Do you or a loved one suffer from seizures and have been diagnosed with epilepsy? Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that is characterized by abnormal brain activity (R). This abnormal activity leads to patients experiencing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, or loss of awareness. Epilepsy can affect anyone, regardless of gender, age, or background. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief, undetectable episodes to long periods of uncontrollable shaking. Stigma and exclusion are common features of epilepsy across the world. It is very important to raise epilepsy awareness to help reduce the impact of the condition on patients. CareClinic is a daily health app that you can use to help manage epilepsy and improve your quality of life.
Table of Contents
Epilepsy in the United States
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological conditions. 3.4 million people in the United States have epilepsy. 1 in 26 people in the United States will develop epilepsy at some point in their lifetime, and there are approximately 150,000 new cases of epilepsy each year (R). Epilepsy affects all ages, socioeconomic and racial groups. Incidences of epilepsy are highest in children and older adults (R). Men are slightly more likely to be diagnosed with epilepsy compared to women.
Symptoms of Epilepsy
Epilepsy is characterized by recurring seizures. At least two unprovoked seizures are usually required to be diagnosed with epilepsy. What is a seizure? A seizure, also known as an epileptic seizure, is a period of symptoms that occur as a result of abnormally excessive neuronal activity in the brain. Since seizures can affect anything that your brain controls, signs and symptoms can vary. However, a patient with epilepsy will generally end up having the same type of seizure each time. Their symptoms will be similar between seizure episodes.
Convulsive seizures are the most common type, these are highlighted by uncontrolled shaking of the body. They make up roughly 60% of all seizures. Most convulsive seizures start as focal seizures, affecting one side of the brain. Over time, these focal seizures become generalized, affecting both sides of the brain. The other 40% of seizures are non-convulsive.
Focal Seizures
Focal seizures are the result of abnormal activity on one side of the brain. There are two types of focal seizures:
- Seizures without loss of consciousness – these seizures may cause emotional or sensory changes along with involuntary jerking of body parts.
- Seizures with impaired awareness – these seizures may cause a change or loss in consciousness or awareness. You may stare off into space and appear dazed of confused and lose track of your surroundings.
Generalized Seizures
Generalized seizures are the result of abnormal brain activity throughout the entire brain. Think of it as random signals firing across your brain, which cause your body to react with jerking movements. There are six types of generalized seizures that you can experience:
- Tonic-clonic – also known as grand mal seizures, can cause unconsciousness, contraction of the body and limbs and shaking. They are the most dramatic of epileptic seizures.
- Tonic – these seizures cause constant muscle contractions.
- Clonic – these seizures cause jerking, stiffening and shaking of the limbs.
- Atonic – these seizures cause the loss of muscle control and can cause you to fall suddenly.
- Myoclonic – these seizures cause sudden and brief muscle spasms throughout the limbs and sometimes the body.
- Absence – also known as petit mal seizures, can be subtle and you may stare off into space or repeatedly blink your eyes. They occur really quickly however you may experience brief unconsciousness.
Causes of Seizures
Around 25% of patients who experience seizures have epilepsy. Studies have shown that epilepsy may be the result of both genetics and environmental factors, or even a mix of both. The cause of epilepsy is unknown in more than half of the patients, and in the other half, the cause may be due to certain factors.
- Genetic influence – has been seen as the main cause in a majority of cases. Specific genes have been linked to certain types of epilepsy. Additionally, certain genes may make you more likely to react to environmental situations that can cause triggers.
- Head injury – trauma to the head can lead to epilepsy.
- Brain trauma – conditions that can damage the brain such as tumors or strokes.
- Infectious diseases – AIDS, meningitis, or encephalitis that affects the brain or central nervous system can lead to epilepsy.
- Prenatal brain injury – babies in the womb may undergo brain damage as the result of poor nutrition, oxygen deficiency or an infection from the mother. These can lead to developmental disorders resulting in epilepsy.
