Do you or someone you know live with Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)? If so, you know that it can be a challenge. However, you’re not alone. AS is a chronic inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the lower back, but can also impact other parts of the body like the hips, knees, and shoulders. It can be a difficult condition to manage, but with early diagnosis and proper treatment, individuals can lead a fulfilling life.
In this article, we’ll explore the basics of AS, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. We’ll also dive into the topic of AS flare-ups, which can be a frustrating and painful aspect of living with this condition. By understanding the triggers, treatment options, and prevention strategies for flare-ups, individuals with AS can take a proactive approach to managing their condition, relieve pain, and improving their overall quality of life.
We understand that living with AS can be daunting, but having the right knowledge can be super useful. By reading on, you’ll gain a better understanding of this condition, which can help you or your loved one manage it more effectively. We’ve compiled the latest information on AS, including its prevalence, causes, symptoms, and diagnosis, to give you a comprehensive overview. We’ll also discuss various treatment options and management strategies, so you can take control of your health and improve your quality of life.
So, whether you’re newly diagnosed or a long-time sufferer, we hope this article will provide valuable insights and tools to help you manage your AS and other symptoms. Let’s dive in and explore the world of Ankylosing Spondylitis together.[1][2]
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS): Understanding the Basics
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a condition that typically affects the joints and spine, causing pain, stiffness, and discomfort. It’s a chronic inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the lower back, but can also affect other parts of the body like the hips, knees, and shoulders. AS can be a challenging condition to manage, but with early diagnosis and proper treatment, individuals can lead a fulfilling life.
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a relatively rare condition, affecting approximately 0.1% to 0.5% of the population. It is more commonly diagnosed in men than women, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 3:1. AS can affect individuals of any age, but it typically develops in the late teens or early 20s. The prevalence of AS also varies by ethnicity, with higher rates reported in individuals of Scandinavian, Caucasian, and Middle Eastern descent.
What Causes Ankylosing Spondylitis
The exact cause of AS is not fully understood, but it is thought that a combination of genetics and environmental factors may play a role in its development.
Genetics
Studies have shown that individuals with the HLA-B27 gene are more likely to develop Ankylosing Spondylitis than those without the gene. This gene helps the immune system recognize and fight off infections. However, in some cases, the immune system may mistakenly attack healthy tissues in the body, leading to inflammation and damage. It’s important to note that not everyone with the gene will develop AS, which suggests that other genetic or environmental factors may also contribute to its development.
Environmental factors
Certain infections or exposure to bacteria may trigger the onset of AS in individuals who are genetically susceptible. For example, infections caused by bacteria such as Klebsiella pneumoniae and Chlamydia trachomatis have been associated with increased risk of AS. These bacteria share a similar structure to the HLA-B27 molecule, which may lead to an autoimmune response in susceptible individuals. In addition, smoking has also been shown to increase the risk of developing AS and worsen symptoms in those who already have the condition.
Symptoms of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis symptoms can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain and stiffness in the lower back that is worse in the morning (morning stiffness) or after
 periods of inactivity
periods of inactivity - Pain and stiff joints in the hips, shoulders, and knees. Sometimes, there is also neck pain and stiffness in the rib cage
- Fatigue
- Loss of flexibility in the spine
- Difficulty breathing if the ribs are affected
- Eye inflammation, known as uveitis, which can cause redness, pain, and sensitivity to light
- Muscle spasms
It’s important to note that symptoms can come and go, and individuals with AS may experience periods of remission where other symptoms improve. However, flare-ups, where symptoms worsen, can also occur. Furthermore, while we listed the physical symptoms, emotional symptoms can also occur.
Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
There is no single test to diagnose AS, and diagnosis is typically based on a combination of factors including symptoms, physical examination, imaging tests, and blood tests.
Physical examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will look for signs other symptoms of inflammation and stiffness in the spine, ribs, and other joints. They may also check for tenderness and pain in certain areas, such as the lower back and hips.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans, can help to detect changes in the joints and spine. These tests can show inflammation and damage, such as bone spurs and fusion of the spine.
Blood tests
Blood tests can help to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as rheumatoid arthritis. In addition, blood tests can detect markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). These tests are not specific to AS, but can be used to monitor disease activity and response to treatment.
