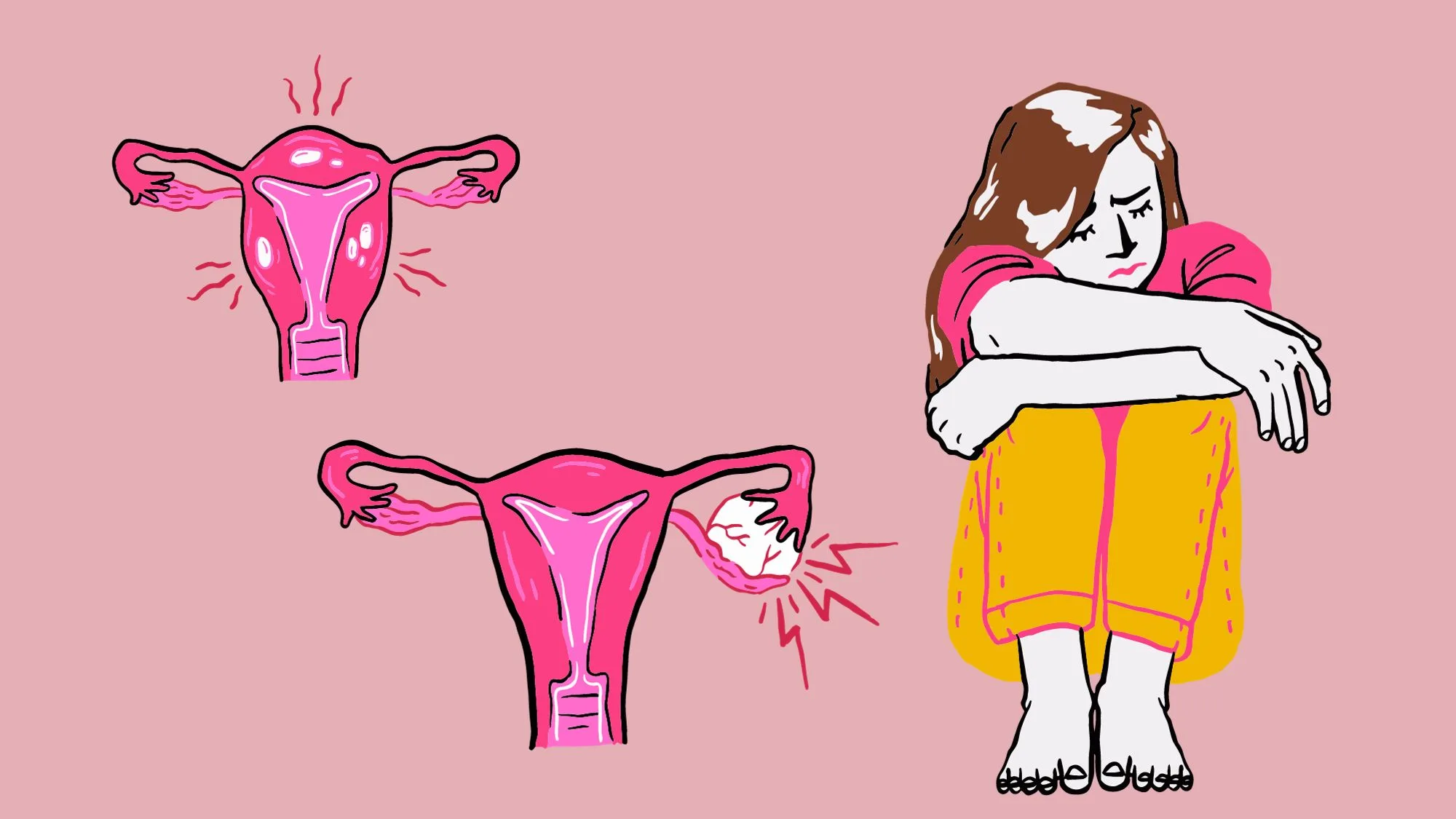
Deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects many women worldwide. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for this condition. As well as provide insights into living with deep-infiltrating endometriosis. [1][2][3][4][5][6]
What is Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis?
