Bipolar hypomania is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Its prevalence is increasing, with more individuals experiencing symptoms that range from hypomanic episodes to full-blown manic episodes. Bipolar disorder encompasses a spectrum of mood episodes. Including bipolar depression characterized by severe hypomanic episode, depressive episodes, and depressive symptoms.
Understanding this fascinating yet challenging disorder, along with its associated manic symptoms and other mental disorders, is crucial for improving the lives of those affected and seeking effective treatment options.[1]
What is Bipolar Hypomania?
To understand bipolar hypomania, it’s essential to first familiarize ourselves with the concept of bipolar disorder as a whole. Bipolar disorder is a psychiatric condition characterized by extreme mood swings, ranging from episodes of intense depression to periods of heightened energy and elevated mood called mania or hypomania.
Hypomania is a less severe form of mania that shares many similarities with its more intense counterpart. However, what sets hypomania apart is its duration and impact on daily functioning. While manic episodes can last for weeks or even months, hypomanic episodes typically endure for shorter periods, usually a few days.
During hypomania, individuals may experience a surge in energy, increased productivity, and a heightened sense of euphoria. They may feel more outgoing, sociable, and confident. However, unlike full-blown mania, hypomania rarely causes significant impairment in functioning and doesn’t require hospitalization.
It’s important to note that while hypomania is often associated with positive feelings and increased creativity, it can also have negative consequences. Some individuals in a hypomanic state may engage in risky behaviors such as overspending, reckless driving, or substance abuse. These impulsive actions can lead to financial, legal, or interpersonal problems.
Additionally, the euphoric highs of hypomania can sometimes transition rapidly into irritability, agitation, or even anger. This sudden shift in mood can be confusing and distressing for both the individual experiencing hypomania and those around them. It’s crucial for individuals with bipolar disorder to monitor their symptoms closely and seek professional help if they notice any concerning changes in their mood or behavior.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Bipolar Hypomania
Bipolar hypomania can manifest in various ways, affecting both the mind and body. Let’s delve into some common symptoms:
Physical Symptoms
- Increased energy levels and decreased need for sleep
- Restlessness and hyperactivity
- Unusually talkative and rapid speech patterns
- Inflated self-esteem and grandiosity
Emotional and Behavioral Symptoms
- Elevated mood and feelings of euphoria
- Heightened creativity and productivity
- Distractibility and racing thoughts
- Engaging in impulsive or risky behaviors
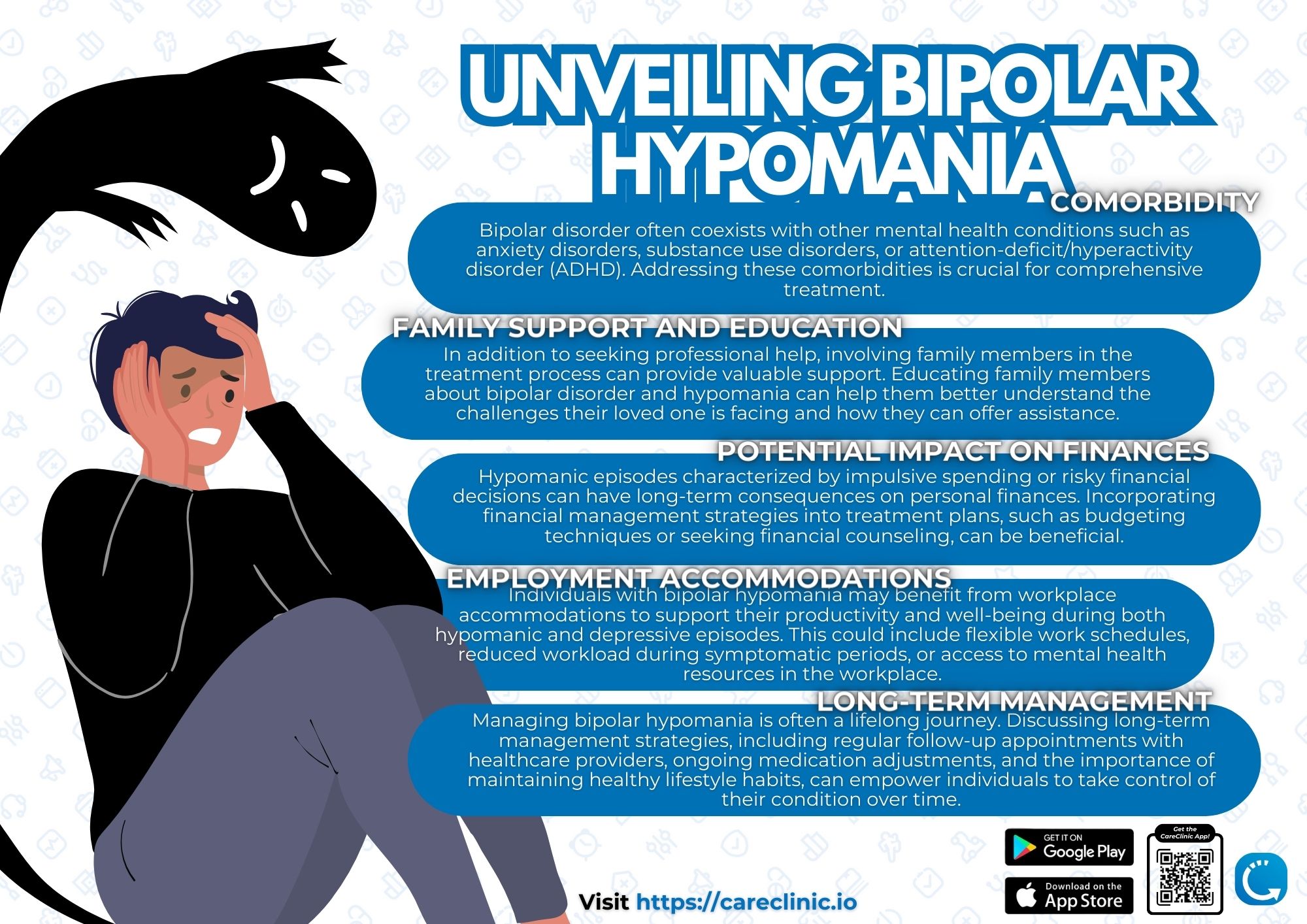
