
Mathematics is a fundamental skill that is essential for success in many areas of daily life. However, for some individuals, learning and understanding numbers, calculations, and mathematical concepts and sequences can be a significant challenge. This learning difficulty is called dyscalculia.
In this article, we will explore the dyscalculia test in-depth and discuss the importance of early detection, diagnosis, and assessment. We will also delve into the components of the ultimate dyscalculia test and how to interpret the results. Additionally, we will explore various intervention strategies and educational accommodations that can support individuals with dyscalculia.[1][2][3][4]
Printable Dyscalculia Quiz
⬇️ Dyscalculia Self-Test PDF Printable
Printable Dyscalculia Self-Test with Mathematical Questions
⬇️ Dyscalculia Self-Test with Mathematical Questions PDF Printable[5]
Understanding Dyscalculia: A Brief Overview
Dyscalculia is a specific learning disability that affects an individual’s ability to understand and perform mathematical operations. It is characterized by difficulties with number recognition, number senses, writing, and mathematical reasoning and sequence.
Individuals with dyscalculia may struggle with basic arithmetic operations, such things as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. They may find it challenging to comprehend mathematical concepts and may have difficulty remembering mathematical facts due to synesthesia. Dyscalculia can affect people of all ages and is often present from early childhood.
The Prevalence of Dyscalculia
While the exact prevalence of dyscalculia is not well-established, research suggests that it affects a significant portion of the population. Studies have for instance, estimated that approximately 3-7% of individuals experience significant difficulties with mathematical learning.
It is important to note that dyscalculia is not a reflection of intelligence or effort. People with dyscalculia may have average or above-average intelligence in other areas. For example,but struggle specifically with mathematical concepts and operations.
Furthermore, dyscalculia can coexist with many other types of learning disabilities, such as dyslexia or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This means that individuals with dyscalculia may face additional challenges in their academic and everyday lives.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Dyscalculia
Dyscalculia can manifest in the brain in various ways, and its symptoms may vary from person to person. Common signs of dyscalculia include:
- Difficulty in determining number concepts and symbols
- Struggles with counting, sequencing, and place value
- Trouble with mathematical operations and problem-solving
- Poor sense of time and estimation
If you or someone in your family or friends that you know or feel like exhibits these symptoms, it is important to seek appropriate tests and support to address the learning difficulties and become aware of it.
It is worth mentioning that dyscalculia can have a significant impact on an individual’s self-esteem and confidence. The constant struggle with numbers and mathematical concepts can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and even avoidance of math-related tasks.
Therefore, early identification, diagnosis, and intervention are crucial in helping individuals with dyscalculia balance and overcome these challenges and develop strategies to succeed in their academic and personal lives.[6][7][8]
Dyscalculia can manifest in the brain in various ways, and its symptoms may vary from person to person. Common signs of dyscalculia include:
- Difficulty in determining number concepts and symbols
- Struggles with counting, sequencing, and place value
- Trouble with mathematical operations and problem-solving
- Poor sense of time and estimation
If you or someone in your family or friends that you know or feel like exhibits these symptoms, it is important to seek appropriate tests and support to address the learning difficulties and become aware of it.
It is worth mentioning that dyscalculia can have a significant impact on an individual’s self-esteem and confidence. The constant struggle with numbers and mathematical concepts can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and even avoidance of math-related tasks.
Therefore, early identification, diagnosis, and intervention are crucial in helping individuals with dyscalculia balance and overcome these challenges and develop strategies to succeed in their academic and personal lives.
The Impact of Dyscalculia on Learning
Dyscalculia can have a significant impact on an individual’s learning experience. Difficulties with mathematics can affect academic performance, hinder career prospects, and impact everyday tasks that involve numbers. Early detection and assessment are crucial to provide appropriate interventions and support to individuals with dyscalculia.
Individuals with dyscalculia may struggle with basic arithmetic operations, understanding mathematical concepts, and applying math skills in real-world situations. This can lead to frustration, anxiety, and a lack of confidence in their academic abilities. Without proper support and intervention, individuals with dyscalculia may face challenges in various aspects of their lives, including education, employment, and daily tasks that require numerical reasoning.
