Skin infections can be caused by a variety of factors, and they can range from mild to severe. They can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or even parasites. Understanding the signs and symptoms of skin infections, as well as knowing when to seek medical attention, is vital to preventing complications and achieving successful treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of skin infections, their causes, and the best ways to recognize and respond to their warning signs.
Understanding Skin Infection
Skin infections are a common problem that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. They can occur anywhere on the body, from the face to the feet and everything in between. These infections are commonly caused by a range of organisms and may be triggered by a cut, scrape, or other skin injury. While some skin infections are mild and can be treated easily, others can be serious and require medical attention.
Types of Skin Infections
There are many different types of skin infections, each with its own set of symptoms and causes. The most common types of skin infections include:
- Impetigo – a highly contagious bacterial infection that causes blisters or sores on the face, nose, and mouth. This infection is most common in young children and infants, but it can affect people of all ages.
- Cellulitis – bacterial infections that can cause redness, swelling, and warmth on the skin’s surface and can spread to deeper tissues. This common bacteria infection is most occurs mainly in adults and can be caused by a range of bacteria, like staphylococcus aureus.
- Fungal infections – a common type of skin infection caused by fungi that live on the skin’s surface, such as athlete’s foot or ringworm. These infections are often characterized by redness, itching, and scaling of the skin.
- Viral infections – caused by different viruses and can manifest as cold sores or warts on the skin’s surface. These infections are often highly contagious and can be spread through skin-to-skin contact or contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Parasitic infection – parasitic skin infection can cause intense itching and redness, such as scabies or lice. Parasitic infections are often spread through close physical contact with an infected person or through contact with contaminated objects.
Causes of Skin Infection
There are many different factors that can contribute to the development of a skin infection. Many skin infections are caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites that enter the body through a cut, scrape, insect bite, or other skin injury. However, some people are more susceptible to skin infections due to underlying conditions that weaken the immune system, such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer. Other factors that can increase the risk of skin infections include:
- Poor hygiene – failing to wash your hands regularly, not taking regular showers or baths, and not keeping your skin clean can all increase your risk of developing a skin infection.
- Exposure to contaminated water or soil – spending time in bodies of water or soil that are contaminated with certain bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, or tiny insects can increase your risk of developing a skin infection.
- Sharing personal items – sharing towels, razors, or other personal items with someone who has a skin infection can increase your risk of developing an infection yourself.
- Skin-to-skin contact with someone who has an infection – close physical contact with someone who has a skin infection can increase your risk of developing an infection yourself.
- Lifestyle choices – smoking, alcohol consumption, and poor diet can all weaken the immune system and increase your risk of developing a skin infection.
Risk Factors for Skin Infection
While skin infections can affect anyone, certain groups of people are more at risk than others. These include:
- Children, especially those who attend daycare or school, are more susceptible to skin infections due to their close proximity to other children and their underdeveloped immune systems.
- Elderly individuals are more susceptible to skin infections due to the natural aging process, which can cause the skin to become thinner and more prone to injury.
- People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or cancer, are more susceptible to skin infections due to their weakened ability to fight off infections.
- People with chronic skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis are more susceptible to skin infections due to the damage to their skin’s protective barrier.
- Athletes who participate in contact sports are more susceptible to skin infections due to the close physical contact with other athletes and the potential for skin injuries.
- People with jobs that require them to work outdoors or in wet environments are more susceptible to skin infections due to prolonged exposure to moisture and potential skin injuries.
Recognizing the Signs of Skin Infection
While the symptoms of skin infections can vary depending on the type of infection and its severity, there are some common signs to look out for. These include:
Redness and Swelling
One of the most common symptoms of skin infection is redness and swelling. This can be localized to the site of the infection or can spread to surrounding areas. The affected skin may also feel warm or tender to the touch.
Pain and Tenderness
 If you have a skin infection, you may experience pain or tenderness in the affected area. This can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
If you have a skin infection, you may experience pain or tenderness in the affected area. This can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Warmth and Heat
When a skin infection occurs, the affected skin can become warm to the touch. This is due to the body’s immune response to the infection, which increases blood flow to the skin surface and affected area and produces heat.
Pus or Discharge
If you notice pus or other discharge coming from a skin lesion, it is a sign of infection. This can be a clear, yellow, or greenish color and may have a foul odor.
Fever and Chills
If a skin infection spreads beyond the skin’s surface and into the bloodstream, it can cause a fever and chills. This is a sign of a severe infection and requires immediate medical attention.
