Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a relatively common condition. For some people, they may have difficulty completing important tasks, even when given specific instructions or knowing the importance of that task. For others, they may get overwhelmed very easily by all the different things going on in their life. While it is something that we commonly hear about, whether in the media or social circles, it is a reality for millions of people around the world. This is a condition that can affect one’s school and professional life as well as personal relationships. Whether you are someone who may be struggling with this condition or just curious to learn more about it, this article will provide you with the information you need.
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects several brain functions. Most people are aware of the classic symptoms of hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention that characterize this disorder. These are common symptoms that we will explore more in this article. However, there are many other lesser known symptoms of ADHD that are just as important to know about.
Beyond just listing a bunch of ADHD symptoms, we also want to give you some practical coping tips. For example, we will talk about mindfulness and meditation, cognitive behavioral therapy, medication management, lifestyle changes, and time management techniques. We not only want to teach you about this condition but also provide you with some management techniques that you can implement into your daily life. Instead of seeing adult ADHD as a disability, we want you to be able to live a purposeful and meaningful life by learning how to thrive with it.[1][2]
ADHD: The Basics
What is ADHD
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate attention, behavior, and emotions. It is a complex disorder that can manifest in a variety of ways, but it is generally characterized by three main ADHD symptoms: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
ADHD is a common disorder, affecting an estimated 5-10% of children and 2.5% of adults worldwide. It can have significant impacts on daily life, including difficulties in academic, social, and occupational settings. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals withadult ADHD can thrive and lead fulfilling lives.
How ADHD Affects the Brain
ADHD affects the brain in various ways, including:
- Difficulty with executive functioning: This refers to the brain’s ability to plan, organize, and
 initiate tasks. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with completing tasks, even when they understand what needs to be done.
initiate tasks. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with completing tasks, even when they understand what needs to be done. - Sensory processing issues: This can refer to overstimulation or understimulation of the senses, leading to difficulties with focus and attention.
- Emotional dysregulation: Individuals with ADHD may struggle with regulating their emotions, leading to quick and intense emotional responses to situations.
- Rejection sensitivity: This refers to a heightened sensitivity to perceived rejection or criticism, leading to feelings of anxiety and low self-esteem.
- Time blindness: This refers to difficulties with perceiving and managing time, leading to issues with punctuality and meeting deadlines.
Inattentive, hyperactive-impulsive, and combined ADHD
ADHD symptoms can be categorized into three main subtypes: inattentive, hyperactive-impulsive, and combined. Inattentive ADHD is characterized by difficulty focus and paying attention, often leading to forgetfulness and disorganization. Hyperactive-impulsive ADHD is characterized by impulsivity and hyperactivity, leading to difficulties with sitting still and engaging in impulsive behaviors. Combined ADHD is a combination of both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
Each subtype of ADHD can manifest in different ways and can have its own unique challenges. For example, individuals with inattentive type ADHD may struggle with completing tasks and following through on commitments, while those with hyperactive-impulsive ADHD may struggle with controlling their impulses and engaging in risky behaviors around other children.
It is important to note that ADHD is a complex disorder and can manifest differently in each individual. A proper diagnosis and understanding of the individual’s symptoms are crucial for the effective treatment and management of ADHD.
Diagnosis of ADHD
Diagnosing adult ADHD can be a complex process that involves multiple steps. A healthcare provider will typically begin by conducting a comprehensive medical and psychological evaluation, which will include questions about the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and family history of ADHD. They may also conduct cognitive and behavioral assessments, such as IQ tests and attention tests, to assess the individual’s cognitive and executive functioning skills and attention abilities.
To be diagnosed with ADHD, an individual must meet specific diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which is published by the American Psychiatric Association. The DSM-5 outlines three main criteria for an ADHD diagnosis:
- The individual must exhibit a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with daily functioning in at least two different settings (e.g., home, school, work).
- The symptoms must have been present before the age of 12.
- The symptoms must be inconsistent with the individual’s developmental level and not solely attributable to another medical or psychiatric condition.
Diagnosing ADHD can be challenging, as many of the symptoms are also present in other conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder. Therefore, a proper diagnosis requires a thorough evaluation and assessment by a qualified healthcare professional.
ADHD in Children and Adults
While ADHD is often associated with children, it is important to note that even adults can be affected. In fact, many adults with ADHD may not have been diagnosed as children, leading to difficulties in their personal and professional lives.
Children with ADHD may struggle in academic and social settings, leading to difficulties with low self-esteem and social relationships. They may also engage in impulsive behaviors, such as interrupting others or acting without thinking.
