ADHD Organization Tools: Useful Ways to Cope with ADHD
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. For some people, they may struggle with organizations, whether it be in their personal or professional lives. For others, time management might be the key problem. ADHD can manifest in different ways for different people, and negatively affect their lives in a variety of forms. However, one thing that is common is that it can lead to stress, anxiety, and difficulties in daily relationships. Even with people without ADHD, keeping track of all the things in our busy lives is quite difficult. In today’s world, there is just always too much going on. In individuals that suffer from ADHD, this difficulty is just exacerbated and can be understandably extremely frustrating.
Fortunately, there are many organization tools available that can help individuals with ADHD to manage their symptoms and stay on top of their responsibilities. In this article, we will start with an introduction to ADHD, including what it is, how it presents itself, and how it is managed. Then, we will explore some of the most effective organization tools for individuals with ADHD, from sticky notes and calendars to digital tools and color coding. Whether you’re looking for a simple and tangible solution or to make use of the new technology around us, there’s an organization tool out there that can help you stay focused and organized. So, whether you personally have ADHD, you have a child that has ADHD, or want to help a friend with ADHD. read on for some useful information and practical solutions![1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
ADHD: The Basics
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can significantly impact daily functioning.
Epidemiological Statistics
ADHD affects around 6-9% of children and 4% of adults in the United States and is more commonly diagnosed in males than females. The prevalence of ADHD has been increasing in recent years, although this may be due in part to better awareness and diagnosis of the condition.
How Does ADHD Affect the Brain?
ADHD is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors that affect the development and function of certain areas of the brain. Research has shown that individuals with ADHD often have differences in the structure and function of the prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum.
The prefrontal cortex is the part of the brain responsible for executive functions, among other tasks such as planning, decision-making, and working memory. In individuals with ADHD, this region of the brain may be smaller and less active than in those without the condition. This can make it more difficult for individuals with ADHD to regulate their attention and behavior during important tasks.
The basal ganglia are a group of structures in the brain that are involved in the regulation of movement and reward processing. In individuals with ADHD, the basal ganglia may be less active than in those without the condition, which can lead to difficulties with motor control, and impulsivity.
The cerebellum is the part of the brain responsible for coordinating movement and balance. Research has shown that individuals with ADHD may have differences in the size and activity of the cerebellum, which can contribute to difficulties with motor control and coordination.
In addition to these structural differences, ADHD is also thought to be related to differences in the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play a key role in regulating attention and behavior, and are targeted by many of the medications used to treat ADHD.
What Are the Common Symptoms of ADHD?
The symptoms of ADHD can vary from person to person, but they typically fall into two categories: inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
Inattention symptoms:
- Difficulty staying focused on tasks or activities.

- Forgetfulness, particularly with regard to routine tasks such as paying bills or bank statements.
- Difficulty staying organized and managing time and tasks compared to organized people.
- Procrastination and difficulty starting or completing tasks.
- Difficulty following through on instructions or completing one task.
- Trouble with sustained mental effort and focus, such as reading a book or listening to a lecture.
- Frequently losing or misplacing things, such as office supplies or a phone.
- Easily distracted by external stimuli or one’s own thoughts.
- Often appearing forgetful or absent-minded, including time blindness.
Hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms:
- Restlessness and fidgeting, such as tapping one’s fingers or feet.
- Talking excessively or interrupting others.
- Difficulty waiting for one’s turn or remaining seated.
- Acting impulsively without considering consequences, such as blurting out answers or making impulsive purchases.
- Taking unnecessary risks or engaging in dangerous activities, such as reckless driving or substance abuse.
- Difficulty engaging in quiet activities, such as reading or working on a computer.
- Frequently feeling the need to be in motion or to do something.
Some individuals with ADHD may experience both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms, while others may experience primarily one type of symptom. The severity of symptoms can also vary, and may depend on factors such as age, gender, and co-occurring conditions.
Symptoms of ADHD can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life, including their academic and occupational performance, relationships, and overall well-being.
It is important to note that some symptoms of ADHD may also be present in individuals without the condition, and that a diagnosis of ADHD should be made by a licensed clinical psychologist using standardized diagnostic criteria.
