Blood Pressure Tracker
Take control of your cardiovascular health by tracking blood pressure readings, medications, and lifestyle factors in one secure place.
High blood pressure affects nearly 50% of American adults, yet many are unaware they have this silent condition. Without consistent monitoring, it is difficult to identify patterns, triggers, or whether treatment is working. CareClinic’s blood pressure tracker helps you log readings, correlate with medications and lifestyle, and share detailed reports with your healthcare provider.
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings
Blood pressure measures the force of blood pushing against artery walls. Moreover, it is expressed as two numbers. Systolic pressure (the top number) measures the force when your heart beats, while diastolic pressure (the bottom number) measures the force between beats when your heart rests.
Normal blood pressure is less than 120/80 mm Hg. Additionally, elevated blood pressure ranges from 120-129 systolic with diastolic less than 80. Hypertension Stage 1 is 130-139 systolic or 80-89 diastolic. Furthermore, Hypertension Stage 2 is 140 or higher systolic or 90 or higher diastolic. A hypertensive crisis requires immediate medical attention when readings exceed 180/120 mm Hg.
Using the hypertension tracker in CareClinic helps you monitor these ranges and identify when readings fall outside healthy parameters. Consequently, you can share this data with your doctor to guide treatment decisions.

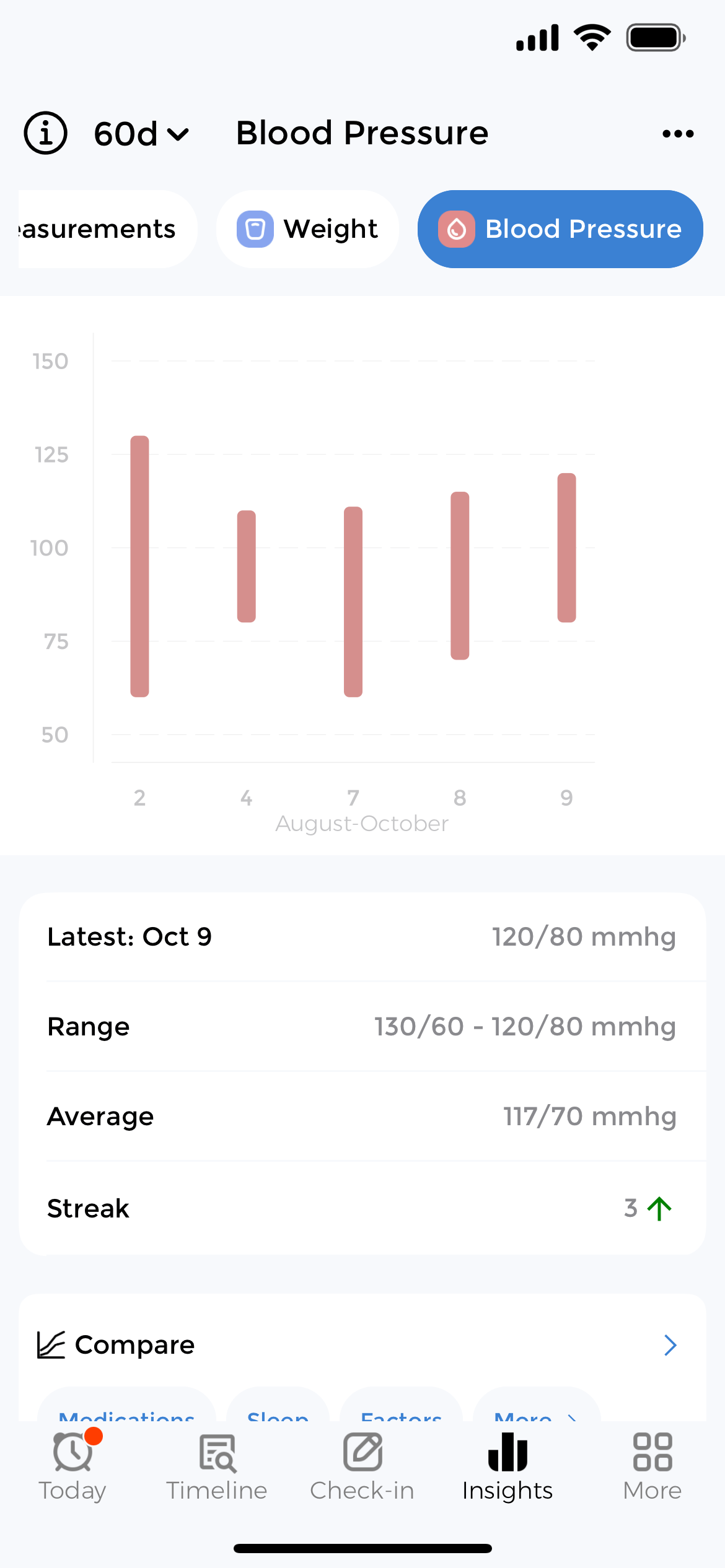
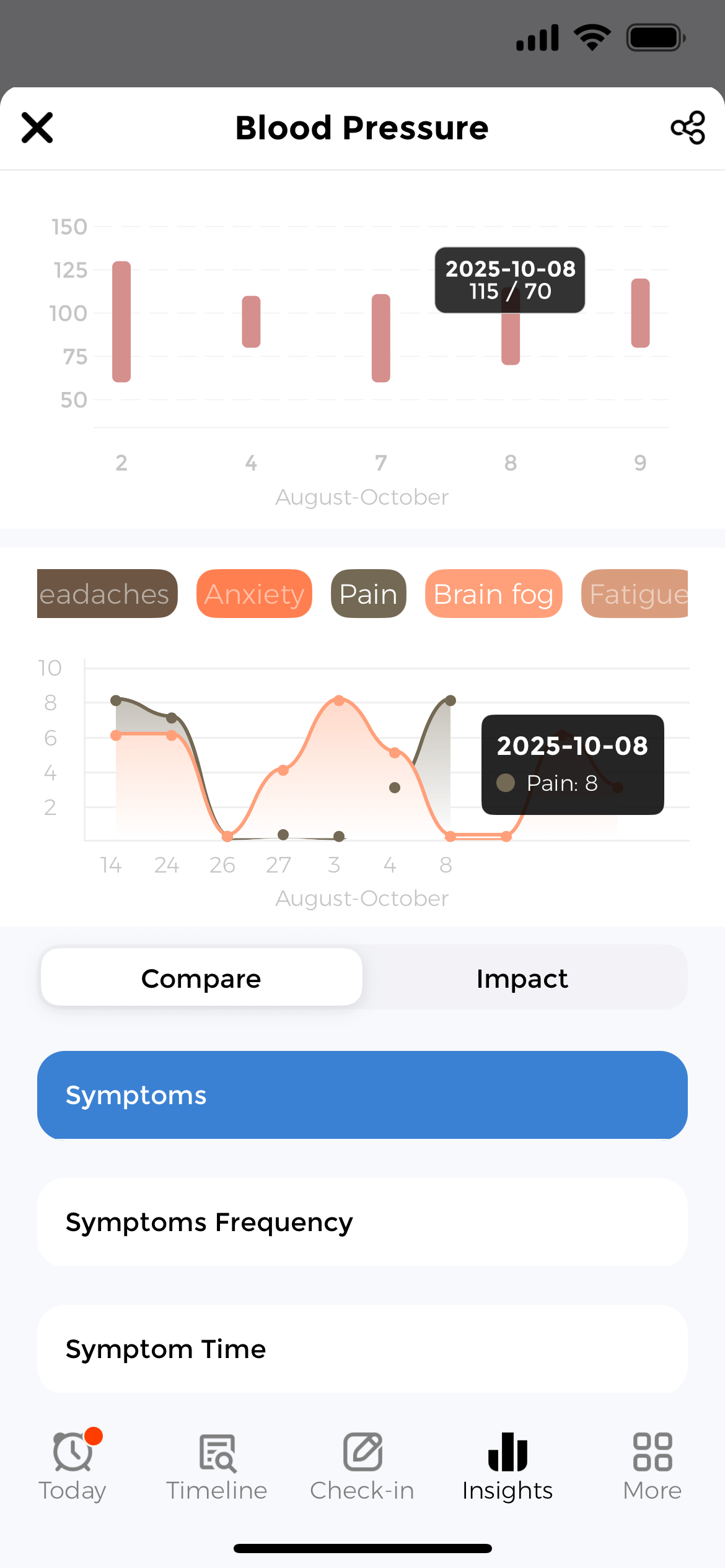
Log and Monitor BP Readings
The best way to track blood pressure is to log every reading consistently. Furthermore, CareClinic makes tracking blood pressure simple with quick entry screens for systolic, diastolic, and pulse measurements. In addition, you can log the time, location, and body position for each reading.