If you or a loved one experience these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. A comprehensive evaluation will help determine if you are dealing with bipolar hypomania or another related condition. Understanding the nuances between hypomanic episodes, manic episodes, depressive episodes, and bipolar depression is essential for proper treatment.
Individuals experiencing bipolar hypomania may exhibit changes in their social interactions and relationships. They might seek out new social connections, engage in excessive socializing, or become more flirtatious than usual. This heightened sociability can sometimes lead to strained relationships or misunderstandings with friends and family. Additionally, increased energy levels, decreased need for sleep, and heightened creativity are common symptoms, which, while sometimes positive, can result in impulsive decision-making and risky behaviors.
Effective management of bipolar hypomania typically involves a combination of medication and therapy. Mood stabilizers and antipsychotic medications help regulate mood swings, while cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches provide strategies for coping with symptoms and improving daily functioning. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, exercising regularly, and reducing stress, are also crucial. By fostering a better understanding of the disorder, we can reduce stigma, support those affected, and promote early intervention and effective treatment.
Cognitive Symptoms
- Rapid thoughts and ideas, making it difficult to focus
- Heightened perception and sensitivity to stimuli
- Difficulty making decisions or impulsively making risky choices
- Memory lapses or forgetfulness
These cognitive symptoms can impact daily functioning and may result in challenges at work or in personal responsibilities. It’s essential to seek professional help to manage these symptoms effectively and maintain overall well-being.
The Causes of Bipolar Hypomania
While the exact causes of bipolar hypomania are still being studied, research suggests that a combination of genetic factors and environmental triggers plays a significant role in its development. Let’s explore these factors further:
Genetic Factors
Studies have shown that bipolar disorder appears to have a genetic component, with a higher incidence among individuals who have family members with the condition. Genetic variations may contribute to the altered brain chemistry and functioning observed in bipolar hypomania.
Furthermore, recent research has delved into the specific genes that may be associated with bipolar disorder. One gene of interest is CACNA1C, which is involved in regulating calcium flow in brain cells. Variations in this gene have been linked to an increased risk of developing bipolar disorder, shedding light on the intricate genetic mechanisms at play.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors can also influence the onset and severity of bipolar hypomania. Stressful life events, such as significant life changes, trauma, or chronic stress, can trigger episodes or exacerbate existing bipolar symptoms. It’s important to be mindful of these triggers and develop healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress effectively.
