
Migraines are a type of headache that can cause intense, debilitating pain. Some people also experience aura with migraines, which are visual or other neurological symptoms that occur before or during the headache. Migraines are thought to be caused by changes in the brainstem and its interactions with the trigeminal nerve, a major pain pathway. Migraines are more common in women than men and often run in families.
Vestibular migraine is a type of migraine that is associated with vestibular (inner ear) symptoms, such as dizziness and vertigo. This type of migraine is often underdiagnosed because the vestibular symptoms can mimic those of other conditions, such as Meniere’s disease or stroke.
Vestibular migraine occurs when the vestibular system, which controls balance and eye movements, is affected by changes in the brainstem and its interactions with the trigeminal nerve. These changes result in vestibular symptoms, such as dizziness, vertigo, and nausea. Vestibular migraine is often associated with other migraine symptoms, such as headache and aura.
Table of Contents
- What are common migraine symptoms?
- Migraine Diagnosis
- What are the common triggers of migraines?
- Atypical migraine symptoms
- Migraine Ear Pain
- Sudden Hearing Loss
- Do you also have Nasal Congestion?
- Other side effects
- Vestibular Disorder
- Managing Inner Ear Pain
- Other Ear diseases that can cause Migraines
- Migraine Management with the CareClinic App
- In Summary
What are common migraine symptoms?
The most common symptom of a migraine is a throbbing or pulsing pain that is often on one side of the head. The pain is usually moderate to severe and can be aggravated by physical activity. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, and vision changes. Some not-so-common symptoms also include vertigo, tingling or numbness in the extremities, and feelings of euphoria.
Migraine Diagnosis
There is no definitive test to diagnose migraines. A diagnosis is usually based on a review of symptoms and a person’s medical history. A physical exam and other tests may also be done to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
What are the common triggers of migraines?
There are many different potential triggers for migraines, and they vary from person to person. Some common triggers include: bright or flashing lights; loud noises; strong smells; weather changes; changes in sleep patterns; skipped meals; dehydration; hormonal changes; stress.
Atypical migraine symptoms
In addition to the typical symptoms of a migraine, some people may experience aura. Aura is a neurological symptom that can involve visual disturbances, such as seeing stars or flashing lights, or other changes, such as tingling in the extremities. Aura usually occurs before or during a headache and can last for several minutes up to an hour. You may also experience migraine-related ear symptoms, including: Ear pain; Ringing in the ears; Sensitivity to sound; Vertigo.
Migraine Ear Pain
If you have unexplained ear pain along with your migraine, it could be because of something called Frey’s syndrome. This occurs when the parasympathetic nervous system, which controls things like salivation and sweating, also affects the facial nerves near your ears. The result is pain in the ear that worsens with chewing or other movements of your jaw. If you think you might have Frey’s syndrome, see a doctor to get a diagnosis.
Migraine ear pain is a common symptom of migraines. Many people who suffer from migraines report having pain in their ears during a migraine attack. The pain can be sharp or throbbing, and it may come and go throughout the course of the attack. Migraine ear pain is often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
Migraine pain behind your ear can be caused by changes in the trigeminal nerve, a major pain pathway. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for transmitting signals from your head and neck to your brain. When this nerve is irritated, it can cause pain in any area that it innervates, including your ear. It happens when changes in the brainstem and its interactions with the trigeminal nerve result in vestibular symptoms.
If you have any type of ear pain along with your migraines, make sure to see a doctor to get a proper diagnosis. While most ear pain during a migraine is not serious, there are some rare conditions that can cause ear pain and migraines. If left untreated, these conditions can lead to serious complications.
Sudden Hearing Loss
Sudden hearing loss can also be a symptom of migraines. This is usually a temporary loss of hearing that occurs on the same side as the migraine pain. It typically goes away within 24 hours, but it can occasionally last for longer periods of time. The reason this occurs is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to changes in blood flow to the inner ear. Try to avoid loud noises and protect your ears if you experience sudden hearing loss during a migraine attack.
If you notice fluctuating hearing loss along with your migraine pain, it’s important to see a doctor. This could be a sign of Meniere’s disease, which is a disorder of the inner ear that can cause vertigo, tinnitus, and fluctuating hearing loss.
Do you also have Nasal Congestion?
Nasal congestion is another common symptom of migraines. This can be caused by changes in blood flow to the sinuses, which can lead to inflammation and swelling. If you have nasal congestion along with your migraine, try using a humidifier or taking a hot shower to ease the symptoms.
Other side effects
Runny nose: Histamine is released during a migraine attack, which can cause symptoms like a runny nose and watery eyes.
Facial flushing: Facial flushing is another common symptom of migraines. It’s caused by the dilation of blood vessels in the face, and it can make the skin on your face feel hot and flushed.