Why Early Detection Matters
Early detection of dyscalculia allows for timely intervention and support. With targeted intervention strategies, individuals with dyscalculia can develop strategies to overcome challenges and improve their mathematical abilities. Detecting and addressing dyscalculia in the early stages can help prevent long-term academic difficulties and boost self-confidence.
Educators and parents play a crucial role in recognizing the signs of dyscalculia, such as difficulty with number sense, poor memory for math facts, and struggles with sequencing objects and organizing numerical information. By identifying these indicators early on, appropriate interventions can be implemented to support the individual’s learning needs and promote mathematical success.
Components of the Ultimate Dyscalculia Test: Cognitive Assessment
The cognitive assessment component of the ultimate dyscalculia test evaluates various cognitive skills and processes that are relevant to mathematical learning. This may include assessments of working memory, attention, spatial reasoning, and executive functions. Understanding an individual’s cognitive strengths and weaknesses can help inform the development of appropriate intervention strategies.
Furthermore, cognitive assessment in the context of dyscalculia testing also delves into questions about the individual’s ability to understand, learn and apply mathematical concepts, problem-solving strategies, and mathematical language comprehension. By assessing these cognitive aspects, a professional doctor can gain a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s mathematical learning profile and tailor interventions accordingly.
Mathematical Skills Evaluation
The mathematical skills evaluation measures how well an individual understands and uses numbers. It focuses on areas such as number sense, basic arithmetic, numeracy, and general mathematical reasoning. This assessment identifies specific skill gaps that may be affecting performance in school or daily life.
In addition to core skills, the evaluation also checks how flexible the individual is in solving problems. It looks at how fluently they apply math concepts and how well they transfer these skills to real-world situations. These insights are key for creating personalized intervention plans that target the person’s unique learning needs.
Memory and Processing Speed Analysis
This part of the test looks at how well the brain handles and recalls math-related information. Memory and processing speed are crucial for learning math, especially when solving problems under time constraints.
The analysis focuses on working memory, which is used to hold and manipulate information during problem-solving. It also measures how quickly someone can retrieve facts and process numbers. Understanding these cognitive skills helps guide the development of strategies that support math learning more effectively.
Interpreting the Test Results
The dyscalculia test includes a scoring system that evaluates multiple areas of math ability. It identifies both strengths and weaknesses across different domains, such as number sense, arithmetic fluency, and spatial reasoning.
Each part of the test is designed to assess a specific type of mathematical thinking. When professionals review the scores, they can pinpoint where the individual struggles most. This leads to more focused and effective interventions.
What the Results Mean for the Individual
The final results allow for a custom support plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Educators, therapists, or caregivers can use this information to design strategies that build math confidence and improve performance over time.
Understanding personal strengths and weaknesses helps individuals feel more in control of their learning. It can increase motivation and encourage a more positive approach to math challenges, turning obstacles into opportunities for growth.
Intervention Strategies for Dyscalculia
Educational Accommodations and Modifications
Implementing educational accommodations and modifications can greatly support individuals with dyscalculia in the academic setting. These may include:
- Providing additional time for math assignments and assessments
- Using manipulatives and visual aids to enhance understanding
- Breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps
- Providing personalized instruction and one-on-one support
By implementing these accommodations, individuals with dyscalculia can access the curriculum and engage in meaningful mathematical learning.
Therapeutic Approaches to Dyscalculia
In addition to educational accommodations, therapeutic approaches can also play a significant role in supporting individuals with dyscalculia. These approaches are designed to address the underlying cognitive difficulties associated with dyscalculia and help individuals develop essential mathematical skills. Some therapeutic approaches include:
- Cognitive training exercises targeting mathematical abilities: These exercises focus on improving working memory, attention, and problem-solving skills, which are essential for mathematical reasoning.
- Working with a specialized tutor or learning support professional: A specialized tutor or learning support professional can provide individualized instruction and support tailored to the specific needs of individuals with dyscalculia.
- Multi-sensory interventions that engage different modalities of learning: These interventions involve using various senses, such as touch, sight, and hearing, to enhance understanding and retention of mathematical concepts.