In addition to stress, studies have shown that disruptions in circadian rhythms, such as irregular sleep patterns or jet lag, can also impact mood stability in individuals with bipolar disorder. The interplay between genetic predispositions and environmental influences highlights the complex nature of bipolar hypomania and underscores the importance of a holistic approach to treatment and management.[3]
The Impact of Bipolar Hypomania on Daily Life
Bipolar hypomania can significantly impact various aspects of an individual’s life, including relationships and work. Let’s explore these implications:
Relationships and Social Interactions
During hypomanic episodes, individuals may exhibit high levels of energy and be more socially active. While this can be initially exhilarating for those around them, it can also be overwhelming. It’s important to communicate with loved ones about your condition, so they understand and can provide support when needed.
Moreover, the increased impulsivity and risk-taking behavior associated with hypomania can strain relationships. Individuals may engage in reckless activities or make decisions that have long-term consequences on their personal connections. Seeking therapy and practicing mindfulness can help individuals navigate these challenges and maintain healthier relationships.
Work and Career Implications
Hypomanic episodes can enhance creativity, productivity, and motivation. However, these bursts of energy can also lead to overworking, impaired judgment, and impulsive decision-making. Finding a balance between harnessing the positive aspects of hypomania and maintaining stability in the workplace is crucial for long-term success and well-being.
The fluctuating nature of bipolar disorder can result in inconsistent work performance. Employers and coworkers may struggle to understand these fluctuations, leading to misunderstandings and potential conflicts in the workplace. It’s essential for workplaces to recognize these challenges and foster an environment of empathy and support.
Open communication, along with a well-defined support system, can help individuals with bipolar hypomania navigate professional challenges. By creating a supportive work environment and encouraging dialogue, employers can help mitigate misunderstandings and provide the necessary accommodations to maintain a healthy, productive work life for those affected by bipolar hypomania.[4]
Treatment Options for Bipolar Hypomania
Fortunately, numerous treatment options are available for individuals struggling with bipolar hypomania. These include:
Medication and Pharmacological Treatments
Medication is often a cornerstone of bipolar hypomania treatment. Mood stabilizers, such as lithium or valproate, are frequently prescribed to help regulate mood swings and reduce the frequency and intensity of hypomanic episodes. Antipsychotic medications and antidepressants may also be used as adjunctive treatments.