It’s important to note that not all skin infections are created equal. Some are more serious than others and require prompt medical attention. For example, cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can be life-threatening if left untreated. It typically starts as a small, red, painful area of skin and can quickly spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms of cellulitis include fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes.
Another type of skin infection is impetigo, which is a highly contagious bacterial infection that primarily affects infants and young children. It typically appears as red sores on the face, especially around the nose and mouth. These sores can quickly burst and develop a honey-colored crust. Impetigo is usually not serious and can be treated with antibiotics.
Fungal infections are also common skin infections, especially in warm and humid climates. Athlete’s foot, for example, is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet and toes. Symptoms include itching, burning, and cracking of the skin, as well as a red, scaly rash. Fungal infections can usually be treated with antifungal medications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you suspect you may have a skin infection, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. While some infections can be treated at home, others require medical intervention to prevent complications and recurrent episodes.
It is important to note that skin infections can be caused by a variety of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. These infections can range from mild to severe, and their symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and which bacteria infect the affected area of the skin.
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If your symptoms do not improve or worsen despite home treatment, you may need to visit a medical professional. Some skin infections can develop into serious conditions if left untreated, so it is crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
For example, a common bacterial skin infection called cellulitis can among many skin infections cause redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. If left untreated, cellulitis can spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream, leading to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
Signs of a Severe Infection
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it may be a sign of a severe skin infection and requires immediate medical attention:
- Fever over 101°F
- Rapid heart rate
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness or fainting
- Confusion or disorientation
- Extreme pain or discomfort
- Blood in the pus or discharge
These symptoms may indicate that the infection has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bloodstream or internal organs, and requires urgent medical attention.
Infections in High-Risk Individuals
If you have a weakened immune system or a chronic health condition, you may be at higher risk for developing severe skin infections.
For example, people with diabetes are more susceptible to skin infections due to poor circulation and nerve damage. They may also have weakened immune systems, making it harder for their bodies to fight off infections.
Similarly, people with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or other chronic illnesses may be more vulnerable to skin infections due to their weakened immune systems.
If you notice any signs of infection, seek medical attention promptly, as these infections can progress quickly in high-risk individuals. Your doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment, such as intravenous antibiotics or antifungal medications, to prevent complications.
Diagnosing Skin Infections
If you suspect that you have a skin infection, it is important to seek medical attention. A medical professional will perform a physical examination to help diagnose the type and severity of the infection. During the examination, they will look for any signs of redness, swelling, or discharge in the affected area. They may also ask you questions about your symptoms and medical history.
After the physical examination, the medical professional may take a sample of the fluid or pus to determine the cause of the infection. This is known as a culture and sensitivity test. The sample will be sent to a laboratory, where it will be analyzed to identify the type of bacteria or fungus causing the infection. The laboratory will also test the sample to determine which antibiotics or antifungal medications will be most effective in treating the infection.
Physical Exam
A medical professional will carefully examine the affected area to determine the extent of the infection. They may also check the lymph nodes to see if the infection has spread. If the infection is located on the face or near the eyes, they may refer you to an ophthalmologist for further evaluation.
In some cases, the medical professional may use a special instrument called a Wood’s lamp to examine the affected area. This lamp emits ultraviolet light, which can help identify certain types of fungal infections.
Laboratory Tests
If a bacterial or fungal infection is suspected, a medical professional may order laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include a skin culture or a blood test. A skin culture involves taking a sample of the affected skin and sending it to a laboratory for analysis. A blood test may be used to check for signs of infection in the bloodstream.
In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. During a skin biopsy, a small sample of skin is removed and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Imaging Studies
If a skin infection is severe, a medical professional may order imaging studies to determine if the infection has spread to deeper tissues. These tests may include an X-ray or a CT scan. These tests can help the medical professional determine the extent of the infection and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
In summary, if you suspect that you have a skin infection, it is important to seek medical attention. A medical professional will perform a physical examination and may order laboratory tests or imaging studies to confirm the diagnosis. With prompt and appropriate medical treatment, most skin infections can be successfully treated.
Treating Skin Infections
The skin is the largest organ of the whole body and serves as a barrier against harmful microorganisms. However, sometimes these microorganisms can penetrate the skin and bacteria enter, causing infections. Skin infections can range from mild to severe and can be caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites. The treatment for skin infections depends on the type and severity of the infection.