Therapeutic approaches can help develop essential foundational skills, improve mathematical reasoning, and build confidence in mathematical abilities.
Importance of Taking Dyscalculia Quiz
 Furthermore, we feel it is important to note that dyscalculia is a complex learning disability that can vary in its presentation and impact on individuals. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment is crucial for accurately identifying and understanding the specific strengths and challenges of each individual with dyscalculia. This quiz may involve evaluating cognitive skills, mathematical abilities, and memory functioning.
Furthermore, we feel it is important to note that dyscalculia is a complex learning disability that can vary in its presentation and impact on individuals. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment is crucial for accurately identifying and understanding the specific strengths and challenges of each individual with dyscalculia. This quiz may involve evaluating cognitive skills, mathematical abilities, and memory functioning.
Once the assessment results are interpreted, personalized intervention and support plans can be developed. These plans may include a combination of educational accommodations and therapeutic approaches, tailored to meet the unique needs of each individual. The goal is to empower individuals with dyscalculia to overcome challenges and reach their full potential in mathematical learning.
Dyscalculia is a specific learning disability that affects the ability to understand and perform mathematical operations. Early detection and tests are essential for providing appropriate interventions and support.
By implementing educational accommodations and therapeutic approaches, individuals with dyscalculia can access the curriculum, develop essential mathematical skills, and build confidence in their abilities. With the right support, individuals with dyscalculia can overcome challenges and thrive academically.
The Difference Between Synesthesia and Dyscalculia
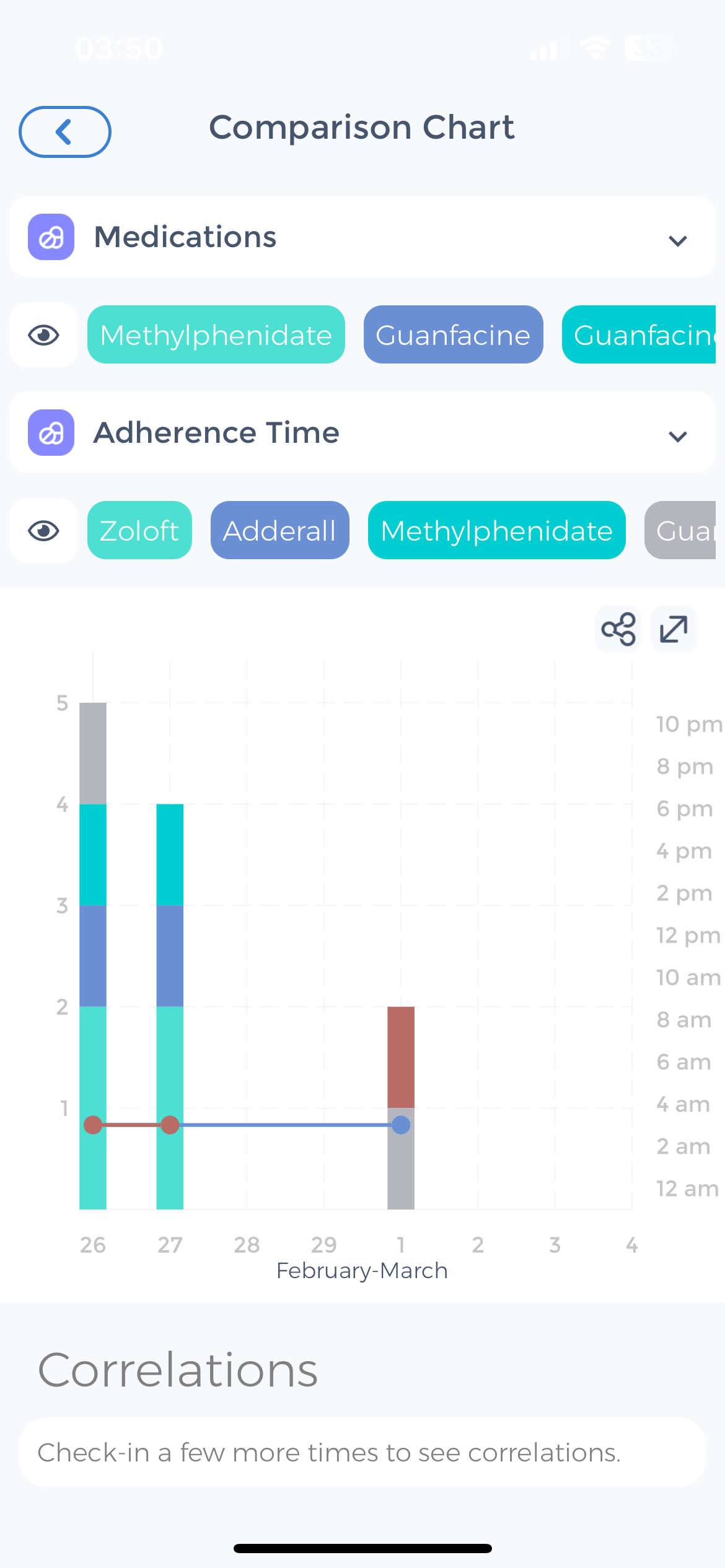 Dyscalculia and synesthesia are two different neurological conditions, although they can sometimes coexist in individuals.