Add notes about what you were doing before the reading, such as exercising, eating, or feeling stressed. Moreover, this context helps identify patterns and triggers that affect your numbers. Consequently, the app functions as both a blood pressure log app and a comprehensive blood pressure diary.
The blood pressure tracker online syncs across devices, ensuring your data is accessible whether you are at home, at the doctor’s office, or traveling. Additionally, you can review your complete history in timeline view to see how your numbers change over days, weeks, or months.
Comprehensive BP Tracking Features
Track systolic and diastolic pressure, pulse rate, medications, weight, and lifestyle factors to understand what influences your cardiovascular health every day.
Systolic & Diastolic Tracking
Log both systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number) readings to monitor the force of blood against artery walls during and between heartbeats.
Pulse Rate Monitoring
Record your pulse alongside blood pressure to track heart rate patterns and identify abnormal rhythms or elevated resting heart rate.
Trend Analysis & Charts
Visualize how your blood pressure changes over time with interactive charts showing daily, weekly, and monthly trends for easier pattern recognition.
Medication Correlation
Track how blood pressure medications like beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics affect your readings to measure treatment effectiveness.
Weight & BP Tracking
Monitor the relationship between body weight and blood pressure as weight loss often leads to significant improvements in cardiovascular health.
BP Check Reminders
Set daily or custom reminders to check your blood pressure at consistent times, ensuring accurate tracking and better trend identification.
BP Monitor Integration
Connect digital blood pressure monitors and wearable devices to automatically sync readings into your blood pressure log for effortless tracking.
Body Position & Location
Record whether you were sitting, standing, or lying down during measurement, plus which arm you used, for accurate clinical context.
High BP Alerts
Get notifications when readings exceed healthy ranges or show concerning patterns that require medical attention or lifestyle adjustments.
Sodium & Nutrition Tracking
Log daily salt intake and meals to correlate dietary sodium with blood pressure fluctuations and identify food-related triggers.
Exercise & Activity Impact
Track how physical activity, exercise timing, and intensity affect your blood pressure readings throughout the day.
Caffeine & Alcohol Tracking
Monitor how caffeine, alcohol, and other beverages influence your blood pressure to identify lifestyle factors affecting cardiovascular health.
BP Reports for Doctors
Generate professional PDF reports with charts, statistics, and reading history to share with your healthcare provider during appointments.
Family BP Tracking
Monitor blood pressure for multiple family members in one app, perfect for caregivers managing elderly parents or family cardiovascular health.
Pregnancy BP Monitoring
Track blood pressure during pregnancy to monitor for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia with specialized pregnancy tracking features.
Syncs with BP Monitors & Devices
Connect your blood pressure monitor and wearable health devices to automatically import readings into one unified blood pressure log. Additionally, CareClinic integrates with Apple Health, Google Fit, Fitbit, and other platforms that sync with digital BP monitors. Moreover, manual entries merge seamlessly with device data to create a complete cardiovascular health picture.