Epileptic Seizure Warnings and Risks
How epilepsy happens is still not understood. However epileptic seizures are not random and can be triggered by certain events. Flickering lights are in fact a trigger, as we all know from warning signs in clubs, games, movies among other things. Other factors such as stress, lack of sleep, or alcohol abuse can also be seizure warning signs.
There are many other factors that can trigger epilepsy. These can include family history, age, past instances of head injury, stroke or brain trauma, and infections.
How is Epilepsy Diagnosed?
To diagnose epilepsy, it usually requires observation of your seizures and their possible cause. Your doctor will have you undergo a few tests to help figure out the cause of your seizures and diagnose epilepsy. They may order blood tests to see if there are any infections or underlying genetic conditions. You may also be ordered to undergo a neurological exam to evaluate for behavior, mental and movement ability or other functions.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) – is the most commonly ordered test to diagnose epilepsy. The goal of the EEG is to help record any changes to the normal pattern of your brain waves. If there are any changes that may possibly be a sign of epilepsy. Your doctor can monitor your brain patterns during and EEG to record any seizures you may experience. An EEG can help distinguish the type of seizure.
- Diagnostic Imaging – a computerized tomography scan (CT scan) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are effective tests to obtain an image of the brain. These tests can help see any structural issues in or around the brain which can help identify any potential causes.
Epilepsy Treatment
If you suffer a second seizure, you will usually end up being prescribed daily medication to help treat epilepsy. Other types of treatments may be offered if medications do not help treat your epilepsy.
Medication
Anti-seizure or anti-epileptic medication is the most common solution to help patients become seizure-free. It can be difficult to find the right medication, and your prescription is based on seizure type, frequency, age, lifestyle and other factors. Usually, you will be prescribed a single type of medication, however, if single medication fails to work then multiple medications can be described. Dosages will be adjusted gradually until your seizures become under control.
As with all medications, anti-seizure medications also come with side effects. Some mild side effects include; dizziness, fatigue, skin rashes, memory issues and others. Some more severe effects include; depression, inflammation of organs, severe rashes and others.
Many patients stop taking medication if they do not experience a seizure for two to four years. There is high chance of recurrence within the first six months, however the majority of adults and children are able to stop taking medication. It usually takes only the first medication for approximately half of the newly diagnosed patients to become seizure-free.
Surgery
If medication does not help you in treating your epilepsy and controlling your seizures, then surgery may be an option for you. The goal of the surgery is to eliminate seizures by removing the area of the brain that is causing your seizures. Surgery is usually an option when you are diagnosed with focal seizures. Your doctor may also suggest surgery if tests show that your seizures do not originate from a brain area with vital functions. There are always risks involved with any surgery, even more so with brain surgery. After successful surgery, many patients are able to stop taking their medication or reduce their dosage.
Diet
If anti-seizure medication does not improve your epilepsy symptoms and you are not a candidate for surgery, then adjusting your diet may be a treatment option. A ketogenic diet, one that is low in carbohydrates and high in fats has been shown to reduce seizures (R). If being on the diet helps eliminate your seizures, then you can slowly transition off of the diet and monitor if your seizures return. The ketogenic diet can be very challenging and has many side effects, an alternative can be less radical diets such as the Atkins diet.
Other Therapies
There are other possible therapies to help you treat your epilepsy, apart from or alongside medication, surgery and diet. Neurostimulation has been an effective therapy option. Vagus nerve stimulation or deep brain stimulation are potential options. In these therapies, electrical nodes are implanted in your heart and connected to your neck or brain to send electrical pulses to your brain to reduce seizures. Neurostimulation is always used alongside medication.
Preventing Epilepsy or Seizures
It is estimated that approximately 25% of epilepsy cases can be prevented. The most effective way to prevent post-traumatic epilepsy is to avoid head injuries. Central nervous infections are a common cause for epilepsy and can be prevented by eliminating environmental parasites. It can be difficult to prevent epilepsy if you have a possible gene, but at least you may be able to avoid environmental factors that could possibly trigger.