Topical Treatments
For mild infections, topical treatments such as antibacterial or antifungal creams may be prescribed.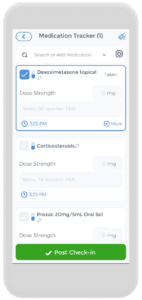 These creams are applied directly to the affected area and can help to clear up the infection. It is important to keep the affected area clean and dry to prevent the infection from spreading. In addition to topical treatments, warm compresses can also be applied to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
These creams are applied directly to the affected area and can help to clear up the infection. It is important to keep the affected area clean and dry to prevent the infection from spreading. In addition to topical treatments, warm compresses can also be applied to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Oral Medications
If a skin infection is more severe or widespread, an oral antibiotic or antifungal medication may be prescribed. These medications are taken by mouth and can help to clear up the infection from within. It is important to take the medication as prescribed and to finish the full course of treatment, even if the symptoms improve before the medication is finished. Failure to complete the full course of treatment can lead to antibiotic resistance, making it more difficult to treat future infections.
Intravenous Antibiotics
If a skin infection is severe or has spread to deeper tissues, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary. These antibiotics are administered through a vein and can help to clear up the infection quickly. This type of treatment is typically reserved for hospital settings and may require a longer hospital stay.
Surgical Intervention
In rare cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove infected tissue or drain abscesses that have formed due to the infection. This is typically reserved for severe infections that do not respond to other treatments. Surgery may also be necessary if the infection has spread to the bloodstream or other organs.
In conclusion, skin infections can be caused by a variety of microorganisms and can range from mild to severe. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection and may include topical treatments, oral medications, intravenous antibiotics, or surgical intervention. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect a skin infection to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
Preventing Skin Infections
Preventing bacterial skin infections also involves adopting certain hygienic practices and lifestyle habits. These include:
Proper Wound Care
Keeping cuts, scrapes, and other skin injuries clean and dry can help to prevent infections from developing. Covering the wound with a sterile bandage can also help to keep it clean while it heals.
It is important to clean the wound with soap and water, and then apply an antiseptic solution to prevent infection. If the wound is deep or does not heal within a few days, it is important to seek medical attention.
Hand Hygiene
Regular hand washing is an important part of preventing the spread of skin infections. This is especially important after touching animals or infected individuals, or after using public restrooms or other shared spaces.
It is recommended to wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, making sure to clean between fingers and under nails. If soap and water are not available, an alcohol-based hand sanitizer can be used.
Avoiding Skin-to-Skin Contact with Infected Individuals
If someone in your household or workplace has a skin infection, it is important to avoid close contact with them until the infection has cleared up. This can help to prevent the spread of the infection to others.
It is also important to avoid sharing personal items such as towels, clothing, and razors with infected individuals.
Keeping Skin Clean and Dry
Showering regularly and keeping skin dry and clean can help to prevent skin infections. This is especially important for people who participate in contact sports or those who work in wet environments.
Avoiding tight-fitting clothing and wearing breathable fabrics can also help to prevent skin infections by reducing moisture and friction on the skin.
By adopting these hygienic practices and lifestyle habits to clean your skin regularly, you can help to prevent skin infections and maintain healthy skin.
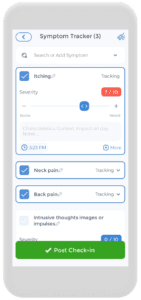
Using the CareClinic App For Your Skin Health Treatment Plan
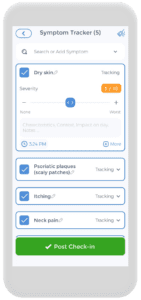 Having a skin health action plan is crucial, and the CareClinic app can help with that. You can use the app as your skin disease diary. Just go to the diary section of the app and enter your daily symptoms, medications, and triggers as they occur. There are also specific sections on the app to track each of these. Next time you visit the doctor, this information will be handy in your pocket.
Having a skin health action plan is crucial, and the CareClinic app can help with that. You can use the app as your skin disease diary. Just go to the diary section of the app and enter your daily symptoms, medications, and triggers as they occur. There are also specific sections on the app to track each of these. Next time you visit the doctor, this information will be handy in your pocket.
Whether you develop eczema, psoriatic arthritis, or another skin disorder, our goal is to help with disease control. You can also track your prescription medications and treatments, whether it be topical corticosteroids, emollient treatment, topical moisturizers, topical antihistamines, topical antibiotics, or topical calcineurin inhibitors.
Recognizing and responding to signs of skin infection is crucial to preventing complications and achieving successful treatment. While skin infections can be caused by a range of factors, most can be effectively treated with the right medical intervention. By adopting proper hygiene practices, staying alert for the signs of infection, and seeking prompt medical attention when needed, you can help protect your skin health and overall well-being .
.
Sources:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/skin-infection
- https://medlineplus.gov/skininfections.html
- https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/ss/slideshow-skin-infections