Psychotherapy and Counseling
Talk therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be incredibly beneficial for individuals with bipolar hypomania. CBT helps individuals identify and modify negative thinking patterns and develop healthy coping strategies for managing stress and mood fluctuations.
Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care Strategies
In addition to professional treatments, self-care strategies are invaluable in managing bipolar hypomania on a day-to-day basis. Taking an active role in your overall well-being can have a significant impact on your mood stability. Here are some self-care tips:
- Establish a consistent sleep routine to optimize rest and promote stability.
- Engage in regular exercise, as physical activity releases endorphins and helps regulate mood.
- Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or journaling.
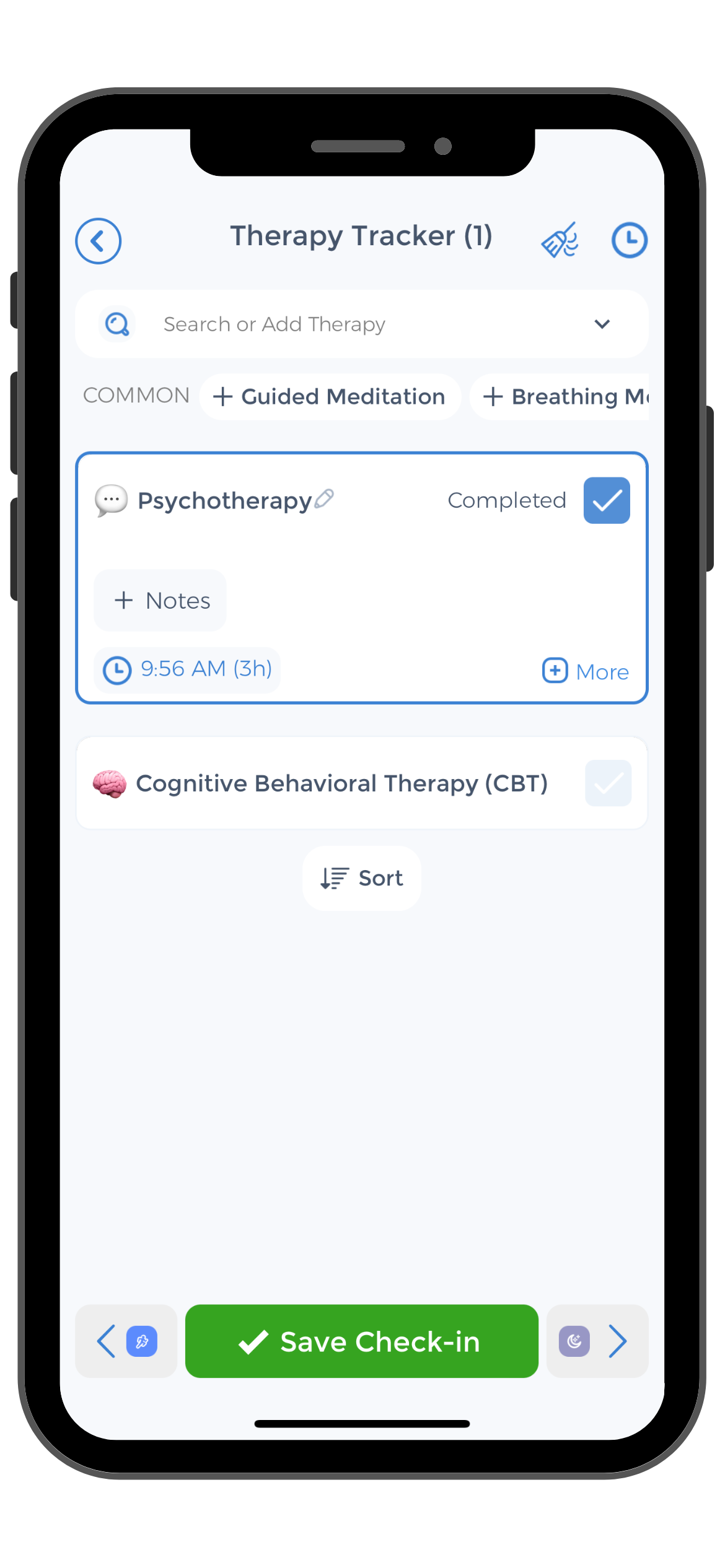
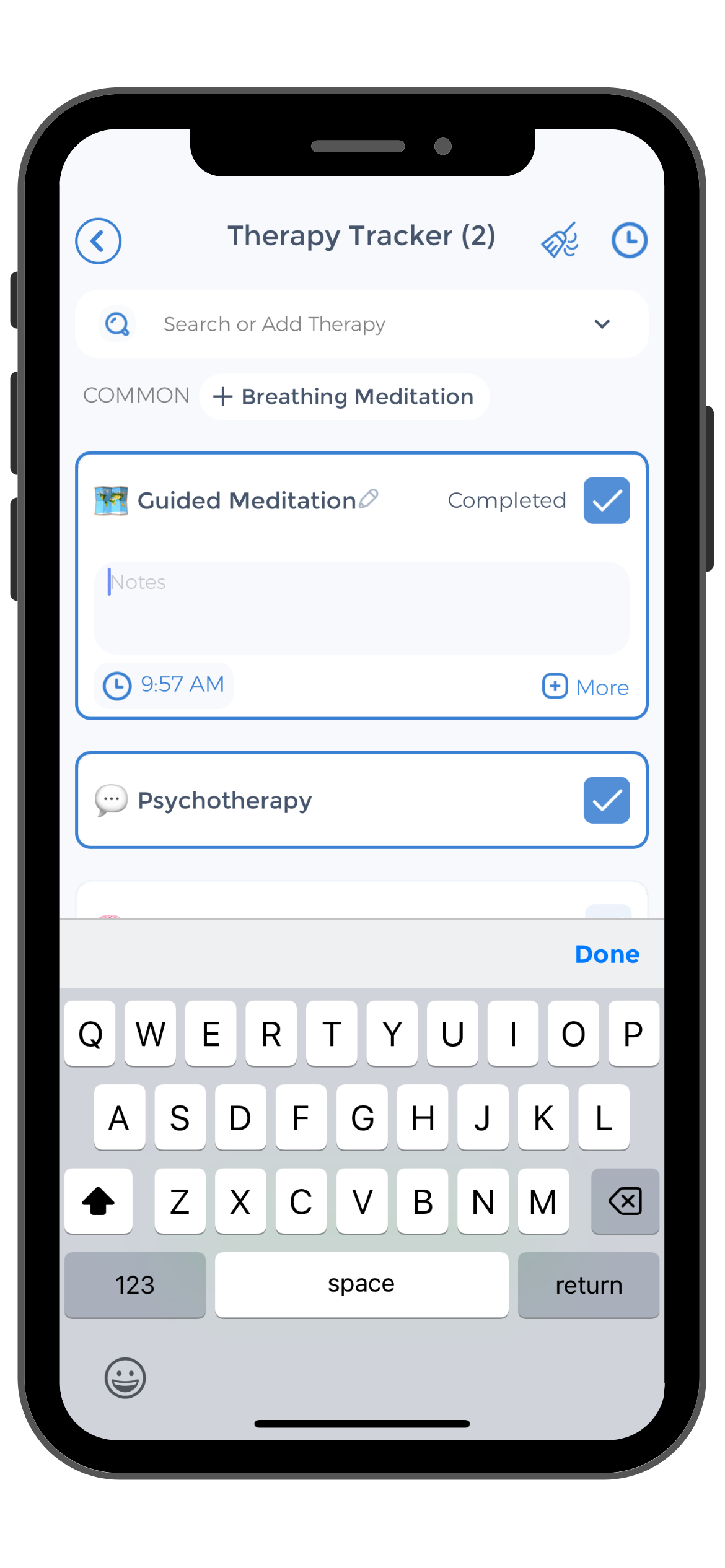
- Monitor your mood and track any triggers or patterns using a dedicated app, like CareClinic, to gain insights and adjust your self-care strategies accordingly.
- Seek support from support groups or online communities where you can connect with others who understand your experiences.
Remember, self-care is a continuous process, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s essential to identify the strategies that resonate with you and make them a part of your daily routine.
 Furthermore, it is important to note that while medication and therapy are crucial components of bipolar hypomania treatment, there are additional approaches that can complement these interventions. One such approach is the incorporation of alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or yoga, into the treatment plan. These practices have shown promise in reducing stress, promoting relaxation, and improving overall well-being.
Furthermore, it is important to note that while medication and therapy are crucial components of bipolar hypomania treatment, there are additional approaches that can complement these interventions. One such approach is the incorporation of alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or yoga, into the treatment plan. These practices have shown promise in reducing stress, promoting relaxation, and improving overall well-being.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet can play a significant role in managing bipolar hypomania. Certain foods, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, have been found to have mood-stabilizing properties. Incorporating foods like fatty fish, nuts, and seeds into your meals can potentially contribute to mood regulation.