Avoiding triggers can also help eliminate or reduce the frequency of seizures. You may notice that our seizures occur as a response to specific stimuli or situations. This is type of epilepsy known as reflex epilepsy. It is important to identify that a seizure occurs shortly after experiencing a certain trigger. The goal would then be to eliminate the possible trigger or reduce it to help lessen the effect it has on you.
Non-Epileptic Seizures
A non-epileptic seizure are short, frequent seizure events which are not the result of abnormal brain activity. Symptoms are similar to epileptic seizures such as shaking and even unconsciousness. Diagnosing non-epileptic seizures usually involves history alongside physical and EEG or diagnostic imaging. Many are misdiagnosed with epilepsy even though they may experience non-epileptic seizures.
Stigma Around Epilepsy
People around the world experience stigma daily around epilepsy. There are parts of the world that still believe that those with epilepsy are cursed as they see seizures as a sign of possession. Many still believe that seizures can be contagious. Those with epilepsy are still denied marriage in certain parts of the world today. It is very important to reduce and eliminate the stigma surrounding epilepsy and seizures so that those suffering can receive proper care and treatment. Increasing epilepsy awareness can eliminate people having to deny that they have suffered seizures.
CareClinic – An Epilepsy App
The CareClinic app can be a very useful tool in managing your epilepsy symptoms. You can effectively use the app as a seizure tracker to see how often they occur and their details.
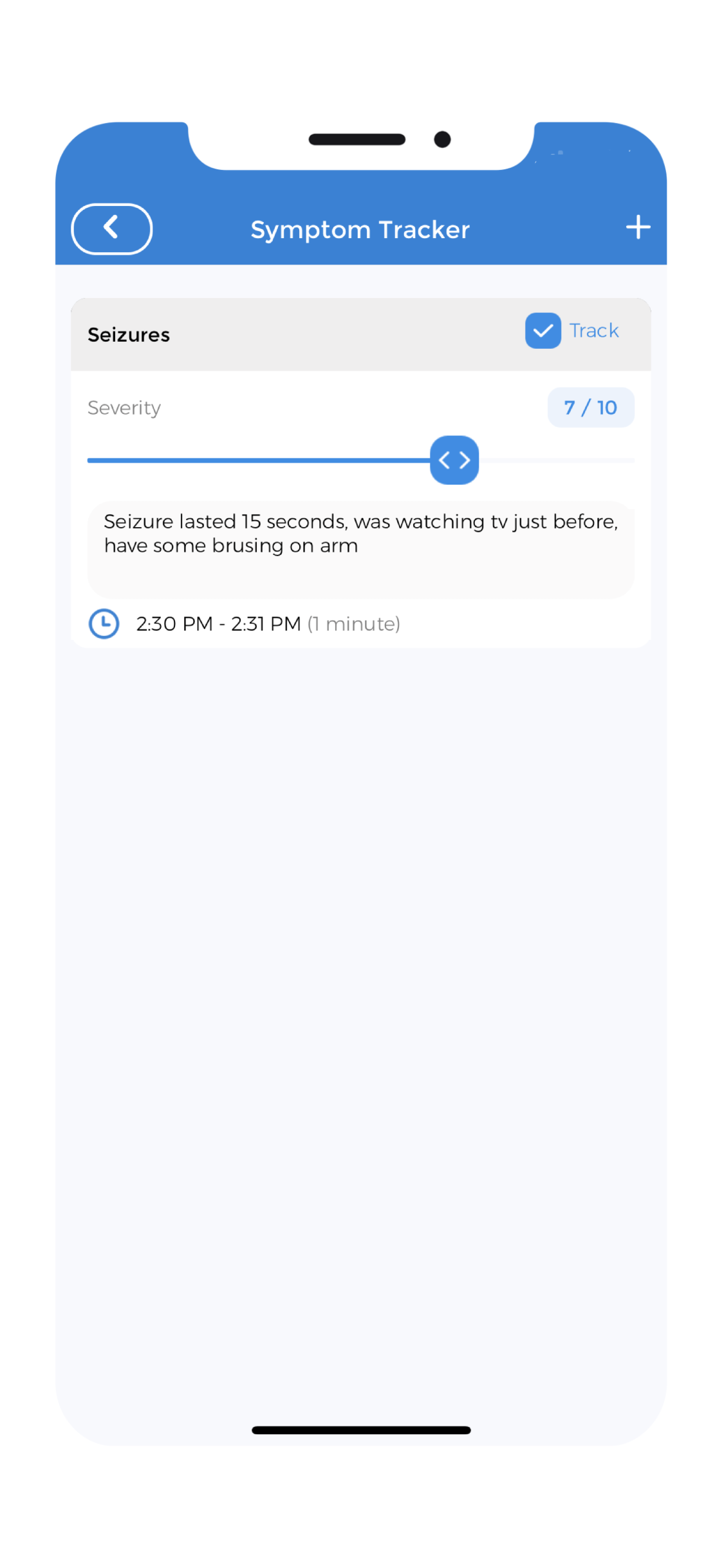 Tracking Seizures
Tracking Seizures
You can use the symptom tracker feature of the app to track your seizures. Make a record of the time and severity of your seizure. You can then share this with your doctor who can use the information to make an informed diagnosis. Observation plays a huge role in diagnosing the type of seizure. This can help you and your family understand how to respond to your seizures.
Not only can you keep track of the occurrence of your seizures, but you can also track any other symptoms you may also experience. Did you experience unconsciousness? Bit tongue or lips? Head injury? Broken or bruised limbs? Keeping track of all of your symptoms will help your doctor come to the right diagnosis.
Managing Treatments
The medicine & supplements feature of the app can help you keep track of any medications you have been prescribed to help manage your seizures. Simply log your medication in the app and you can even set reminders so that you are notified when you need to take it. The app will also let you know if there are any harmful interactions between your anti-seizure medication and any other prescriptions you may be taking. This will help eliminate any harmful side effects. You can even set a refill reminder in the app so that you and your doctor are notified when it is time to refill your prescription.
