Discover comprehensive online tests for neurodiversity, covering ADHD, Aspergers, Autism, Developmental Language Disorder, Disability Confidence, Dyscalculia, Dysgraphia, Dyslexia, Dyspraxia, Hyperlexia, Irlen Syndrome, OCD, Synesthesia, and Tourette’s Syndrome. We provide detailed resources for each condition, enabling you to understand and explore your neurodivergent traits at your own pace. While these tests offer valuable insights, they’re not formal diagnostic tools, and significant results should prompt consultation with a healthcare professional for a formal evaluation.
Neurodiversity and Neurodivergent Tests Explained
Neurodiversity emphasizes the unique development of each brain, akin to the distinctness of snowflakes or fingerprints. This concept shifts the focus from assessing ‘normal’ functioning to recognizing individual variations in brain development and processing.
Neurodivergent tests are tools to understand these unique cognitive patterns, offering insights into how individuals learn, process information, and navigate life. The term ‘neurodivergent,’ in contrast to the inclusive ‘neurodiversity,’ specifically refers to people with developmental differences, like autism. These tests vary, including self-assessments and symptom-based evaluations.
Neurodivergence vs. Neurotypical: Key Differences
Neurodivergence involves unique cognitive processes, presenting both challenges and strengths like advanced problem-solving or memory skills. Neurotypical people align more closely with standard cognitive profiles. This understanding is essential when considering the results of neurodivergent tests.
Cognitive and Attention Tests
ADHD Test
Evaluate your attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity levels to assess potential ADHD traits. For a better understanding of your attention patterns, take the ADHD Test now.
Social and Communication Tests
Aspergers Test
Explore social interaction and communication patterns that might indicate Asperger’s traits. To discover more about your social and communication skills, take the Aspergers Test.
Autism Test
Assess traits related to social communication, behaviors, and interests indicative of Autism Spectrum Disorder. For insights into Autism-related traits, take the Autism Test.
Learning, Processing, and Inclusivity Tests
Developmental Language Disorder Test
Identify challenges in language acquisition and usage, suggesting Developmental Language Disorder traits. To evaluate your language skills, take the Developmental Language Disorder Test.
Dyscalculia Test
Examine difficulties with numbers and math, which could suggest traits of Dyscalculia. For an assessment of numerical skills, take the Dyscalculia Test.
Dysgraphia Test
Assess challenges in writing abilities that might indicate Dysgraphia. To explore your writing skills, take the Dysgraphia Test.
Dyslexia Test
Explore reading, writing, and spelling difficulties to assess for Dyslexia traits. For a deeper understanding of reading and writing challenges, take the Dyslexia Test.
Disability Confident Test
Evaluate your workplace’s inclusivity and awareness regarding disabilities and neurodiversity. To assess your workplace’s disability confidence, take the Disability Confident Test.
Motor and Coordination Tests
Dyspraxia Test
Identify coordination and movement challenges potentially pointing to Dyspraxia. To assess your motor skills, take the Dyspraxia Test.
Hyperlexia Test
Evaluate advanced reading skills paired with social and communication challenges, indicating Hyperlexia traits. For insights into your reading abilities, take the Hyperlexia Test.
Sensory and Behavioral Tests
Irlen Syndrome Test
Discover sensitivity to visual stimuli and difficulties with reading, suggestive of Irlen Syndrome. To explore visual processing, take the Irlen Syndrome Test.
OCD Test
Assess for repetitive behaviors and intrusive thoughts characteristic of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. For an understanding of OCD traits, take the OCD Test.
Synesthesia Test
Explore sensory experiences, like seeing colors when hearing sounds, indicating Synesthesia. To delve into sensory perception, take the Synesthesia Test.
Tourette’s Syndrome Test
Identify involuntary vocal and motor tics that are hallmarks of Tourette’s Syndrome. For an evaluation of Tourette’s traits, take the Tourette’s Syndrome Test.
Identifying Neurodivergence
Neurodivergence refers to variations in brain function, not a set medical condition with a specific list of symptoms. It represents a spectrum of experiences and traits, making it unique to each individual. Understanding this helps interpret test results in the context of personal cognitive patterns.