Dyscalculia and synesthesia are two different neurological conditions, although they can sometimes coexist in individuals.
Dyscalculia is a specific learning disability that affects a person’s ability to understand and work with numbers. Individuals with dyscalculia may have difficulty understanding mathematical concepts, performing arithmetic operations, and grasping numerical relationships. It can impact various aspects of daily life, from managing finances to telling time.
On the other hand, synesthesia is a perceptual phenomenon where stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway. For example, someone with synesthesia might picture things and see colors when they hear music or associate specific colors with letters or numbers. It’s essentially a blending or mixing of sensory experiences that are typically separate in most people. If you ever wonder, it is advisable to take a synesthesia test or even for non-synesthetes.
While dyscalculia affects mathematical abilities, synesthesia involves the way the brain perceives and processes sensory information. While they can coexist in some individuals, they are distinct conditions with different characteristics and impacts.
Use the CareClinic App to Monitor Symptoms
Discover a new way to manage dyscalculia with the CareClinic App, a comprehensive tool designed to track and support your journey towards improved mathematical abilities. By utilizing the app’s features, you can monitor progress, set reminders for practice sessions, and record successful strategies that aid in overcoming dyscalculia’s challenges.
The CareClinic App provides a structured platform to keep track of cognitive exercises, therapeutic sessions, and daily course of accomplishments, making it easier to see your growth over time and adjust your approach as needed.
Download the CareClinic App Today
With the CareClinic App, you can expect a personalized experience that aligns with the educational and therapeutic approaches discussed in this article. The app’s diary and reporting features allow for detailed documentation of your learning patterns, which is crucial for identifying the most effective interventions.
By consistently using the CareClinic App, you can gain insights into your learning process and work towards achieving better health outcomes. Take the first step in transforming your approach to dyscalculia by choosing to Install App today.
References
- “Effective Dyscalculia Accommodations in Education – Magrid”. https://magrid.education/effective-dyscalculia-accommodations-in-education/
- “Dyscalculia Accommodations for Effective Learning – Acibadem Health Point International”. https://www.acibademhealthpoint.com/dyscalculia-accommodations-for-effective-learning/
- “Classroom accommodations for dyscalculia”. https://www.understood.org/en/articles/classroom-accommodations-for-dyscalculia
- “School Accommodations”. https://www.dyscalculia.org/dyscalculia/school-accommodations
- “The Dyscalculia Information Centre – Dyscalculia Centre introduces free, preliminary test for dyscalculia”. https://www.dyscalculia.me.uk/
- “The Diagnosis and Treatment of Dyscalculia – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6440373/
- “Math disabilities hold many students back. Schools often don’t screen for them”. https://apnews.com/article/1365774aecc6c04fd40ece9e5082a2b2
- “Developmental dyscalculia – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15559892/
- “How does dyscalculia affect learning? – California Learning Resource Network”. https://www.clrn.org/how-does-dyscalculia-affect-learning/
- “Early Detection And Intervention For Dyscalculia – Klarity Health Library”. https://my.klarity.health/early-detection-and-intervention-for-dyscalculia/