Bipolar hypomania is a multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive understanding to navigate successfully. By recognizing the mild and severe symptoms, understanding the underlying causes, and exploring available treatment options, individuals with bipolar hypomania can lead fulfilling lives. It’s important to partner with healthcare professionals, develop a support network, and prioritize self-care to manage the challenges and embrace the unique gifts that come with this condition.[5][6][7][8]
Use the CareClinic App to Keep Track of Manic Episode and Depressive Episodes
Managing bipolar hypomania effectively requires consistent monitoring and a proactive approach to treatment. The CareClinic App is designed to empower people with bipolar disorder and bipolar hypomania by providing a comprehensive platform for tracking mood fluctuations, medication adherence, and identifying triggers. With features like mood tracking, medication reminders, and a personal health diary, the app helps users maintain stability and gain insights into their condition.
By using CareClinic to document daily experiences, users can work closely with healthcare providers to tailor their treatment plans for optimal outcomes.
Download the CareClinic App and Manage Bipolar I Disorder and Bipolar II Disorder
Understanding the patterns in your mental illness such as bipolar disorder symptoms and manic depression can lead to better management and improved health. The CareClinic App offers a structured way to observe and record these patterns, making it easier to recognize early warning signs and take preventative action.
The app’s analytics can reveal correlations between lifestyle choices and mood changes. Guiding users toward healthier habits. To take control of your bipolar hypomania and embark on a path to better well-being, Install App and discover the difference it can make in managing your mental health.
References
- “Bipolar disorder”. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/bipolar-disorder
- “Hypomania: What Is It, Comparison vs Mania, Symptoms & Treatment”. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21774-hypomania
- “Bipolar disorder”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bipolar_disorder
- “Mindfulness-Based Treatment for Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review of the Literature – PMC”. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5590538/
- “Mood stabilizer”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mood_stabilizer
- “Interpersonal and social rhythm therapy”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interpersonal_and_social_rhythm_therapy
- “Treatment of bipolar disorder”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Treatment_of_bipolar_disorder
- “Dark therapy”. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dark_therapy