
Anxiety is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it is well-known for causing emotional distress and mental turmoil, many may not be aware of its physical manifestations. One such physical symptom that can accompany anxiety is an increase in body temperature. Answer the question, “Can anxiety raise body temperature?”
In this article, we will explore the relationship between anxiety and body temperature, the science behind this phenomenon, and effective strategies for managing anxiety to regulate body temperature.[1]
Understanding Anxiety and Its Effects
Anxiety, in essence, is a natural response to stress. It is a normal part of life and can even be beneficial in certain situations, as it helps us prepare for and cope with challenging circumstances like post traumatic stress and fever like symptoms. However, when anxiety becomes excessive or chronic, it can have profound effects on our physical and mental well-being.
It’s important to note that anxiety is a complex and multifaceted emotion that can vary in intensity and duration from person to person. While some individuals may experience mild, transient anxiety in response to specific stressors, others may struggle with severe and persistent anxiety that significantly impairs their daily functioning.
Defining Anxiety: A Closer Look
Anxiety can be defined as a state of apprehension, fear, or uneasiness. It often manifests as excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and muscle tension are also common with anxiety. When anxiety triggers the body’s fight-or-flight response, adrenaline floods the system and can intensify both psychological and physical symptoms. The surge of adrenaline not only elevates heart rate and breathing but can also contribute to temperature fluctuations and sweating. For individuals experiencing these overwhelming physiological responses, understanding how to reduce adrenaline anxiety becomes essential for managing both the immediate symptoms and long-term anxiety patterns.
Moreover, anxiety can manifest in different forms, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. Each of these forms of anxiety presents unique symptoms and challenges, requiring tailored approaches to treatment and management.
How Anxiety Attack Affects the Body
Prolonged exposure to stress hormones due to chronic anxiety can contribute to a range of physical health issues, including cardiovascular problems, gastrointestinal disturbances, weakened immune function, and even increased susceptibility to chronic diseases.
Additionally, the impact of anxiety on mental health should not be overlooked, as it can exacerbate conditions such as depression, insomnia, and substance abuse disorders.
The Connection Between Anxiety and Body Temperature
Research suggests that there is a close relationship between anxiety and body temperature, particularly in relation to the body’s stress response.
Understanding the intricate connection between anxiety and body temperature can shed light on how our bodies react to stress and emotional turmoil. The relationship between these two factors is not only fascinating but also crucial in comprehending the complex interplay of our physiological and psychological states.
The Stress Response and Body Temperature
When we experience anxiety, the chronic stress triggers physiological changes in the body, one of which is an increase in body temperature. This rise in temperature is a result of heightened metabolism and increased blood circulation, as the body prepares for action.
Moreover, the body’s temperature regulation is controlled by the hypothalamus, a vital region in the brain responsible for maintaining homeostasis. During times of stress and anxiety, the hypothalamus plays a key role in orchestrating the body’s response, including the regulation of body temperature to cope with the perceived threat.
Anxiety and Hyperthermia: Is There a Link?
 Hyperthermia, or an abnormal increase in body temperature, can occur as a result of severe anxiety. While it is relatively rare, individuals with certain psychological stress, such as panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder, may experience episodes of anxiety-induced hyperthermia. It is important to note that these episodes are distinct from fever and are not caused by infections or other medical conditions.
Hyperthermia, or an abnormal increase in body temperature, can occur as a result of severe anxiety. While it is relatively rare, individuals with certain psychological stress, such as panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder, may experience episodes of anxiety-induced hyperthermia. It is important to note that these episodes are distinct from fever and are not caused by infections or other medical conditions.
Furthermore, the phenomenon of anxiety-induced hyperthermia underscores the intricate connection between the mind and body. The manifestation of physical symptoms in response to psychological distress highlights the profound impact that our mental state can have on our physiological well-being. By delving into the mechanisms underlying anxiety-related changes in body temperature, researchers aim to unravel the complexities of the human stress response and its implications for overall health.[2][3]
The Science Behind Anxiety-Induced Body Temperatures Changes
The interplay between the nervous system and hormonal changes helps explain the complex relationship between anxiety and core body temperature.
Understanding how anxiety affects body temperature involves delving into the intricate mechanisms of the human body’s stress response. When faced with anxiety-inducing situations, the body undergoes a series of physiological changes that are orchestrated by the nervous system and hormonal fluctuations.
The Role of the Central Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system, a component of the peripheral nervous system responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, plays a pivotal role in the body’s response to stress induced hyperthermia. In the context of anxiety, the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system takes center stage. This branch, often referred to as the “fight or flight” system, becomes activated in response to perceived threats, triggering a cascade of events that includes the elevated body temperature.
