can improve their treatment outcomes and work towards long-term recovery.[22]
Coping Mechanisms for Individuals with ADHD and Alcoholism
Developing effective coping mechanisms is crucial for individuals with co-occurring ADHD and alcoholism to manage their conditions and maintain sobriety.
Living with both ADHD and alcoholism can present unique challenges, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can lead fulfilling and healthy lives. In addition to therapy and counseling, there are various coping mechanisms that can be explored to address the specific needs of individuals with these dual diagnoses.
Therapy and Counseling
Therapy and counseling play a crucial role in helping individuals with ADHD and alcoholism. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing (MI) are two commonly used therapeutic approaches that can address underlying issues, promote healthy coping strategies, and empower individuals to overcome challenges.
In CBT, individuals learn to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to their ADHD symptoms and alcohol use disorders. By challenging irrational beliefs and developing healthier coping mechanisms, individuals can develop a better understanding of their conditions and make positive changes in their lives.
On the other hand, MI focuses on exploring and resolving ambivalence about change. This approach helps individuals with ADHD and alcoholism to identify their personal motivations to stop binge drinking and develop a strong commitment to change. Through collaborative conversations with a trained therapist, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the consequences of their behaviors and develop strategies to maintain their recovery.
Medication and Treatment Options
Medication can be a valuable tool in managing ADHD symptoms and alcoholism. Taking ADHD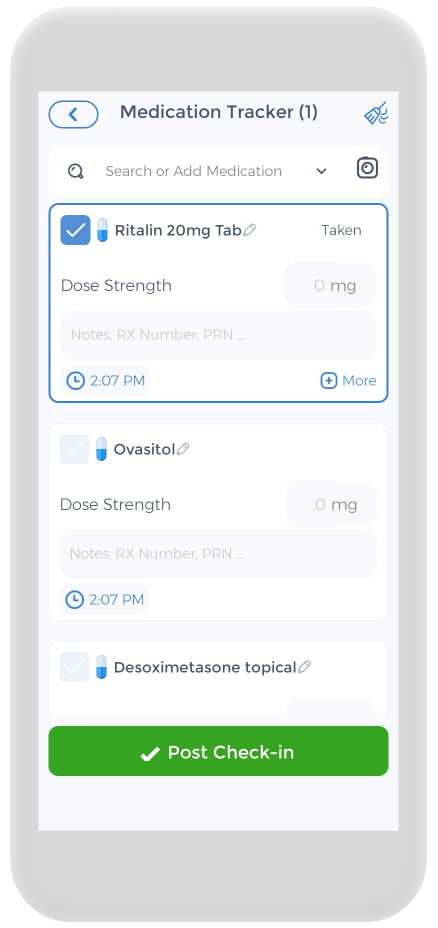 medication, such as stimulants or non-stimulant medications, may help individuals with ADHD regain focus and reduce impulsivity, thus supporting their recovery journey.
medication, such as stimulants or non-stimulant medications, may help individuals with ADHD regain focus and reduce impulsivity, thus supporting their recovery journey.
Stimulant ADHD medications, such as methylphenidate or amphetamines, can help individuals with ADHD improve their attention span, increase their ability to concentrate, and reduce hyperactivity. These medications work by affecting the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, helping to regulate the symptoms of ADHD.
Non-stimulant ADHD medications, such as atomoxetine or bupropion, may be prescribed when stimulant medications are not suitable or well-tolerated. These medications work differently than stimulants but can still be effective in managing ADHD symptoms and supporting recovery from alcoholism and drug addiction.
It is important to note that medication should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional who specializes in dual diagnosis treatment. They will carefully assess the individual’s unique needs and circumstances to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage.
Furthermore, in addition to therapy and medication, individuals with ADHD and alcoholism can benefit from a comprehensive treatment approach that includes support groups, lifestyle changes, and healthy coping strategies. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness or meditation, and maintaining a balanced diet can all contribute to overall well-being and support recovery.[23][24][25][26]
The Role of Support Systems in Managing ADHD and Alcoholism
Support systems are instrumental in the recovery process for individuals struggling with both ADHD and alcoholism.
Family and Friends
Family and friends play a crucial role in providing emotional support, understanding, and guidance to individuals with co-occurring ADHD and alcoholism. Their involvement can enhance the overall treatment outcomes and contribute to long-term recovery.