How Is ADHD Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ADHD is a complex process that typically involves a combination of assessments, including interviews, questionnaires, cognitive tests, and physical exams. While there is no single test that can diagnose ADHD, healthcare professionals rely on a variety of tools to gather information about an individual’s symptoms, behavior, and medical history to make an accurate diagnosis.
If you suspect that you have ADHD, consider speaking to your healthcare professional. An early diagnosis of ADHD can help with management and treatment options.
How Is ADHD Managed?
Medications
 There are several medications that can be used to help people with ADHD, including stimulants and non-stimulants. Stimulants such as methylphenidate and amphetamines are the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD. These medications can help to improve attention, reduce impulsivity, and control hyperactivity. Non-stimulant medications such as atomoxetine and guanfacine can also be effective for treating ADHD, particularly in individuals who cannot tolerate stimulant medications. It’s important to note that medication is not a cure for ADHD, but rather a tool that can help to manage symptoms.
There are several medications that can be used to help people with ADHD, including stimulants and non-stimulants. Stimulants such as methylphenidate and amphetamines are the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD. These medications can help to improve attention, reduce impulsivity, and control hyperactivity. Non-stimulant medications such as atomoxetine and guanfacine can also be effective for treating ADHD, particularly in individuals who cannot tolerate stimulant medications. It’s important to note that medication is not a cure for ADHD, but rather a tool that can help to manage symptoms.
Stimulants can be addictive for some individuals, especially if they are prone to addiction, so they should be used with caution. It is important to work with a healthcare provider and discuss the potential pros and cons of starting stimulant medication, as well as assessing one’s risk. The thought of addiction could also make an individual uncomfortable for a variety of reasons, so that is something to take into account.
Behavioral therapy
Behavioral therapy can be an effective complement to medication for managing ADHD. Therapy can help individuals with ADHD to learn coping strategies and improve their executive functioning skills, such as planning, organization, and time management. Some examples of behavioral therapy for ADHD include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), social skills training, and parent training. Behavioral therapy can be especially helpful for children with ADHD, as it can teach them skills that they can use throughout their lifetime.
Lifestyle changes
In addition to medication and therapy, lifestyle changes can also help people with ADHD. Regular exercise can help to reduce symptoms of ADHD, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being. A healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can also be helpful. Avoiding foods that are high in sugar, artificial flavors, and preservatives may also help to reduce symptoms. Good sleep habits, such as getting enough sleep each night and maintaining a regular sleep schedule, can also be important for managing ADHD symptoms.
Like with a lot of medical conditions, lifestyle is often an overlooked factor. However, by changing one’s daily habits, a large improvement can be seen over time.
Other treatments
In addition to medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes, there are several other treatments that may be helpful for managing ADHD. For example, neurofeedback is a type of therapy that uses computer-based exercises to help individuals with ADHD learn how to regulate their brainwaves. Mindfulness meditation and yoga may also be helpful for reducing stress and improving attention.
It’s important to note that managing ADHD is often a long-term process that requires ongoing support and monitoring. Working with a healthcare provider who specializes in ADHD can be helpful for developing a comprehensive treatment plan that is tailored to an individual’s specific needs and goals. With a focus on the right combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes, individuals with ADHD can lead productive and fulfilling lives.[8][9][10][11][12]
ADHD Organizational tools: Managing ADHD Smartly
Effective organization is essential for individuals with ADHD to manage their symptoms and stay on top of daily tasks. Organization tools can help to create structure and provide an important reminder to stay on track, reducing stress and anxiety. At some point, relying on yourself is just too overwhelming to deal with all te things going on in your life. This is even true for people that do not suffer from ADHD. Luckily, especially in today’s world, there is an abundance of tools that can help people keep organized. Here are some organizational tools that can be particularly helpful for individuals with ADHD.