Adult ADHD is a similar experience with similar difficulties, such as difficulties with organization and time management, but may also face additional challenges, such as maintaining employment and managing finances. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, both children and adults with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
It is important for individuals with ADHD and their loved ones to seek professional help if they suspect they may be experiencing symptoms of the disorder. A proper ADHD diagnosis and understanding of the individual’s symptoms can lead to effective treatment and management of ADHD.[3][4][5]
Lesser Known ADHD Symptoms
In this section, we will explore some of the lesser-known symptoms that ADHD presents, including emotional dysregulation, rejection sensitivity, lose track of time, sensory processing and working memory issues, and difficulty with executive functioning and impulse control. By providing examples and real-life scenarios, we hope to shed light on how these symptoms can affect individuals with ADHD. Additionally, we will provide practical tips and strategies for coping with these symptoms, emphasizing the importance of seeking professional help if they are significantly affecting daily life.
Common signs and symptoms of ADHD
First, let’s recap some of the very common and well known symptoms of ADHD. This way, you can get a better idea of obvious symptoms and the differences with the lesser known symptoms.
- Inattention: Difficulty with sustained attention and focus, often leading to forgetfulness and disorganization.
- Hyperactivity: Difficulty with sitting still and engaging in sedentary activities.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, often leading to impulsive behaviors and poor decision-making.
Lesser known symptoms of ADHD
- Emotional dysregulation, which can involve difficulty identifying, expressing, and managing emotions, as well as intense mood swings and a tendency to overreact to situations. This can
 impact relationships, work, and daily life.
impact relationships, work, and daily life. - Rejection and emotional sensitivity, which is a heightened sensitivity to rejection, criticism, and perceived slights from others. This can lead to social anxiety, avoidance, and difficulty forming relationships.
- Time blindness, which can involve difficulty with time management, planning, and organization. This can lead to missed deadlines, forgetfulness, and difficulties with punctuality as individuals lose track of time.
- Sensory processing issues, which can involve hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to sensory input, such as sounds, touch, or smells. This can lead to discomfort, anxiety, and avoidance behaviors.
- Executive function deficits, which can involve difficulties with tasks such as planning, prioritizing, initiating tasks, staying focused, and completing tasks. This can impact work, daily life, and academic performance due to being easily distracted, making careless mistakes, and having difficulty concentrating.
Misdiagnosed ADHD symptoms
While there are lesser known signs of ADHD symptoms, there are also common traits of other disorders that sometimes are mistaken as ADHD. It is important to differentiate between these and obtain the correct diagnosis.
Sleep Problems
While sleep disturbances such as difficulty sleeping are not officially recognized as a symptom by the DSM-5, sleep problems are often reported by individuals with ADHD. These sleep problems can include difficulty sleeping, staying asleep, and waking up in the morning.
However, sleep problems can also be a very common symptom of other conditions, including sleep disorders such as insomnia or sleep apnea. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to consider all possible causes of sleep problems and conduct a thorough evaluation and assessment before making a diagnosis of ADHD.
If you are experiencing sleep problems, it is important to seek professional help to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Effective treatment for sleep problems can improve overall mental health and quality of life.
Mood Swings
People with ADHD may experience mood swings, which can be a challenging symptom to manage. It is important to note that mood swings may not always be caused by ADHD. In fact, there are many possible underlying causes of mood swings, including hormonal changes, stress, and poor sleep.
One approach to managing mood swings in individuals with ADHD is to identify and address any underlying causes. This may involve working with a healthcare provider to rule out any medical conditions that may be contributing to the mood swings. Additionally, individuals with ADHD may benefit from a combination of medication and therapy to help manage their symptoms and improve their overall mental health.
It is also important to note that mood swings can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life, including their relationships, work, and overall quality of life. Therefore, it is important for individuals with ADHD to seek support from friends, family, and healthcare providers to help manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Real life examples
- Emotional dysregulation: Sarah, a college student with ADHD, often struggles with intense mood swings and a tendency to overreact to situations. To cope with these symptoms, she practices mindfulness and meditation, which help her to identify and manage her emotions more effectively. She also attends therapy sessions to work on building healthy coping mechanisms for dealing with stress and anxiety.
- Rejection sensitivity: John, a professional with ADHD, often experiences heightened sensitivity to perceived criticism or rejection from his colleagues. To cope with these symptoms, he works with a therapist to develop strategies for managing social anxiety and building stronger relationships with his coworkers. He also engages in regular exercise, which helps to reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
- Time blindness: Maria, a mother with ADHD, often struggles with managing her time effectively, leading to missed appointments and deadlines. To cope with this symptom, she uses a planner and sets reminders on her phone to help her stay organized and on track. She also makes sure to schedule regular breaks throughout the day to avoid becoming overwhelmed and stressed.
- Sensory processing issues: Mark, a student with ADHD, often experiences hypersensitivity to sensory input, such as sounds and touch. To cope with this symptom, he uses noise-cancelling headphones to block out distracting noises in class and takes frequent breaks to move around and release excess energy. He also works with a therapist to develop strategies for managing anxiety and avoiding sensory overload.
- Difficulty with executive functioning: Jane, a professional with ADHD, often struggles with completing tasks and staying organized. To cope with this symptom, she breaks down large projects into smaller, more manageable tasks and sets specific deadlines for each one. She also uses tools such as to-do lists and time-blocking to help her stay focused and on track.