Deep infiltrating endometriosis is a severe form of endometriosis where the endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, grows outside the uterine cavity. Unlike superficial endometriosis, which affects the ovaries and pelvic lining, deep infiltrating endometriosis infiltrates the surrounding organs and tissues, such as the bladder, bowel, and even the lungs.
This condition is characterized by the formation of lesions or implants that can cause significant pain and discomfort for affected individuals. The severity of the symptoms can vary from person to person, with some experiencing debilitating pain and others being relatively asymptomatic.
Defining Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis
The term “deep infiltrating endometriosis” refers to the infiltration of endometrial tissue into the walls of organs and tissues beyond the lining of the pelvis. This infiltration can cause adhesions and scarring, leading to pain and potentially affecting organ function in severe cases.
Deep infiltrating endometriosis is a complex condition that can have far-reaching effects on the body. When the endometrial tissue infiltrates the gastrointestinal tract, it can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. In some cases, the endometrial tissue may even obstruct the bowel, causing severe pain and requiring surgical intervention.
The urinary system can also be affected by deep infiltrating endometriosis. When the endometrial tissue infiltrates the bladder, it can cause symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, and even blood in the urine. This can greatly impact a person’s quality of life and may require specialized treatment approaches.
In rare cases, deep infiltrating endometriosis can even affect the respiratory system. The endometrial tissue may infiltrate the lungs, leading to symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain. This manifestation of the condition requires careful management and coordination between gynecologists and respiratory specialists.
The Prevalence of Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis
Deep infiltrating endometriosis is estimated to affect approximately 20% of women with endometriosis. However, due to the variability of symptoms and the challenging nature of accurate diagnosis, the true prevalence of this condition may be higher.
It is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of deep infiltrating endometriosis to seek medical attention from healthcare professionals with expertise in this field. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected.
Research and awareness efforts are ongoing to better understand the underlying causes of deep infiltrating endometriosis and develop more effective treatment options. By expanding our knowledge and providing comprehensive care, we can strive to alleviate the burden of this complex condition on individuals and improve their overall well-being.[7][8][9][10][11]
The Causes of Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis
Deep infiltrating endometriosis is a complex condition with various potential causes. While the exact cause remains unknown, researchers have identified several factors that may contribute to its development.
Genetic Factors in Endometriosis
Genetics is believed to play a role in the development of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Studies have shown that women with a family history of endometriosis are at a higher risk of developing this severe form of the condition. This suggests that certain genetic factors may predispose individuals to the development of deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Further research is needed to understand the specific genes and genetic variations involved in the development of deep infiltrating endometriosis. By identifying these genetic factors, scientists can gain a better understanding of the condition and potentially develop targeted therapies or preventive strategies.
Hormonal Influences on Endometriosis
Hormonal imbalances, particularly high levels of estrogen, have been associated with the development and progression of endometriosis. Estrogen, a hormone primarily produced by the ovaries, promotes the growth of endometrial tissue. When there is an excess of estrogen, it can contribute to the formation of endometrial implants in various locations outside the uterus.
However, hormonal imbalances alone do not fully explain the development of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Other factors, such as inflammation and an altered immune response, likely interact with hormonal influences to contribute to the severity and progression of the condition.
Research is ongoing to better understand the complex interplay between hormones, inflammation, and the immune system in the development of deep infiltrating endometriosis. This knowledge could potentially lead to more effective treatment options and management strategies.
Environmental Triggers for Endometriosis
Environmental factors may also play a role in the development of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins in the environment has been suggested as a potential trigger for the condition. These environmental factors can disrupt the hormonal balance in the body and potentially contribute to the abnormal growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
Identifying specific environmental triggers and understanding their mechanisms of action is an area of active research. By gaining a better understanding of these triggers, scientists can develop preventive strategies and interventions to reduce the risk of developing deep infiltrating endometriosis.