Sticky Notes
Sticky notes are a simple and effective way to capture reminders and tasks quickly. They can be placed in visible locations, such as on a desk or computer monitor, to serve as a visual reminder. Sticky notes can be used to capture important tasks, phone numbers, and other important information that needs to be remembered. They can also be used to create a to-do list, with each particular task written on a separate note. Sticky notes come in a variety of colors and sizes, which can be useful for color-coding and organizing tasks.
Calendars
Calendars are a classic organizational and time management tool that can be used to keep track of appointments, meetings, and due dates. Both paper calendars and electronic calendars can be effective, depending on individual preference. Electronic calendars, such as Google Calendar or Apple Calendar, can be accessed from a computer or mobile device and can be set to send reminders for appointments and tasks. Paper calendars can be placed in a visible location, such as on a refrigerator or desk, to serve as a visual reminder.
Digital Tools
There are a variety of digital tools available that can be helpful for individuals with ADHD. For example, Trello is a project management tool that allows users to create boards, lists, and cards to track tasks and projects. RescueTime is a time management and tracking tool that can help individuals to monitor their computer use and identify areas where time is being wasted. They can help individuals to stay on track and manage their time more effectively.
Create To Do Lists
To do lists can be an effective way to break down tasks into manageable steps and keeping track of things to ensure that nothing is forgotten. To do lists can be created using a variety of tools, including sticky notes, paper, and digital tools. One popular digital tool is Todoist, which allows users to create and prioritize tasks, set deadlines, and receive reminders.
Paper Planner and Task Planner
Paper planners and task planners can be helpful for individuals with ADHD who prefer a physical, tangible tool to help them stay organized. Planners can be customized to include daily, weekly, and monthly views, as well as space for notes and to-do lists. Some popular paper planner options include the Passion Planner and the Panda Planner. Task planners, such as the Pomodoro Technique, can be used to break tasks into manageable chunks of time and can help individuals with ADHD to focus and avoid distractions.
Reminder Apps
Reminder apps can be helpful for individuals with ADHD who struggle with forgetfulness. These apps can be used to set reminders for appointments, tasks, and other important events. Popular reminder apps include Apple Reminders, Google Keep, and Todoist.
Color Coding
Color coding can be an effective way to visually organize tasks and information. For example, different colors can be assigned to different types of tasks or to different family members. Color coding can be used in conjunction with other organizational tools, such as sticky notes and calendars, to create a visual system for managing tasks and deadlines in professional life.
How Organization Tools Can Help Individuals with ADHD
By using organization tools such as sticky notes, calendars, to do lists, and reminder apps, individuals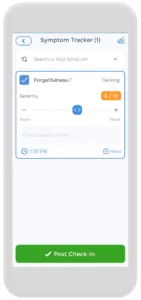 with ADHD can better manage their symptoms and reduce stress and anxiety. These tools can help individuals with establishing goals to stay on track and manage their time more effectively, breaking down tasks into manageable steps and ensuring that nothing is forgotten. By incorporating organization tools into their daily routine, individuals with ADHD can create structure and establish routines that can improve their productivity and not feel overwhelmed. For example, using a paper calendar or planner to schedule daily tasks and appointments can provide a clear visual overview of the day ahead, while a reminder app can ensure that important deadlines and events are not forgotten. Overall, by using a combination of organizational tools that work for them, individuals with ADHD can better manage their symptoms and lead a more structured, organized life.[13][14][15][16]
with ADHD can better manage their symptoms and reduce stress and anxiety. These tools can help individuals with establishing goals to stay on track and manage their time more effectively, breaking down tasks into manageable steps and ensuring that nothing is forgotten. By incorporating organization tools into their daily routine, individuals with ADHD can create structure and establish routines that can improve their productivity and not feel overwhelmed. For example, using a paper calendar or planner to schedule daily tasks and appointments can provide a clear visual overview of the day ahead, while a reminder app can ensure that important deadlines and events are not forgotten. Overall, by using a combination of organizational tools that work for them, individuals with ADHD can better manage their symptoms and lead a more structured, organized life.[13][14][15][16]
Using a Health App as Part of Your Organizational Tool
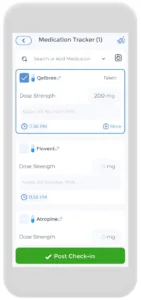
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder can be challenging to live with, especially when it causes you to be distracted easily, lose track of time, or undergo chronic disorganization. As we have already established, there is an obvious benefit to using great tools to help people with ADHD. One app that can help is the CareClinic app. When used with other apps, it can make the lives of adults with ADHD much easier.