Neurodiversity is categorized into three distinct types, each reflecting different origins and characteristics:
Innate Neurodiversity: Includes conditions present from birth or early development, such as Dyslexia and Dyspraxia. These affect areas like learning, reading, and motor skills, shaping an individual’s cognitive and physical abilities from a young age.
Developmental Neurodiversity: Encompasses conditions like ADHD and Autism Spectrum Disorder. These typically manifest in childhood and can affect attention, social interactions, communication, and behavior, often persisting into adulthood.
Acquired Neurodiversity: Refers to neurodivergent conditions that are acquired due to health issues, injuries, or environmental factors later in life. This can include cognitive changes resulting from brain injuries or illnesses, leading to alterations in memory, concentration, or other cognitive functions.
Is Having Anxiety Neurodivergent?
Understanding mental health within the neurodiversity paradigm presents challenges. Yet, statistics show higher rates of co-occurring disorders such as depression and anxiety with conditions like autism, dyspraxia, and ADHD. For instance, 3 out of 10 children with ADHD also experience an anxiety disorder. Autism, similarly, is linked to high rates of anxiety, mood disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and personality disorders, among others.
Exploring genetics offers explanations for these overlaps. In ADHD, for instance, many genes linked to the condition also relate to dopamine transporter dysfunction. Dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter for pleasure, plays a significant role in motivation and enthusiasm. Incorporating a neurodivergent test into the diagnostic process can help identify these co-occurring conditions, providing a clearer picture of an individual’s mental health landscape and facilitating more targeted interventions.
Symptoms of Being Neurodivergent
In addition to these conditions, many individuals experience frequent mood swings, a significant aspect often observed in their behavior. These mood fluctuations can be more pronounced and occur more frequently than in neurotypical individuals, largely due to the different ways their brains process emotions and external stimuli.
Understanding and managing these mood swings is crucial for the overall mental health and well-being of neurodivergent individuals. Furthermore, these variations in mood highlight the importance of examining brain functions to gain deeper insights into how neurodivergent individuals experience and navigate the world differently.
Social anxiety, in particular, is a common challenge for many neurodivergent individuals, characterized by intense fear or anxiety in social situations, often stemming from a heightened sensitivity to social stimuli and a fear of negative evaluation by others. This can significantly impact their daily interactions and quality of life.
Take away or reduce the neurotransmitter, the motivation and optimism will disappear. This puts the individual at a greater risk of developing a mental health disorder, such as depression. This dopamine imbalance is also found in autism, Tourette’s, and dyspraxia. Moreover, this correlation proves that clearly defined neurodivergent disorders do go hand in hand with many mental. 6
Mental Illness in the Neurodivergent Spectrum
Mental health presents blurred lines. Consider a child raised in a harmful environment who develops autistic-like functioning due to an event. How should one classify them? Do they fit as neurotypical, autistic, and neurodivergent? Does their non-innate neurodivergence exclude them from the broader neurodivergent category? 8
Most agree the answer is no. Here, the concept of acquired neurodivergence emerges. Environmental factors can lead to the acquisition of a neurodivergent way of thinking, which appropriate intervention can often resolve. In short, most people consider mental illnesses as part of the neurodivergent spectrum, typically under the acquired category.
Guide to Neurodivergent Testing
If there is one thing you should remember, it is that neurodivergence is simply an umbrella term for a unique way of thinking and functioning. Disorders that show this alternate cognitive processing are all neurodivergent disorders. Because neurodivergence does not have a specific list of symptoms, neurodivergent testing to figure out if your brain functions differently is simply an extensive range of tests for well-known neurodivergent disorders.
A neurodivergent test could include autism spectrum tests, dyslexia tests, ADHD and many more. A neurodivergent spectrum test uses questions from all these types of tests to formally diagnose you with one of these disorders. Your neurodivergent test results help identify diversities and uniqueness, and understand the question “Am I neurodivergent?” This helps determine your behavioral differences more generally. Overall, a neurodivergent disorders test aims to compare neurotypical vs neurodivergent patterns of processing.
RAADS-R Test
The Ritvo Autism Asperger’s Diagnostic Scale is one example of a neurodivergent test 9. This test, also known as RAADS-R, is quite simply an autism spectrum disorder screening tool. Comprised of 80 self-report questions based on implemented and approved diagnostic criteria, the RAADS-R test asses where the patient falls on the autism spectrum and therefore, functions as a type of neurodivergent spectrum test.