It is important to note that while these factors have been identified as potential contributors to the development of deep infiltrating endometriosis, the condition is likely multifactorial, meaning that multiple factors may interact to cause the condition. Further research is needed to fully understand the complex nature of deep infiltrating endometriosis and develop effective treatment and prevention strategies.[12][13][14][15][16]
Recognizing the Symptoms of Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis
Recognizing the symptoms of deep infiltrating endometriosis is crucial for early intervention and appropriate management of this condition. Endometriosis is a chronic condition where the tissue that normally lines the uterus grows outside of it, causing pain and other symptoms.
Deep infiltrating endometriosis refers to a more severe form of the condition, where the endometrial tissue infiltrates deeply into the surrounding organs and tissues, such as the bowel, bladder, and pelvic wall. This can lead to a range of physical symptoms and have a significant impact on a person’s emotional well-being and fertility.
Physical Symptoms and Signs
The physical symptoms of deep infiltrating endometriosis can vary widely and may include severe pelvic pain, painful bowel movements or urination, heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding, and pain during sexual intercourse. These symptoms can significantly affect a person’s quality of life and daily activities.
In some cases, deep infiltrating endometriosis can cause intestinal obstruction, leading to symptoms such as abdominal distension, constipation, and nausea. The presence of endometrial implants on the bowel can cause inflammation and scarring, resulting in these digestive symptoms.
Additionally, women with this condition may experience chronic fatigue, back pain, and increased sensitivity to pain in the pelvic region. The chronic inflammation and hormonal imbalances associated with deep infiltrating endometriosis can contribute to these symptoms.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with deep infiltrating endometriosis can take a toll on an individual’s emotional and psychological well-being. The chronic pain and limitations imposed by the condition can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression.
Women with deep infiltrating endometriosis may struggle with the uncertainty of their symptoms and the impact it may have on their daily lives. The pain and discomfort can make it challenging to engage in social activities, work, or maintain relationships. It is crucial for individuals with deep infiltrating endometriosis to seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and loved ones to manage the emotional and psychological impact effectively.
Impact on Fertility and Pregnancy
Deep infiltrating endometriosis can significantly impact fertility and pregnancy. The presence of adhesions and scarring can interfere with the normal function of the reproductive organs, making it more challenging to conceive naturally.
Endometriosis can affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus, leading to issues such as ovarian cysts, blocked fallopian tubes, and distorted uterine anatomy. These factors can reduce the chances of successful conception and increase the risk of complications during pregnancy.
However, with appropriate medical interventions and fertility treatments, many women with deep infiltrating endometriosis have been able to conceive and have successful pregnancies. Techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and surgical interventions can help improve fertility outcomes for individuals with this condition.
It is important for individuals with deep infiltrating endometriosis who wish to conceive to consult with a fertility specialist who can provide personalized guidance and treatment options based on their specific circumstances.[17]
Diagnostic Methods for Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis
Accurate diagnosis of this condition is crucial to facilitate appropriate management and improve the quality of life for those affected. Various diagnostic methods can be employed to identify the presence and extent of the condition.
Deep infiltrating endometriosis is a complex and often debilitating condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It occurs when endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, grows outside of the uterus and infiltrates nearby organs and tissues. This can lead to severe pain, infertility, and other symptoms that significantly impact a woman’s physical and emotional well-being.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The initial step in diagnosing deep infiltrating endometriosis involves a detailed medical history and physical examination by a healthcare professional with expertise in this field. These assessments can provide valuable insights into the individual’s symptoms, medical background, and potential risk factors for endometriosis.
During the medical history assessment, the healthcare provider will inquire about the nature and duration of the symptoms, such as pelvic pain, painful periods, and pain during sexual intercourse. They will also ask about the individual’s menstrual cycle, previous surgeries, and any family history of endometriosis.
Following the medical history assessment, a thorough physical examination is conducted. The healthcare provider may palpate areas of tenderness and conduct a pelvic exam to assess the condition of the reproductive organs. This can help identify any palpable masses or abnormalities that may indicate the presence of deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Imaging Techniques for Diagnosis
Imaging techniques, such as transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can aid in the diagnosis of deep infiltrating endometriosis. These imaging modalities can help visualize and characterize the endometrial implants, lesions, and other structural abnormalities in the pelvic region.