Apple Health

Fitbit
BP Monitors
Garmin
Samsung Health

Google Fit
Monitor Conditions Affecting BP
Identify patterns in blood pressure fluctuations and discover specific health conditions and lifestyle factors affecting your cardiovascular health daily.
Hypertension Management
Track chronic high blood pressure with detailed logs showing medication effectiveness, lifestyle changes, and long-term trends for better control.
Kidney Disease & BP
Monitor blood pressure closely when managing chronic kidney disease, as kidney function directly affects blood pressure regulation and cardiovascular risk.
Stress & Anxiety Impact
Track how stress levels and anxiety episodes affect blood pressure readings to identify emotional triggers and manage stress-induced hypertension.
Obesity & Heart Health
Monitor the relationship between weight loss efforts and blood pressure improvements as even small reductions significantly lower cardiovascular risk.
Sleep Apnea & BP
Track blood pressure patterns related to sleep quality and sleep apnea symptoms as poor sleep directly contributes to elevated daytime readings.
White Coat Hypertension
Identify white coat hypertension by comparing home readings with doctor’s office measurements to distinguish anxiety-related spikes from true hypertension.
Discover What Affects Your BP
See how medications, lifestyle factors, and daily habits influence your blood pressure through visual charts and correlation insights.
Log Daily Readings & Factors
Record blood pressure readings manually or sync from monitors. Additionally, track BP alongside medications, diet, exercise, stress, sodium intake, and sleep quality. Consequently, the app captures everything affecting your cardiovascular health.
Discover Correlations
The app analyzes relationships between blood pressure and your daily activities. Furthermore, see how medications lower readings, or how sodium intake raises them. Moreover, charts reveal patterns you might otherwise miss, showing which factors have the greatest impact.
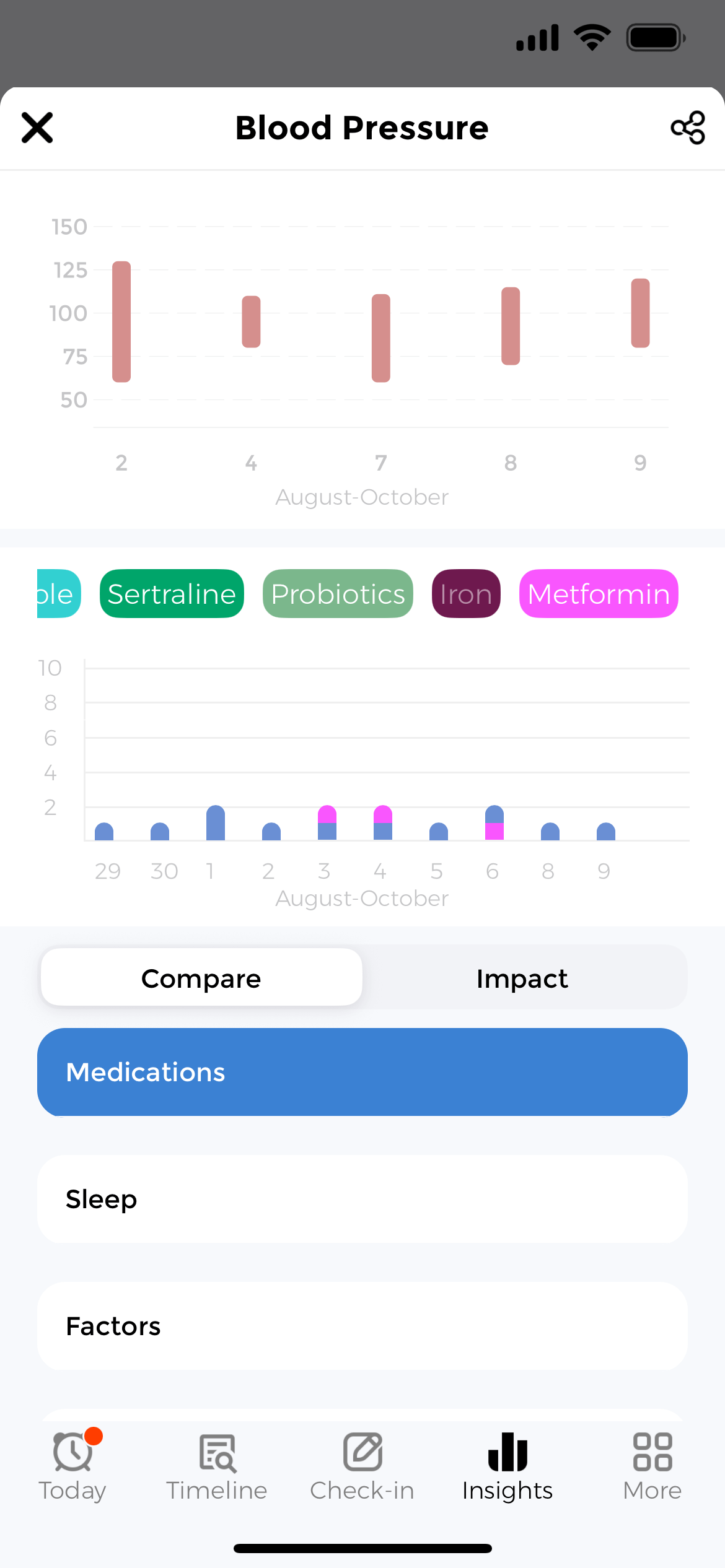
Lower Your Blood Pressure
Use insights to make informed lifestyle changes. Consequently, share detailed BP reports with your doctor to adjust medications, reduce sodium, increase exercise, or address other contributing factors. Moreover, your blood pressure log becomes a powerful tool for improving cardiovascular health.
Track Related Health Factors
See the complete picture of what influences your blood pressure by tracking all the factors affecting cardiovascular health. Furthermore, CareClinic correlates BP data with medications, nutrition, activity, mood, weather, and vital signs to reveal exactly which daily habits impact your readings.