Vision changes: Some people experience changes in vision during a migraine attack, such as temporary blindness, tunnel vision, or seeing flashes of light. These symptoms are caused by changes in blood flow to the eyes.
Hives: Hives are a common side effect of migraines. They’re raised, red, itchy welts that can appear on the skin during or after a migraine attack. Hives are caused by histamine release, and they usually go away within 24 hours.
Anxiety: Many people who suffer from migraines also experience anxiety. This can be a side effect of the migraine itself, or it can be caused by the stress of dealing with chronic migraines.
Depression: Depression is another common side effect of migraines. If you’re struggling with depression, talk to your doctor about treatment options.
Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom of migraines, and it can be caused by the migraine itself or by the medications used to treat migraines. If you’re struggling with fatigue, talk to your doctor about treatment options.
Vestibular Disorder
Migraines can also cause a vestibular disorder, which is a problem with the inner ear that can lead to vertigo and dizziness. The vestibular system helps us keep our balance, and when it’s not working properly, we can feel off-balance and unsteady. A vestibular disorder can also cause nausea and vomiting. If you have these symptoms along with your migraines, see a doctor to get a diagnosis.
Managing Inner Ear Pain
If you experience ear pain during a migraine attack, there are a few things you can do to try to ease the pain:
- Take over-the-counter pain medication such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Place a warm compress on your ear.
- Try relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Get some rest in a quiet, dark room.
If you find that your ear pain is severe or persists for more than a few days, see a doctor to rule out other conditions.
Other Ear diseases that can cause Migraines
Migraines can also be caused by other ear diseases such as Meniere’s disease, vestibular migraines, and acoustic neuromas. If you have any of these conditions, talk to your doctor about treatment options. Acoustic Neuromas are non-cancerous tumors that grow on the nerve that connects the ear to the brain. These tumors can cause hearing loss, balance problems, and vertigo. If you have an acoustic neuroma, your doctor will likely recommend surgery to remove the tumor. Meniere’s disease is a disorder of the inner ear that can cause vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. There is no cure for Meniere’s disease, but there are treatments that can help relieve the symptoms.
Migraine Management with the CareClinic App
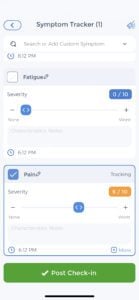
When tracking your migraines in a diary app, be sure to include information on the following:
- The date and time of the migraine
- The intensity of the pain (on a scale of 1-10)
- The location of the pain
- Any other symptoms you experience (nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light/sound/smells, etc.)
- What, if anything, seems to trigger the migraines
- What medications do you take for the migraine, and how effective are they
Keeping track of this information can help you and your doctor determine what might be triggering your migraines and the best way to treat them. You can use a faces pain scale to rate the intensity of your migraines, which can help track how well your treatments are working. If you find that certain foods or activities seem to trigger your migraines, be sure to avoid them as much as possible. If you’re unsure what might be triggering your migraines, keeping a food and migraine journal can help you narrow it down. Be sure to keep track of everything you eat and drink, as well as any other potential triggers, such as stress or lack of sleep.
If your migraines are severe or don’t respond well to over-the-counter medications, your doctor may prescribe preventive medication or stronger pain relief. They may also refer you to a migraine specialist for further evaluation and treatment.
The CareClinic app is available for both iPhone and Android devices. You can download the app for free from the App Store or Google Play by clicking here.
In Summary
Migraines are a type of headache that can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, nausea, and vision changes. They can also cause side effects such as anxiety and depression. Migraine ear pain is a common symptom, and it can be managed with over-the-counter pain medication and home remedies. If you’re looking for a way to manage your migraines, the CareClinic app can help. With this app, you can track your migraine attacks, symptoms, and triggers.
References
- “Vestibular Migraine | Johns Hopkins Medicine”. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/vestibular-migraine
- “Unusual Migraine Symptoms: Recognize Signs Beyond Headache”. https://jimstrophies.com/uncommon-signs-of-migraine-exploring-odd-symptoms.html
- “Migraine Diagnosis”. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Migraine-Diagnosis.aspx
- “Migraine – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic”. https://www.akamai.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/migraine-headache/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20360207
- “Neurology | Migraine Diagnosis | Corewell Health”. https://www.beaumont.org/conditions/migraines-diagnosis
- “The Most Common Migraine Triggers | Body & Mind | Allure”. https://www.allure.com/story/most-common-migraine-triggers
- “Understand Migraine Triggers to Identify Ways to Avoid”. https://migrawell.com/migraine-basics/migraine-triggers
- “Understanding Vestibular Migraines – ENT Health”. https://www.enthealth.org/be_ent_smart/understanding-vestibular-migraines/
- “Migraine-Associated Otalgia: An Underappreciated Entity – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8996084/
- “Frey Syndrome – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment | NORD”. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/frey-syndrome/