These questions aim to measure 4 subscales: social relatedness (39 questions), circumscribed interest (14 questions), language (4 questions) and sensory-motor symptoms (20 questions). Participants must answer each statement on a scale from 0 to 3. Each number has meaning, for example, zero means the statement is never true, while 3 means the statement has been true for their entire life9.
Click here to try a RAADS-R Test as your first neurodivergence test. While it’s always good to speak to a healthcare provider for a full and accurate assessment, trying this neurodivergent brain test for free can help you get an initial understanding. At the bottom of the neurodivergent quiz, you will find scoring criteria.
Neurodivergent Music Test
8-dimensional audio is a special type of effect that separates distinct parts of recording10. As a result, different record parts play in different headphones (or speakers) and create a unique sensory experience. Imagine standing in a huge concert hall and different musicians and singers are all walking around the room around you – this is what listening to 8-dimensional music mimics. Engaging in sensory activities like listening to 8D audio can significantly enhance the auditory experience. Recently, a large amount of neurodivergent individuals, people with ADHD, claim that listening to 8D helps them focus and decrease sensory overload10.
Neurodivergent Song Test
The neurodivergent song test is a tool to help assess whether an individual has neurological differences that may impact their ability to process and understand music. This test can be used to identify individuals who may benefit from specialized musical training or accommodations.
The test consists of two parts: a listening comprehension portion and a performance portion. In the listening comprehension portion, the test taker will be asked to listen to a song and answer questions about the lyrics. In the performance portion, the test taker will be asked to sing or play the song on an instrument.
Bangor Dyslexia Test
The Bangor Dyslexia test (BDT) is a short, easy screening test used across all age groups, making it ideal for determining neurodivergent children and adults11. The test focuses on verbal and phonological processing skills, without considering literacy ability. The test uses 10 subtests: identifying left versus right (8 questions), polysyllabic words (5 questions), subtraction (6 questions), tables (3 questions), months forward (1 question), months reverse (1 question), digits forward (12 questions), digits reversed (6 questions), B-D confusion (1 question) and familial incidence (1 question).
These subtests are designed to evaluate a variety of applicable skills, including verbal/phonological working memory, recall and executive function of sequencing, arithmetic skill, and verbal short-term memory. Additionally, the test is quite easy to take, with no time constraints. Moreover, the lack of testing on reading and spelling ensures that only the distal markers of dyslexic literacy difficulties are tested11.
Other Neurodivergent Tests
Recall that neurodivergent is a way to identify yourself and your way of thinking. That being said, some people with certain disorders may decide not to classify themselves as neurodivergent1. Others without the “typical” neurodivergent conditions, may choose to1.
There are many neurodivergent tests available for diseases such as anxiety (the GAD-7 test), bipolar disorder screening, or dyspraxia questionnaires, they may not necessarily all test for “neurodivergence”. However, an individual can choose to identify themselves as neurodivergent along with their condition or they may not.
You can try taking the GAD-7 anxiety and neurodivergent test free here. This is a quick and simple neurodivergent quiz that allows you to see your level of anxiety.
There is no set of medical criteria they must meet to be neurodivergent, it acknowledges various neurological differences. Keep in mind that the disorders we have listed throughout our talk about neurodivergence are only those conditions that are most common amongst those who identify themselves as neurodivergent1. There are no hard or fast rules.
The CareClinic App has some of these screening tools built right in! Under the Scales & Assessments tab, you have easy access to the GAD-7 test, as well as an Adult ADHD Self-Report scale and mood disorder questionnaire. These tools are key to figuring out what you may be experiencing and how you can alter your lifestyle you best accommodate how you function!
Key Steps and Insights
Recognizing signs of neurodivergence involves understanding the unique ways in which individuals experience the world. Key indicators include varied communication styles, learning differences, and sensory sensitivities, distinguishing a neurodivergent person from a neurotypical one. When considering a neurodivergent condition, it’s crucial to observe how someone manages daily tasks, responds to sensory information, and navigates social interactions, such as making eye contact.