Transvaginal ultrasound involves the insertion of a small probe into the vagina to obtain high-resolution images of the pelvic organs. This technique allows for the visualization of endometrial implants and cysts that may be present in the ovaries or other pelvic structures.
Magnetic resonance imaging uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the pelvic region. It can provide valuable information about the location, size, and extent of endometrial lesions, as well as their involvement with nearby organs and tissues.
It is important to note that imaging alone may not provide a definitive diagnosis. In cases where a diagnosis is still uncertain, further investigation through surgical methods may be necessary.
Surgical Methods for Diagnosis
Laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, is considered the gold standard for diagnosing deep infiltrating endometriosis. During this procedure, a thin, lighted instrument called a laparoscope is inserted through small incisions in the abdomen to visualize and assess the pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy allows for direct visualization of the pelvic structures, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding tissues. It enables healthcare professionals to identify and assess the extent of endometrial implants, adhesions, and other abnormalities that may be present.
Biopsies of suspicious areas may be taken during laparoscopy to confirm the presence of endometriosis and determine the extent of tissue infiltration. These tissue samples are examined under a microscope by a pathologist to definitively diagnose deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Surgical diagnosis enables healthcare professionals to plan appropriate treatment strategies tailored to the individual’s specific needs. It provides valuable information about the location and severity of the disease, which can guide decisions regarding medical management, fertility preservation, and surgical interventions.
Accurate diagnosis of deep infiltrating endometriosis is essential for effective management and improved quality of life. Through a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, imaging techniques, and surgical methods, healthcare professionals can confidently diagnose and evaluate the extent of the disease. This comprehensive approach allows for personalized treatment plans that address the unique needs and goals of each affected individual. [18][19]
Treatment Options for Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis
Treatment options for deep infiltrating endometriosis aim to alleviate symptoms, preserve fertility when desired, and improve quality of life. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the desire for future pregnancy, and the individual’s overall health.
Deep infiltrating endometriosis is a condition where endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, grows outside of the uterus and infiltrates nearby organs and tissues. This can cause severe pain, fertility issues, and other complications.
Medication Therapies
Medication therapies are often the first line of treatment for deep infiltrating endometriosis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation, providing temporary relief.
However, it’s important to note that medication therapies alone may not be sufficient for managing deep infiltrating endometriosis in the long term. They can help alleviate symptoms, but they do not address the underlying cause of the condition.
Hormonal therapies, such as oral contraceptives, progestin-only medications, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs, can also be prescribed to regulate hormonal imbalances and slow down the growth of endometrial tissue. These medications help manage symptoms and prevent disease progression.
It’s worth mentioning that hormonal therapies may have side effects, and their effectiveness can vary from person to person. Therefore, close monitoring and regular follow-ups with healthcare professionals are necessary to ensure the treatment is working effectively.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions play a crucial role in the management of deep infiltrating endometriosis, especially in cases where symptoms are severe or fertility preservation is a priority.
Laparoscopic excision surgery, also known as deep excision surgery, involves removing the endometrial implants and lesions from affected organs and tissues. This approach aims to restore normal anatomy, alleviate pain, and improve overall function.
During the surgery, the surgeon carefully excises the abnormal tissue while preserving healthy tissue as much as possible. This procedure requires specialized skills and expertise in endometriosis surgery.
It’s important to note that surgery is not a cure for deep infiltrating endometriosis. The condition can recur even after surgery, and additional treatments may be required in the future.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, yoga, and dietary modifications, may help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being in affected individuals. These approaches can provide additional support alongside conventional medical treatments.
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to help regulate the flow of energy and promote healing. Some affected individuals have reported reduced pain and improved quality of life after acupuncture sessions.