The app has a diary part where you can jot down all of the tasks you need to do. Other features of the app include a medicine section, where you can monitor all of your pills and receive daily reminders, and a symptoms part, where you can record all of your symptoms. All of this information will come in helpful the next time you see the doctor!
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing ADHD symptoms can be a daily challenge for many individuals. However, by using good habits and incorporating organizational tools into their daily routine, individuals with ADHD can take control of their lives and reduce the stress and anxiety that often comes with the disorder. Sticky notes, calendars, digital tools, to-do lists, paper planners, reminder apps, and color coding are just a few examples of the many organization tools available to help individuals with ADHD stay on track and manage their symptoms effectively. By finding the right combination of tools that work for them, individuals with ADHD can increase their productivity and achieve their goals with greater ease. Remember, the journey towards managing ADHD symptoms is unique to each individual, but with the right tools, and strategies, success is within reach.
Sources
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html
- Klarity (2023). ADHD Tools For Organization & Time Management https://www.klarityadhd.com/post/adhd-tools/
- MayoClinic (2023). Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/adult-adhd/symptoms-causes/syc-20350878
- National Institute of Mental Health. (2021). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd/index.shtml
References
- “10 Simple ADHD Organization Tools to Make Life Easier – A Beautifully Fit Soul”. https://abeautifullyfitsoul.com/2023/01/21/adhd-organization-tools/
- “Top 6 ADHD Organization Tools | Reclaim”. https://reclaim.ai/blog/top-6-adhd-organization-tools
- “The Best ADHD Organization Tools: Apps, Planners, Lists, & More”. https://www.psychiatryraleigh.com/post/the-best-adhd-organization-tools-apps-planners-lists-more
- “Best 8 ADHD organization tools for Adults to boost productivity – Saner.AI”. https://saner.ai/adhd-organization-tools-for-adults/
- “Time Management Strategies for People with ADHD | New York, NY | Festivals.com”. https://www.festivals.com/time-management-strategies-for-people-with-adhd-90031
- “Time Management Tips for Adults with ADHD for Work and Home”. https://www.additudemag.com/time-management-for-adhd-adults/
- “Time Management: A Guide for Adults with ADHD | Adult ADHD Centre”. https://adultadhdcentre.com/article/time-management-a-guide-for-adults-with-adhd/
- “Data and Statistics on ADHD | Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) | CDC”. https://www.cdc.gov/adhd/data/
- “Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) – National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)”. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-adhd
- “More than 15 million US adults have ADHD, new study estimates”. https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/more-than-15-million-us-adults-have-adhd-new-study-estimates-2024-10-10/
- “Rise in diagnoses is prompting more US adults to ask: 'Do I have ADHD?'”. https://apnews.com/article/d6834e1c644e17f1e702603dfaae9448
- “What's Driving the Demand for ADHD Drugs Like Adderall”. https://time.com/6271049/adhd-diagnoses-rising/
- “How to Plan Ahead When You Have ADHD: Understand Time”. https://www.additudemag.com/how-to-plan-ahead-when-you-have-adhd-understand-time/
- “5 Essential Time Management Techniques for ADHD Adults”. https://www.ourmental.health/adhd/5-essential-time-management-techniques-for-adhd-adults
- “ADHD Time Management Strategies for Adults | Time Timer”. https://www.timetimer.com/blogs/news/are-you-an-adult-living-with-adhd-time-management-strategies-can-make-all-the-difference
- “25 Strategies for Time Management for those with ADHD – Ellen's Blog, Professional Organizing for Kingwood & Houston”. https://professional-organizer.com/WordPress/25-strategies-for-time-management-for-those-with-adhd/
- “28 Effective Coping Skills for ADHD — Talkspace”. https://www.talkspace.com/mental-health/conditions/articles/coping-skills-for-adhd/