BP Medications
Track blood pressure medications like ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and diuretics to measure how effectively they lower your readings.
Sodium & Diet
Log meals and sodium intake to identify how dietary salt affects blood pressure and discover foods that raise or lower readings.
Exercise & Activity
Track physical activity and see how exercise timing, duration, and intensity affect blood pressure readings throughout the day.
Weight & BMI
Monitor body weight alongside blood pressure to track how weight loss correlates with improved cardiovascular health metrics.
Stress & Mood
Monitor daily stress levels and mood to understand how emotional state and anxiety episodes affect blood pressure readings.
Sleep Quality
Track sleep duration and quality to correlate with morning blood pressure readings and identify sleep-related cardiovascular impacts.
BP Tracking Success Stories
Real stories from people who lowered blood pressure through consistent tracking, discovered medication effectiveness, and achieved healthier cardiovascular numbers through data-driven lifestyle changes.
Understanding Blood Pressure Science
Learning how blood pressure works helps you make better decisions about cardiovascular health and treatment options.
What Is Blood Pressure
Blood pressure measures the force of blood pushing against artery walls. Moreover, systolic pressure (top number) occurs when the heart beats and pumps blood. Additionally, diastolic pressure (bottom number) measures the pressure between beats when the heart rests. Furthermore, both numbers matter for cardiovascular health assessment.
Why High BP Is Dangerous
High blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, damaging arteries over time. Additionally, this increases risk for heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, and heart failure. Furthermore, hypertension often has no symptoms, earning its reputation as the silent killer. Consequently, regular monitoring is essential for early detection and prevention.
How to Lower Blood Pressure
Lifestyle changes significantly lower blood pressure. Moreover, reducing sodium intake, losing weight, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol, and managing stress all help. Additionally, medications like ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and diuretics work when lifestyle changes are not enough. Furthermore, tracking shows which interventions work best for you.
Blood Pressure Research
Consistent blood pressure monitoring and tracking significantly improves cardiovascular outcomes, medication adherence, and long-term heart health management.