Keeping track of your medication will also give you an idea of what is working and what is not. Do your seizures get better or worse on a certain anti-seizure medication? Maybe it’s time to try something new? You will also be able to see any side effects you may be experiencing on a certain anti-seizure medication. You can view the reports generated in the app from your symptoms and medication details to get an understanding.
Tracking Nutrition
Take advantage of the app to track your diet. Your doctor may prescribe you to try a ketogenic diet to help manage your epilepsy. Create a ketogenic diet food list for epilepsy in the app to keep track of exactly what you are eating and when you are eating. Over time you will be able to see the correlations between your diet and your symptoms and that can help adjust your treatment. If your diet is not working, then you can make adjustments easily to try something different.
Identifying Triggers
The CareClinic app comes with a diary feature that you can use to make any supplemental notes to go with your symptoms or diet or medication. Or any thoughts that you may have regarding your epilepsy diagnosis. One possible use of the diary feature is to identify and note any potential seizure triggers. Making note of when a seizure occurs and writing down exactly what happened around that time can help you and your doctor identifies potential triggers. You can use any findings from the diary feature to help you make changes to your lifestyle to get better control of your seizures.
Track Your Appointments
The app also features an appointment tracker. You can record any doctor appointments or any testing you may have scheduled. You can set reminders to alert you when you have something coming up so that you never miss an appointment or an important test.
Your Care Team
One of the greatest benefits of the CareClinic app is the Care Team feature. This feature allows you to add family members, friends or any healthcare professionals. You can connect with your Care Team at any point and let them know how you are doing. They can provide you with the support that you need and help monitor your progress.
Increase Epilepsy Awareness
Epilepsy has no set cure, and most patients do manage to get their seizures under control with medication. It is important to reduce the stigma behind epilepsy by increasing epilepsy awareness so that patients can receive the necessary treatment. A seizure tracker like CareClinic can help you manage your seizure and take control of your life.