Moreover, the sympathetic nervous system’s activation prompts the release of neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine, which can further contribute to the increase in body temperature. This intricate interplay between the nervous system and thermoregulation sheds light on how anxiety can manifest physically through temperature changes.
Hormonal Changes and Elevated Body Temperature
 Stress hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol, are key players in the body’s response to stress and anxiety. These hormones not only impact the functioning of the nervous system but also exert influence over body temperature regulation. Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is responsible for stimulating thermogenesis, the process by which the body generates heat. Additionally, cortisol, often termed the “stress hormone,” can induce vasoconstriction, the narrowing of blood vessels, which in turn can contribute to an increase in body temperature.
Stress hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol, are key players in the body’s response to stress and anxiety. These hormones not only impact the functioning of the nervous system but also exert influence over body temperature regulation. Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is responsible for stimulating thermogenesis, the process by which the body generates heat. Additionally, cortisol, often termed the “stress hormone,” can induce vasoconstriction, the narrowing of blood vessels, which in turn can contribute to an increase in body temperature.
By understanding the intricate relationship between stress hormones and thermoregulation, we gain insight into how anxiety-induced temperature changes are not merely psychological manifestations but also involve a complex interplay of physiological processes. The dynamic interactions between the nervous system and hormonal pathways underscore the multifaceted nature of anxiety and its effects on the human body’s temperature regulation.[4][5]
Symptoms of Anxiety-Induced Temperature Changes: Psychogenic Fever
Recognizing the signs of anxiety-related hyperthermia is crucial for understanding and managing this phenomenon.
Anxiety-induced temperature changes can manifest in various ways, with hyperthermia being a common occurrence. When experiencing anxiety-related hyperthermia, individuals may notice symptoms such as flushed or red skin, excessive sweating, and feeling hot to the touch. It is important to differentiate these symptoms from those caused by fever, as fever typically involves other signs of illness, such as body aches or a sore throat.
Recognizing the Signs of Anxiety-Related Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia caused by anxiety may present with symptoms such as flushed or red skin, excessive sweating, and feeling hot to the touch. It is important to differentiate these symptoms from those caused by fever, as fever usually involves other signs of illness, such as body aches or sore throat.
Moreover, anxiety can trigger a cascade of physical and emotional responses beyond temperature changes. Individuals may also experience rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, nausea, trembling, feelings of dread, and a sense of impending doom. These additional symptoms can further exacerbate the overall feeling of unease and discomfort associated with anxiety.
Physical and Emotional Symptoms to Watch For
In addition to changes in body temperature, anxiety can also present with a myriad of physical and emotional symptoms. These may include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, nausea, trembling, feelings of dread, and a sense of impending doom.[6]
Managing Anxiety to Regulate Body Temperature
While anxiety-induced changes in body temperature can be distressing, there are various effective strategies for managing anxiety and promoting overall well-being.
One technique for anxiety reduction is engaging in relaxation techniques. Deep breathing exercises, for example, can help calm the nervous system and reduce anxiety. By taking slow, deep breaths and focusing on the sensation of the breath entering and leaving the body, individuals can activate the body’s relaxation response, leading to a decrease in anxiety levels.
Another relaxation technique that can be beneficial is progressive muscle relaxation. This involves tensing and then releasing different muscle groups in the body, one at a time. By consciously tensing and relaxing the muscles, individuals can release physical tension and promote a sense of relaxation and calmness.
Mindfulness meditation is yet another effective technique for managing anxiety. By bringing attention to the present moment and observing thoughts and sensations without judgment, individuals can cultivate a sense of inner peace and reduce anxiety levels. This practice can be particularly helpful for those who tend to ruminate or worry excessively during emotional events.
Regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and getting adequate sleep are also essential for managing anxiety effectively. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters, and helps reduce stress and anxiety, as well as physical conditions. A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, can support overall brain health and contribute to a stable mood. Additionally, getting enough sleep is crucial for regulating emotions and reducing anxiety levels.
Medical Interventions for Anxiety and Hyperthermia
 In some cases, individuals with severe anxiety or anxiety-induced hyperthermia may benefit from medical interventions. Psychological therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be highly effective in helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. Through CBT, individuals can learn coping skills and strategies to manage anxiety symptoms.
In some cases, individuals with severe anxiety or anxiety-induced hyperthermia may benefit from medical interventions. Psychological therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be highly effective in helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. Through CBT, individuals can learn coping skills and strategies to manage anxiety symptoms.