Professional Support Networks
Professional support networks, including healthcare providers, therapists, and support groups, provide specialized knowledge and guidance for individuals with ADHD and alcoholism. These professionals can offer practical strategies, monitor progress, and provide ongoing support throughout the recovery process.[27][28]
Using the CareClinic App to Help with ADHD
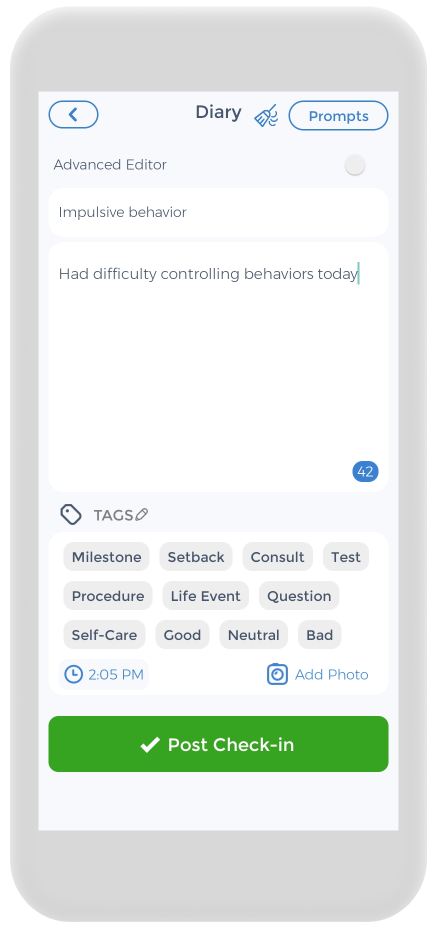
Keeping track of your mental health condition and prescribed medications is crucial. and the CareClinic app can help with that. You can use the app as your clinical journal. Just go to the diary section of the app and enter your daily symptoms, ADHD medication, and other triggers, as they occur. There are also specific sections on the app to track each of these. For example, if you have ADHD symptoms, you can track down symptoms you have on a daily basis.
The app also has a medication section where you can precisely track the doses of the pills you are taking and receive reminders. Whether you are taking stimulant medication or herbs for ADHD or anxiety disorders, we know how difficult but important keeping track of your medications is, so we hope to make it as easy and streamlined as possible. This way, you can take your medications and experience consistent relief.
⬇️ Download the CareClinic App
Sources
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html
- Klarity (2023). ADHD Tools For Organization & Time Management https://www.klarityadhd.com/post/adhd-tools/
- MayoClinic (2023). Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/adult-adhd/symptoms-causes/syc-20350878
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd/index.shtml
References
- “Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attention_deficit_hyperactivity_disorder
- “Alcohol use disorders and ADHD – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34265320/
- “Relationship Between Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Alcohol Dependence: A Genetic View – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4070128/
- “Common and distinct neural connectivity in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and alcohol use disorder studied using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33690916/
- “More than 15 million US adults have ADHD, new study estimates”. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/more-than-15-million-us-adults-have-adhd-new-study-estimates-2024-10-10/
- “Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) – National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)”. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd
- “Rise in diagnoses is prompting more US adults to ask: 'Do I have ADHD?'”. https://apnews.com/article/d6834e1c644e17f1e702603dfaae9448
- “What's Driving the Demand for ADHD Drugs Like Adderall”. https://time.com/6271049/adhd-diagnoses-rising/
- “Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adult_attention_deficit_hyperactivity_disorder
- “Alcohol”. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/alcohol
- “Alcoholism”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alcoholism
- “Women Are Now Drinking Almost as Much as Men”. https://time.com/4544706/women-alcohol-consumption-study/
- “Gender Differences in the Epidemiology of Alcohol Use and Related Harms in the United States – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7590834/
- “Hazardous drinking and alcohol use disorders – PMC”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10284465/
- “Genetic and environmental influences on externalizing behavior and alcohol problems in adolescence: A female twin study – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2758781/
- “Alcohol and ADHD: How They're Linked”. https://www.townsendla.com/blog/alcohol-and-adhd
- “Alcohol and ADHD: How They're Linked | Gateway Foundation”. https://www.gatewayfoundation.org/blog/adhd-alcohol-relationship/
- “ADHD and Addiction – Understanding the Connection”. https://www.insideaddiction.co.uk/mental-health/adhd-and-addiction
- “Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Alcohol and Other Substance Use Disorders in Young Adulthood: Findings from a Canadian Nationally Representative Survey”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34343246/
- “Alcohol and drug use disorders in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Prevalence and associations with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptom severity and emotional dysregulation”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33014721/
- “The Clinically Meaningful Link Between Alcohol Use and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6683828/
- “Integrated cognitive behavioral therapy for patients with substance use disorder and comorbid ADHD: two case presentations”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25706067/
- “Managing ADHD to Reduce Alcohol Dependence – ACI Rehab”. https://acirehab.org/adhd-and-alcohol/
- “Why Adults with ADHD Are More Prone to Addiction—and How to Find Support”. https://www.envisionadhd.com/single-post/why-adults-with-adhd-are-more-prone-to-addiction-and-how-to-find-support
- “The Link Between ADHD and Substance Abuse: Strategies for Dual Recovery”. https://www.woodhavenohio.com/adhd-and-substance-abuse-strategies-for-dual-recovery
- “ADHD Impulsivity Alcohol: Exploring the Complex Relationship and Risks”. https://www.ourmental.health/impulsivity/understanding-the-link-adhd-impulsivity-and-alcohol-use-risks
- “Family Roles in Addiction & the Importance of Family Support in Recovery”. https://lagunatreatment.com/family-resources/addiction-and-family/
- “Guide for Family Members – Recovery Research Institute”. https://www.recoveryanswers.org/resource/guide-family-members/