Yoga, a mind-body practice that combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation, can help reduce stress, improve flexibility, and promote relaxation. It may be beneficial for affected individuals. It can help manage pain and improve overall well-being.
Dietary modifications, such as avoiding inflammatory foods and incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, may also play a role in managing deep infiltrating endometriosis. Some studies suggest that certain dietary changes. Such as reducing red meat consumption and increasing intake of fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may help alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation.
However, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals before integrating alternative therapies into the treatment plan. To ensure their safety and effectiveness. Not all alternative therapies have been extensively studied in the context of deep infiltrating endometriosis, and individual responses can vary.
Treatment options for deep infiltrating endometriosis include medication therapies, surgical interventions, and alternative and complementary therapies. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors, and a personalized approach is necessary to effectively manage the condition and improve quality of life.[20][21][22][23]
Living with Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis
It is a challenging journey that requires a multidimensional approach to manage symptoms and improve the overall quality of life. This condition, characterized by the abnormal growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, can cause debilitating pain, fertility issues, and a range of other symptoms that significantly impact daily life.
This health condition is a complex condition that affects not only the physical well-being of individuals but also their emotional and mental health. The constant pain and discomfort can lead to feelings of frustration, helplessness, and even depression. Coping with these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
Coping Mechanisms and Support Systems
Developing effective coping mechanisms and establishing a strong support system are crucial for navigating the physical and emotional challenges. Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals can provide valuable guidance, understanding, and empathy throughout the journey. Support groups and online communities also offer a safe space for individuals to connect with others who share similar experiences, providing a sense of validation and solidarity.
Additionally, exploring various coping strategies can help individuals manage the pain and emotional distress associated with deep infiltrating endometriosis. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and journaling can provide a sense of calm and help individuals regain a sense of control over their bodies and emotions.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care
Lifestyle changes and self-care practices can significantly contribute to managing the symptoms and improving overall well-being. Adopting a balanced diet that includes anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate some of the pain associated with deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines can also have a positive impact on symptom management. Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as yoga or swimming, can help improve flexibility, strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, and reduce pain. It is important, however, to listen to the body and avoid overexertion, as pushing too hard can exacerbate symptoms.
Managing stress levels is another crucial aspect of self-care for affected individuals. Stress can worsen symptoms and trigger flare-ups, so finding healthy outlets for stress relief, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, or seeking therapy, can be beneficial.
Future Research and Hope for a Cure
Advancements in research and understanding offer hope for better treatments and even a cure in the future. Ongoing studies continue to shed light on the underlying mechanisms, potential biomarkers, and innovative treatment approaches for this complex condition.
Researchers are exploring various avenues, including hormonal therapies, surgical interventions, and targeted therapies, to improve symptom management and fertility outcomes for affected individuals. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop non-invasive diagnostic tools that can accurately detect and monitor the progression of the disease.
By investing in robust research efforts and raising awareness, we can empower affected individuals and work towards a future where effective management options are readily available. Allowing impacted individuals to lead fulfilling lives. It is crucial to advocate for increased funding and support for research initiatives. To accelerate progress in understanding and treating this condition.
Understanding this kind of health condition requires comprehensive knowledge. Including the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatment options. By recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals affected by this condition can take positive steps towards managing their symptoms, improving their quality of life, and finding hope for a better future. It is essential to approach this health condition with empathy, support, and a commitment to ongoing research. To ensure that those affected receive the care and understanding they deserve.[24][25]
When trying to get pregnant with endometriosis, tracking early signs becomes really important. Understanding 14 dpo symptoms can help you know if conception happened, especially when fertility treatments are involved. This timing knowledge helps you and your doctor make better decisions about your care.
Use CareClinic App To Manage Your Treatment Journey
The CareClinic App can be a valuable ally in managing your symptoms and treatment. With features designed to track your pain levels, medication schedule, and dietary habits, the CareClinic App helps you maintain a comprehensive record of your health journey.