Medications can also be prescribed to help manage anxiety. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly used to treat anxiety disorders. These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood, in the brain. Benzodiazepines, another class of medications, can provide short-term relief from anxiety symptoms by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for anxiety and hyperthermia. They can assess the individual’s specific needs and develop a personalized treatment plan that may include a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications.
Anxiety can indeed raise body temperature, particularly through the activation of the body’s stress response and blood flow. Understanding the science behind anxiety-induced temperature changes and recognizing the associated symptoms are crucial for effective management. By utilizing relaxation techniques, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate medical interventions when necessary, individuals can take control of their anxiety and regulate their lower body temperature. Remember, self-care is essential for overall well-being, and by prioritizing your mental health, you can achieve a calmer, more balanced state of being.[7][8]
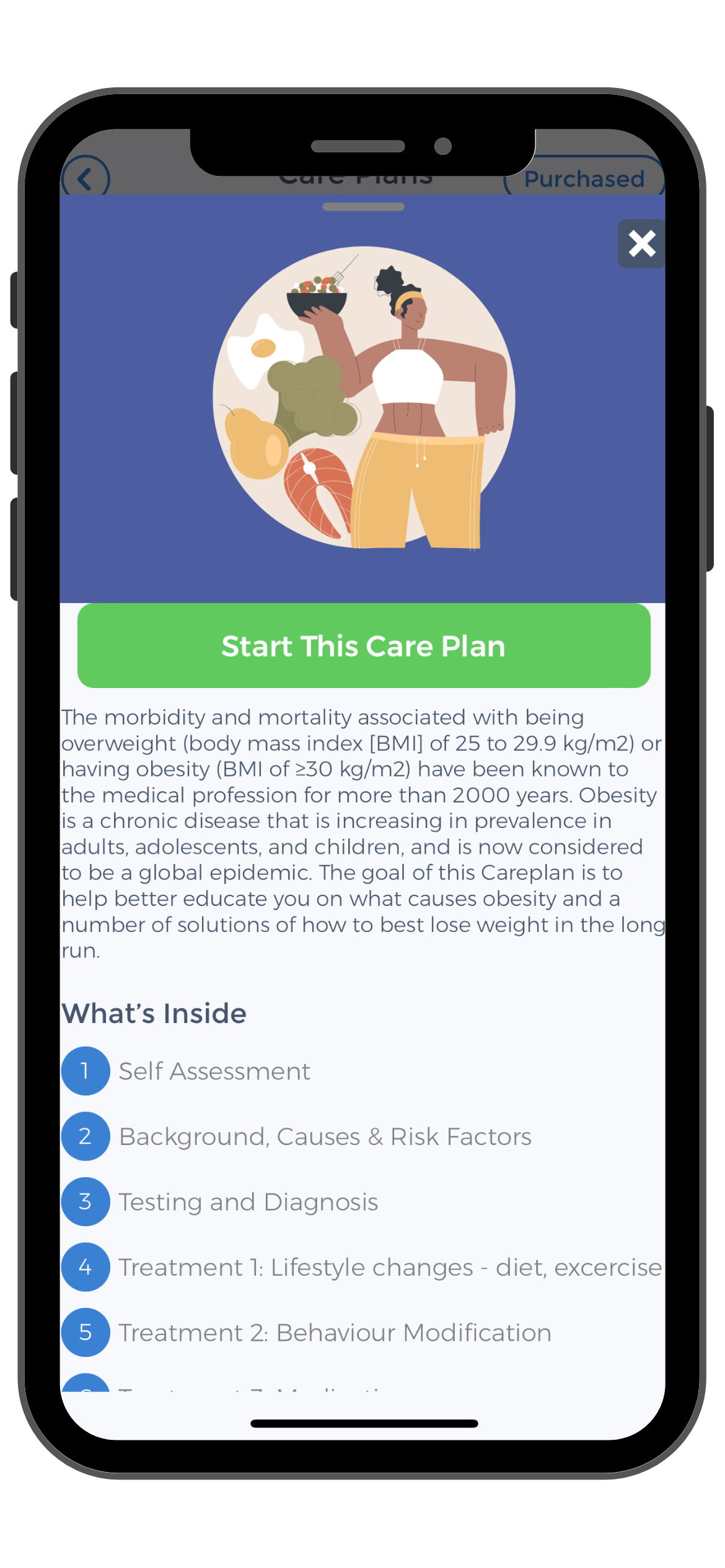
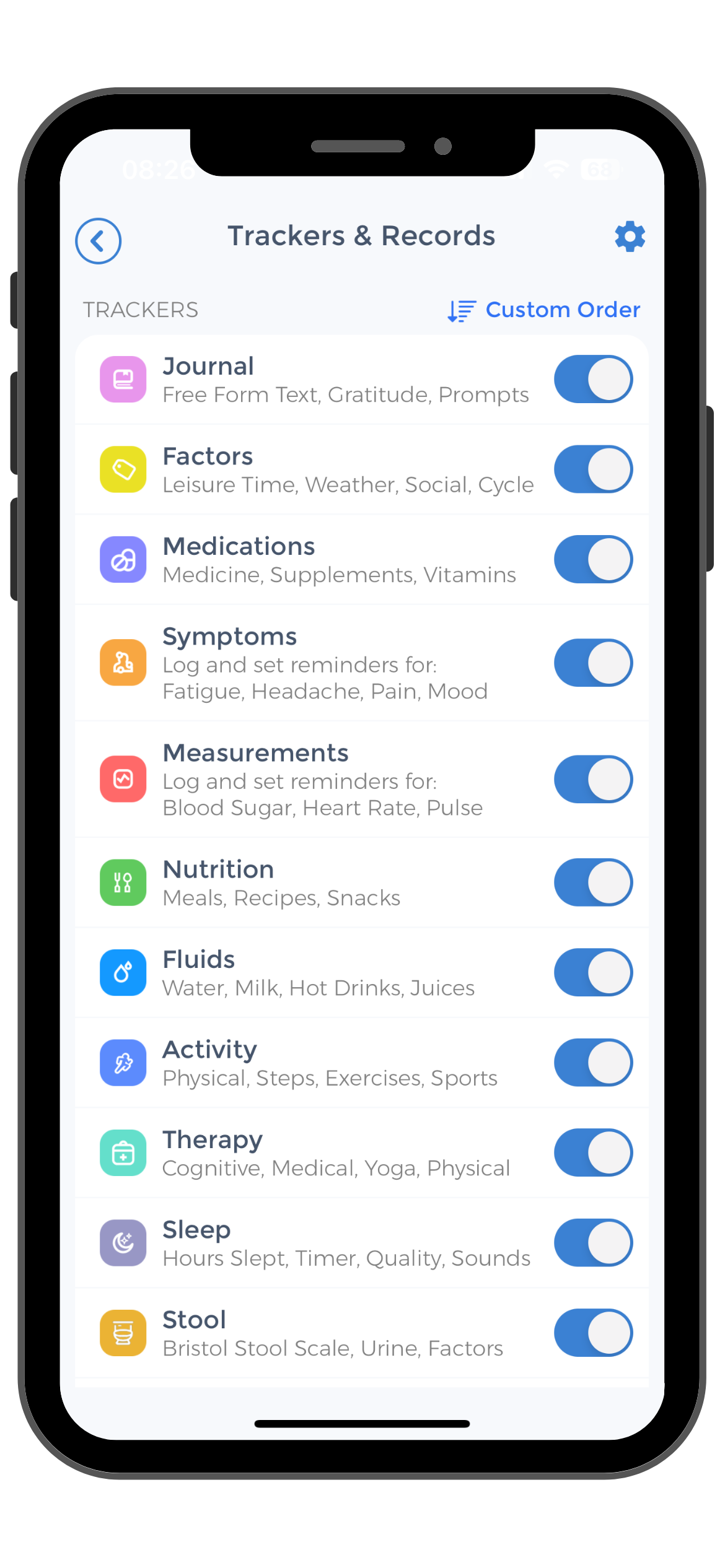
Use the CareClinic App to Manage Anxiety Symptoms and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Take control of your anxiety, body heat and body temperature regulation with the CareClinic App. Our comprehensive health app allows you to track symptoms, including fluctuations in body temperature, blood pressure and monitor the effectiveness of your anxiety management strategies.
By logging your daily experiences, you can identify patterns and triggers, helping you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your treatment plan. The CareClinic App is designed to be a personal health assistant, providing you with the insights necessary to manage anxiety attacks and maintain optimal well-being.