Private and Secure BP Tracking
We protect your blood pressure logs and cardiovascular health information with bank-level encryption, HIPAA compliance, and biometric security. Moreover, you control exactly who sees your data, and your information is never sold or shared without explicit permission.
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about tracking blood pressure, choosing monitors, sharing data with doctors, and improving cardiovascular health through consistent monitoring.
A blood pressure tracker is an app that logs your systolic and diastolic readings, pulse rate, and related health factors like medications and lifestyle. CareClinic helps you monitor BP trends, identify patterns, and share reports with your doctor for better cardiovascular health management.
The CareClinic app makes tracking blood pressure simple. Measure your BP with a home monitor, then enter the systolic and diastolic numbers into the app. Add the date, time, and any notes about medications or activities. The app creates charts showing how your numbers change over time.
The best way to track blood pressure is to measure at the same time daily, sit quietly for 5 minutes before taking readings, and log every measurement consistently. Use a validated home BP monitor and record readings in CareClinic to identify trends, correlate with medications, and share data with your healthcare provider.
Yes, CareClinic offers free blood pressure tracking features including unlimited BP logging, trend charts, and basic reports. Premium features unlock advanced analytics, medication correlation analysis, and enhanced sharing options, but core BP tracking remains free for all users.
Validated automatic upper-arm blood pressure monitors provide accurate readings when used correctly. Look for devices validated by the American Medical Association or British Hypertension Society. Wrist and finger monitors are less accurate. Always follow manufacturer instructions and log readings in CareClinic for reliable tracking.
Blood pressure tracking itself does not lower readings, but consistent monitoring helps you identify triggers, measure medication effectiveness, and track lifestyle changes that do lower BP. CareClinic shows correlations between diet, exercise, stress, and blood pressure so you can make informed decisions to improve cardiovascular health.
CareClinic syncs with digital BP monitors that connect to Apple Health, Google Fit, or other health platforms. Popular compatible monitors include Omron, Withings, QardioArm, and other Bluetooth-enabled devices. You can also manually enter readings from any blood pressure monitor into the app.
Most doctors recommend checking blood pressure twice daily if you have hypertension. Measure once in the morning before medications and once in the evening. Take 2-3 readings each time, one minute apart, and log the average in CareClinic. Your doctor may recommend a different schedule based on your specific condition.
Yes, CareClinic generates professional PDF reports with BP charts, statistics, and reading history you can export and share with healthcare providers. You can email reports, print them for appointments, or give your doctor secure read-only access to view your blood pressure logs directly.
CareClinic tracks medications, sodium intake, exercise, weight, stress levels, sleep quality, caffeine, and alcohol alongside blood pressure. These factors directly influence cardiovascular health. Correlating them with BP readings reveals which lifestyle changes and medications work best for lowering your numbers.
Blood pressure tracker apps reveal patterns you cannot see from individual readings. CareClinic identifies medication effectiveness, lifestyle triggers, and concerning trends. Consequently, consistent tracking provides objective evidence for treatment decisions, helps achieve BP goals faster, and reduces cardiovascular risk through better management.
Yes, CareClinic supports multiple family profiles in one account. You can track blood pressure for elderly parents, children, or anyone in your care. Each person has separate records, charts, and medications, making it easy to manage cardiovascular health for your entire family.
Blood pressure monitoring with CareClinic helps you identify whether medications are working, spot concerning trends early, and measure how lifestyle changes affect readings. Detailed logs guide doctors in adjusting treatment plans, optimizing medication dosages, and preventing cardiovascular complications from uncontrolled hypertension.
Yes, CareClinic helps pregnant women monitor blood pressure to detect gestational hypertension and preeclampsia early. Log readings daily and share reports with your OB-GYN. Tracking symptoms like headaches, vision changes, and swelling alongside BP helps identify warning signs that require immediate medical attention.
Blood pressure monitoring refers to taking individual readings with a BP cuff. Blood pressure tracking means logging those readings over time and analyzing patterns. CareClinic combines both by providing a place to record measurements and tools to visualize trends, correlations, and long-term cardiovascular health changes.