By monitoring your symptoms and the effectiveness of various treatments, you can work closely with your healthcare provider to make informed decisions and adjust your care plan for better health outcomes. The app’s reminder system ensures you stay on top of medication and appointments, while the diary feature allows you to reflect on your emotional well-being. Experience the benefits of personalized health management by installing the CareClinic App today.[26]
References
- “Deep Endometriosis introduction”. https://www.isuog.org/education/visuog/gynecology/endometriosis/deep-endometriosis/deep-endometriosis-intro.html
- “Diagnosis, management, and long-term outcomes of rectovaginal endometriosis – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3825702/
- “Deep infiltrating endometriosis: Evaluation and management | MDedge”. https://www.mdedge.com/obgyn/article/164711/gynecology/deep-infiltrating-endometriosis-evaluation-and-management
- “Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis: Unraveling the Complexities of a Severe Endometriosis Subtype – DoveMed”. https://www.dovemed.com/health-topics/focused-health-topics/deep-infiltrating-endometriosis-unraveling-complexities-severe-endometriosis-subtype
- “Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment For Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis”. https://wowrxpharmacy.com/blog/womens-health/deep-infiltrating-endometriosis/
- “Surgical Treatment of Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis | Article | GLOWM”. https://www.glowm.com/article/heading/vol-8–gynecological-endoscopy–surgical-treatment-of-deep-infiltrating-endometriosis/id/420703
- “Diagnosis and management of endometriosis – PMC”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10120420/
- “Urinary tract endometriosis in patients with deep infiltrating endometriosis: prevalence, symptoms, management, and proposal for a new clinical classification – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25439849/
- “How Common Is Deep Infiltrating (Extrapelvic) Endometriosis?”. https://endometriosis.net/clinical/deep-infiltrating
- “Endometriosis: Subtypes, Symptoms, and Patient Impact – Pelvic Pain Digital Hub”. https://digitalhub.painweek.org/subtypes-symptoms-patient-impact/
- “Endometriosis”. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/endometriosis%E2%81%A0
- “The Etiology of Endometriosis | Article | GLOWM”. https://www.glowm.com/article/heading/vol-3–endometriosis–the-etiology-of-endometriosis/id/417633
- “Epithelial Cells of Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis Harbor Mutations in Cancer Driver Genes – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8065889/
- “Endometriosis, Pain, and Related Psychological Disorders: Unveiling the Interplay among the Microbiome, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress as a Common Thread – PMC”. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11203696/
- “The Main Theories on the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis”. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/5/4254
- “Environmental and host-associated risk factors in endometriosis and deep endometriotic nodules: a matched case-control study – PubMed”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16781705/
- “[Fertility and deep infiltrating endometriosis]”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29129409/
- “Endometriosis: An update on diagnosis and medical management | British Columbia Medical Journal”. https://bcmj.org/articles/endometriosis-update-diagnosis-and-medical-management
- “How do healthcare providers diagnose endometriosis? | NICHD – Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development”. https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/endometri/conditioninfo/diagnose
- “Conservative treatment of deep infiltrating endometriosis: review of existing options”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28952821/
- “The role of the multidisciplinary team in the management of deep infiltrating endometriosis | Gynecological Surgery | Full Text”. https://gynecolsurg.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s10397-017-1018-0
- “Integrative Therapies for Endometriosis – iCareBetter”. https://icarebetter.com/integrative-therapies-for-endometriosis/
- “DEEP INFILTRATING ENDOMETRIOSIS: UNDERSTANDING AND MANAGING A COMPLEX CONDITION | Mya Care”. https://myacare.com/blog/deep-infiltrating-endometriosis-understanding-and-managing-a-complex-condition
- “Self-Care And Treatment Options For Endometriosis | Franciscan Health”. https://www.franciscanhealth.org/community/blog/endometriosis-treatment-options
- “Living With Endometriosis: 5 Tips to Improve Your Quality of Life”. https://www.conwaymedicalcenter.com/news/topic/living-with-endometriosis-5-expert-tips-for-managing-pain-and-fatigue/
- “CareClinic: Free Health & Wellness App | Sugggest”. https://sugggest.com/software/careclinic