Coping with ADHD symptoms
If left untreated, ADHD can be extremely disruptive to a person’s daily life. However, there are practical ways to cope with ADHD symptoms.
- The following are some effective approaches to treating mental health conditions:
- Mindfulness and meditation, which help in achieving mental clarity and inner peace. These practices can help manage stress and anxiety, reduce negative emotions, and increase self-awareness.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy, which is a type of talk therapy that focuses on changing negative
 patterns of thinking and behavior. This therapy can help individuals recognize and challenge distorted thoughts, and learn coping skills that can help them deal with difficult situations.
patterns of thinking and behavior. This therapy can help individuals recognize and challenge distorted thoughts, and learn coping skills that can help them deal with difficult situations. - Medication management, which involves working with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage to manage symptoms. This can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall mental health.
- Lifestyle changes, such as exercise and a healthy diet, which can improve physical health and have positive effects on mental health. Regular exercise can help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression, and a healthy diet can provide the necessary nutrients for optimal brain function.
- Time management techniques, which can help individuals prioritize tasks, manage stress, and increase productivity. Effective time management can lead to a more balanced and less stressful life.
It is crucial to seek professional help if these symptoms are affecting daily life significantly. Mental health professionals can provide the necessary support and guidance in managing symptoms and improving overall mental health.[6][7][8]
Using an App to Cope with ADHD Symptoms
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder can be difficult to deal with in one’s life, especially when it causes sleep disturbances, difficulty focusing, and racing thoughts. People with ADHD experience things differently from the general population.
However, the CareClinic can make things a lot easier. The app has a dedicated diary section that allows you to write down all the things that you need to complete. Furthermore, other things on the app include a medication section, where you can track all the medications you are taking and get daily reminders for them, and a symptoms section, where you can record all the symptoms you experience. Next time you visit the doctor, all this information will be handy in your pocket!
In conclusion, ADHD is a complex disorder that can manifest in a variety of ways. While many people are familiar with the classic symptoms of hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention, there are a host of other symptoms that can also have a significant impact on daily life. Emotional dysregulation, rejection sensitivity, time blindness, sensory processing, sleep issues, and difficulty with executive functioning can all affect individuals with ADHD. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals with ADHD can learn to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
It is important to seek professional help if you suspect you or a loved one may be experiencing symptoms of ADHD. A proper diagnosis and understanding of the individual’s symptoms can lead to effective treatment and management of ADHD. By working with healthcare professionals and implementing practical coping strategies, individuals with ADHD can thrive and achieve their goals.
Sources
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html
- MayoClinic (2023). Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/adult-adhd/symptoms-causes/syc-20350878
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd/index.shtml
References
- “Data and Statistics on ADHD | Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | CDC”. https://www.cdc.gov/adhd/data/index.html
- “More than 15 million US adults have ADHD, new study estimates”. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/more-than-15-million-us-adults-have-adhd-new-study-estimates-2024-10-10/
- “The global prevalence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: An umbrella review of meta-analyses – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37495084/
- “The prevalence of adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A global systematic review and meta-analysis – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33692893/
- “ADHD Statistics, Facts & Prevalence”. https://www.thetreetop.com/statistics/adhd-statistics-facts-prevalence
- “Lesser Known ADHD Symptoms Beyond the DSM-5 — Peaks & Valleys Behavioral Health”. https://www.peaksandvalleysbh.com/blog/lesser-known-adhd-symptoms-beyond-the-dsm-5
- “Spotting Lesser Known Symptoms of ADHD”. https://www.americanfrontlinenurses.org/post/spotting-lesser-known-symptoms-of-adhd
- “Unlocking the Hidden Struggles of ADHD: Beyond Fidgeting and Forgetfulness”. https://drtulikamindcare.com/en/blog/adhd/unmasking-overlooked-adhd-symptoms
- “Root to Rise Therapy | Los Angeles Marriage & Family Therapists-Lesser Known ADHD Symptoms”. https://rootrisetherapyla.com/blog/2024/lesser-known-adhd-symptoms
- “The ADHD Iceberg: 12 Overlooked Symptoms | Bozeman, MT — Bridger Peaks Counseling”. https://www.bozemancounseling.org/blog/2023/5/23/the-adhd-iceberg-12-overlooked-symptoms

 initiate tasks. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with completing tasks, even when they understand what needs to be done.
initiate tasks. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with completing tasks, even when they understand what needs to be done.
 impact relationships, work, and daily life.
impact relationships, work, and daily life.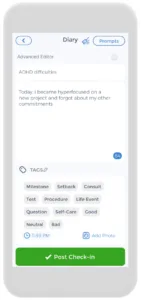 patterns of thinking and behavior. This therapy can help individuals recognize and challenge distorted thoughts, and learn coping skills that can help them deal with difficult situations.
patterns of thinking and behavior. This therapy can help individuals recognize and challenge distorted thoughts, and learn coping skills that can help them deal with difficult situations.