It’s important to note that while there is no cure for AS, early diagnosis and proper treatment can help to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The treatment of AS focuses on the major symptoms: relieving pain, reducing inflammation, reducing![]() stress, and preventing complications. Treatment options for chronic pain may include the following:
stress, and preventing complications. Treatment options for chronic pain may include the following:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and pain medication to reduce pain and inflammation
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), such as sulfasalazine and methotrexate, to slow down the progression of the disease
- Biologic drugs, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, to target specific proteins involved in the inflammatory process
- Physical therapy and exercise to improve flexibility and range of motion as well as hot and cold therapy
- Surgery, in rare cases, to correct spinal deformities or joint damage
Treatment plans may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment. If you are seeking treatment for your AS, make sure you speak with your doctor about the options and best one for you.
Management of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Managing AS involves taking a comprehensive approach to address the physical, mental health, and emotional aspects of the condition. This may include:
- Regular physical activity, such as stretching and gentle exercise, to maintain flexibility and reduce pain. This can also prevent muscle spasms
- Good posture and ergonomics to minimize strain on the back and joints
- Stress management techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, to reduce stress and improve overall well-being
- A healthy diet to maintain a healthy weight and support overall health
- Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends to cope with the emotional impact of the conditions
Ankylosing Spondylitis Flare Ups: When Bad Get Worse
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) can be a challenging condition to manage as it causes pain, stiffness, and discomfort in the joints and spine. While early diagnosis and proper treatment can help to manage symptoms and prevent complications, individuals with AS may still experience pain or a disease flare where symptoms worsen. In this section, we will explore the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of AS flare-ups, so that individuals with AS can better manage this aspect of their condition to ease pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Why do Ankylosing Spondylitis Flare Ups Occur?
Flare-ups are a common occurrence in individuals with Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS). These disease flare episodes are characterized by a worsening of symptoms, such as pain and stiffness, and can be triggered by a variety of factors. While the exact cause of flare-ups is not fully understood, research suggests that inflammation may play a key role.
Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to injury or infection. When the body is exposed to a harmful substance, such as a virus or bacteria, the immune system sends out white blood cells to attack the invader. This process leads to the production of inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines, which help to destroy the pathogen. In normal circumstances, inflammation is a temporary response that resolves once the threat has been eliminated.
In individuals with AS, however, inflammation can become chronic and flare symptoms are ongoing. This can lead to damage in the joints and spine, as well as other parts of the body. Flare-ups may occur when the inflammatory response becomes heightened, which can happen for a few weeks for a variety of reasons.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Flare Up Triggers
Flare-ups of Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) can have a variety of possible triggers, including:
- Infection: Certain bacterial infections, such as Klebsiella pneumoniae and Chlamydia trachomatis, have been associated with the onset of AS and flare-ups.
- Stress: Emotional stress and physical stress on the body can trigger inflammation and worsen symptoms.
- Poor sleep: Lack of sleep or poor-quality sleep can disrupt the body’s immune system and exacerbate inflammation.
- Injury: Physical trauma or injury to the joints and spine can trigger a flare-up.
- Smoking: Smoking has been shown to increase the risk of developing AS and worsen symptoms in those who already have the condition.
It’s important for individuals with AS to identify their personal triggers and work with their healthcare providers to develop strategies for preventing and managing flare-ups.
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Flares
The treatment of flare-ups can be complex and may require a combination of medications and therapies. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids can be used to reduce inflammation and manage pain, but there are also other options available.
For example, physical therapy can help to restore strength and flexibility in the affected joint, which can promote healing and reduce the risk of future flare-ups. Rest is also important during flare-ups, as it allows the body to recover and reduces the risk of exacerbating symptoms. In addition, stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga can be used to manage the emotional and psychological effects of flare-ups, which can be significant. Alternative therapies include hot and cold therapy or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Therefore, a comprehensive treatment plan that incorporates a combination of medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes may be the most effective way to manage flare-ups in the long-term.
How to Prevent Ankylosing Spondylitis Flare Ups
 Preventing flare-ups is an essential part of managing this condition. One way to prevent flares is by identifying and avoiding triggers. For example, stress, poor sleep, and infection are all common triggers that can lead to flare-ups. However, not everyone will have the same triggers, or flare symptoms, which is why it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to identify your specific triggers and manage flares. Getting enough sleep to avoid fatigue can help you to begin gradually decrease how often you feel discomfort.