Neurodivergent tests, including online quizzes and self-administered assessments, feature quiz questions designed to uncover these nuances. Firstly, these tools ask specific questions related to common symptoms under the neurodivergent umbrella, such as difficulties with problem-solving or managing one task at a time. However, they’re just the starting point toward a formal diagnosis. Consequently, this guidance helps individuals understand what next steps to take.
For anyone seeking insights into potential neurodivergence, it’s important to choose tests that relate questions to real-life scenarios, offering a glimpse into a person’s unique strengths and challenges. The possible results from these assessments can illuminate the path to understanding a neurodivergent condition, highlighting the best way to support learning and communication.
Using the CareClinic App to Test Your Neurodivergence
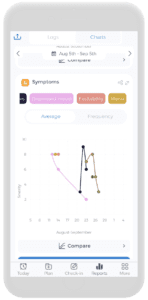 Neurodivergence is challenging to evaluate, but by keeping track of your symptoms, experiences, and daily management strategies, you can start to determine if you have a specific neurodivergent disorder.
Neurodivergence is challenging to evaluate, but by keeping track of your symptoms, experiences, and daily management strategies, you can start to determine if you have a specific neurodivergent disorder.
Incorporating a neurodivergent test into your assessment routine can offer additional clarity.
Using tools like the symptom tracker, therapy tracker, diary, and factors tab allows you to record a comprehensive snapshot of your health, enhancing your understanding and management of neurodivergence.
Next Steps to Neurodiversity Awareness
It’s essential to recognize the extraordinary complexity and uniqueness of each mind. The online assessments we’ve discussed are stepping stones toward a deeper understanding of neurodivergent conditions like ADHD, Autism, and Dyslexia. These tools initiate your journey into the vibrant world of neurodiverse thinking, a journey that’s both personal and profound.
We recommend the CareClinic app, it’s a companion in your exploration of neurodiversity. With specific, user-friendly tests, the CareClinic app provides a nuanced understanding of your cognitive landscape. Download the CareClinic app now, and start navigating the unique contours of your neurodiverse mind with confidence and clarity.
References
- Legault, M., Bourdon, J-N., & Poirier, P. (2021). From neurodiversity to neurodivergence: the role of epistemic and cognitive marginalization. Synthese, 199, 12843-12868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-021-03356-5
- Skelling, J. (2019). Neurodiversity: An overview. The Education Hub. Retrieved from: https://theeducationhub.org.nz/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Neurodiversity-An-overview.pdf
- Jones, P. B. (2013). Adult mental health disorders and their age at onset. The British Journal Psychiatry, 202, s5-s10. https://doi.org/ 10.1192/bjp.bp.112.119164
- Tannock, R. (2009). ADHD with anxiety disorders. In T. E. Brown (Ed.), ADHD comorbidities: Handbook for ADHD complications in children and adults (pp. 131–155). American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.
- Kirby, A. (2021, August 26). Is There a Link Between Neurodiversity and Mental Health?. Psychology Today. Retrieved from: https://www.psychologytoday.com/ca/blog/pathways-progress/202108/is-there-link-between-neurodiversity-and-mental-health
- Volkow, N. D., Wang, G-J., Kollins, S. H., Wigal, T. L., Newcorn, J. H., Telang, F., Fowler, J. S., Zhu, W., Logan, J., Ma, Y., Pradhan, K., Wong, C., & Swanson, J. M. (2009). Evaluating Dopamine Reward Pathway in ADHD. JAMA, 302(10), 1084-1091. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.1308
- Chapman, R. (2019, July 30). Mental Disorder Within the Neurodiversity Paradigm. Psychology Today. Retrieved from: https://www.psychologytoday.com/ca/blog/neurodiverse-age/201907/mental-disorder-within-the-neurodiversity-paradigm
- Jones, S. L., Johnson, M., Alty, B., & Adamou, M. (2021). The Effectiveness of RAADS-R as a Screening Tool for Adult ASD Populations. Autism Research and Treatment, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9974791
- Couneene, B. (n.d.). Why ADHD and Neurodivergent People Are Into 8D Audio. Neuropedia. Retrieved from: https://neuropedia.com/8d-audio-autism-adhd/
- Reynolds, A, E., & Caravolas, M. (2016). Evaluation of the Bangor Dyslexia Test (BDT) for use with Adults. Dyslexia, 22(1), 27-46. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.1520