Download the CareClinic App to Track Elevated Body Temperature Caused by Chronic Stress
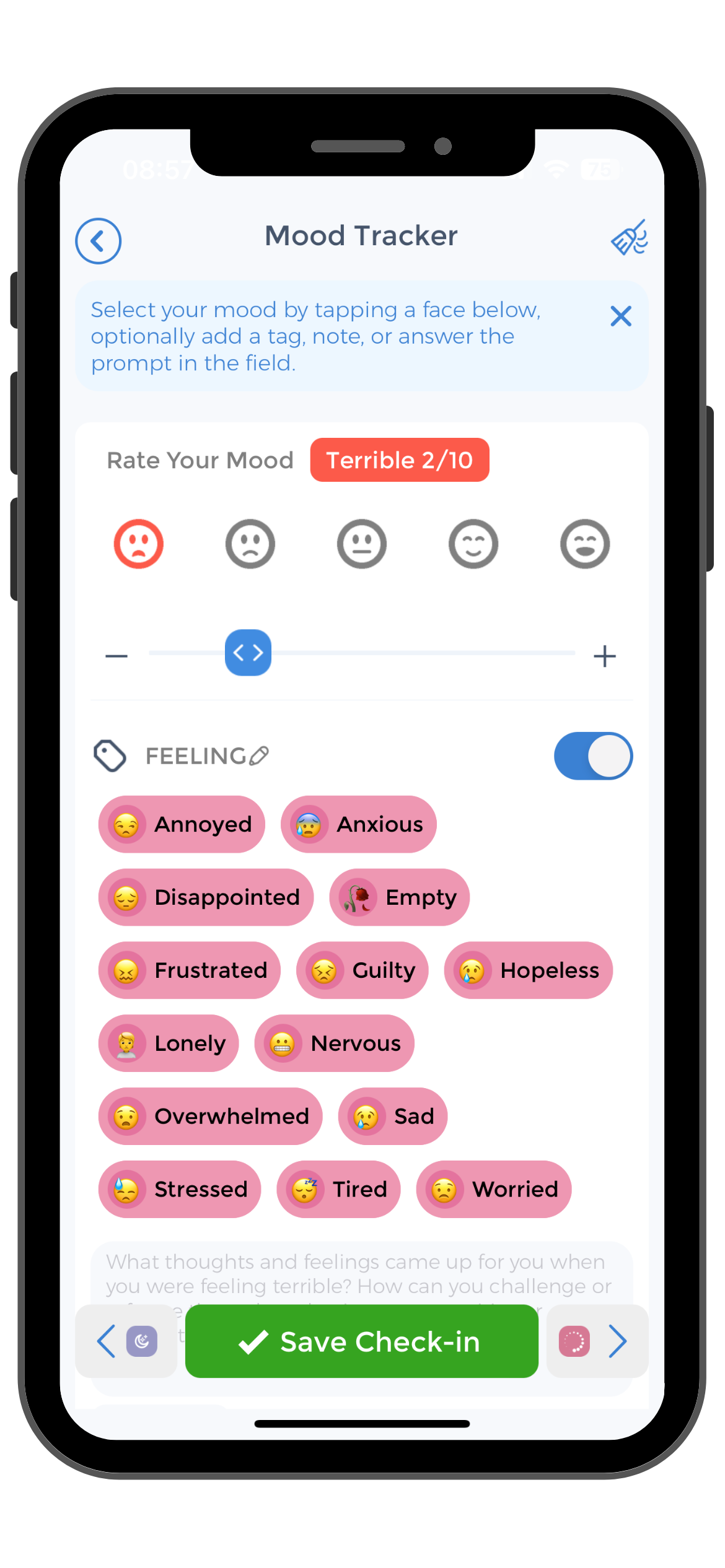
With the CareClinic App, you can also set medication reminders, ensuring you stay consistent with any prescribed treatments for anxiety. The app’s mood tracking feature enables you to record your emotional fever and state, offering valuable data to correlate with physical symptoms like hyperthermia.
By using the CareClinic App, you’re not just tracking your health; you’re actively participating in your journey to improved health outcomes. Install App today and experience the benefits of having a comprehensive health management tool at your fingertips.[9]
References
- “Psychogenic fever: how psychological stress affects body temperature in the clinical population – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4843908/
- “Neural circuit for psychological stress-induced hyperthermia – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4843917/
- “Psychogenic fever: how psychological stress affects body temperature in the clinical population – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27227051/
- “Neural circuit for psychological stress-induced hyperthermia”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27227049/
- “[Central Circuit Mechanism for Psychological Stress-Induced Hyperthermia]”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26450073/
- “Recognizing and easing the physical symptoms of anxiety – Harvard Health”. https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/recognizing-and-easing-the-physical-symptoms-of-anxiety
- “Relaxation Techniques for Anxiety | Psychology Today”. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/all-about-cognitive-and-behavior-therapy/202401/relaxation-techniques-for-anxiety
- “Simple Moves Can Lead to a Less Stressed-Out You”. https://time.com/4649899/simple-moves-can-lead-to-a-less-stressed-out-you/
- “Tracker, Reminder – CareClinic on the App Store”. https://apps.apple.com/us/app/tracker-reminder-careclinic/id1455648231