Preventing flare-ups is an essential part of managing this condition. One way to prevent flares is by identifying and avoiding triggers. For example, stress, poor sleep, and infection are all common triggers that can lead to flare-ups. However, not everyone will have the same triggers, or flare symptoms, which is why it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to identify your specific triggers and manage flares. Getting enough sleep to avoid fatigue can help you to begin gradually decrease how often you feel discomfort.
In addition to trigger identification, maintaining good posture and following a regular exercise routine can also help to prevent flares. Regular exercise can help to reduce inflammation and joint pain, improve joint mobility, and increase strength, which can all contribute to better management of this condition. Furthermore, good posture can help to reduce strain on your joints, which can also help to prevent flare-ups.
Overall, preventing flare-ups is a crucial aspect of managing this condition. By working with your healthcare provider to identify triggers and implementing lifestyle changes, such as exercise and good posture, you can improve your overall quality of life and reduce the risk of flare-ups.
Complications of Ankylosing Spondylitis Flare Ups
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) flares can lead to various complications, which can impact a person’s quality of life. These complications can arise due to the inflammation and damage caused by the condition. Some common complications of Ankylosing Spondylitis flare-ups include:
- Spinal deformities: Chronic inflammation of the spine can lead to the formation of new bone tissue, which can cause the spine to fuse in a fixed position. This can lead to a loss of mobility and flexibility in the spine, as well as a forward curvature of the spine (known as kyphosis).
- Reduced lung function: Inflammation of the rib cage and chest wall can cause the chest to become stiff, which can make it difficult to breathe deeply. This can lead to reduced lung function over time.
- Eye problems: Inflammation can also affect the eyes, causing a condition known as uveitis. Uveitis can cause redness, pain, and sensitivity to light, and can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated.
- Cardiovascular disease: Chronic inflammation can also increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack and stroke. This is because inflammation can cause damage to the blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaque in the arteries).
To further reduce symptoms and prevent these complications, it’s important to work closely with physical therapist and your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses emotional symptoms and your specific needs. This may include a combination of medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes, such as exercise, stress management techniques, and good posture. By taking a proactive approach to managing your AS and preventing flare-ups, you can improve your overall quality of life and reduce the risk of complications.[5]
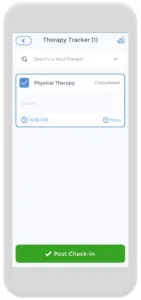
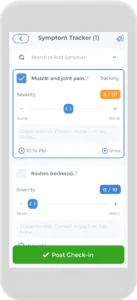
Using an App to Track Flare Ups
Having an AS flare up plan is crucial, and the CareClinic app can help with that. You can use the app as your AS diary. Just go to the diary section of the app and enter your daily symptoms, medications, and triggers as they occur. There are also specific sections on the app to track each of these. Next time you visit the doctor, this information will be handy in your pocket. The app can also keep track of all the data you input and create visual or textual summaries. This way, you can always keep track of your health in whichever way you prefer.
The app also has a medication section where you can precisely track the doses you are taking and receive reminders on when to take each medication. We know how difficult but important keeping track of your medications is, so we hope to make it as easy and streamlined as possible.
Final Thought on Ankylosing Spondylitis Flares
Living with Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) can be a challenging and painful experience, but with the right knowledge and management strategies, individuals can take control of their condition and improve their overall quality of life. In this article, we explored the basics of AS, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. We also discussed the topic of AS flare-ups, which can be a frustrating and painful aspect of living with this condition. By understanding the triggers, treatment options, and prevention strategies for flare-ups, individuals with AS can take a proactive approach to managing their condition and improving their overall quality of life. It’s important to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses your specific needs. By taking a proactive approach to both managing symptoms of your AS and preventing flare-ups, you can improve your overall quality of life and reduce the risk of complications.
Sources
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ankylosing-spondylitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354808
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16595-ankylosing-spondylitis-as
- https://www.hopkinsarthritis.org/arthritis-info/ankylosing-spondylitis/
References
- “Ankylosing Spondylitis Causes & Treatment | NIAMS”. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/ankylosing-spondylitis
- “Ankylosing spondylitis – Mayo Clinic Press”. https://mcpress.mayoclinic.org/living-well/ankylosing-spondylitis/
- “Ankylosing Spondylitis – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470173/
- “Genetics, environment, and gene-environment interactions in the development of systemic rheumatic diseases – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4250576/
- “Ankylosing Spondylitis | Johns Hopkins Medicine”. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/ankylosing-spondylitis


 periods of inactivity
periods of inactivity